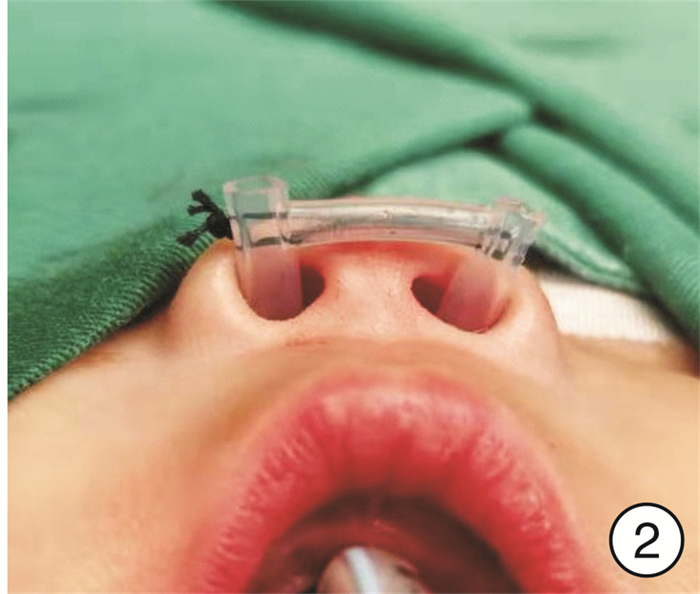
The efficacy of endoscopic plasty for children with bilateral congenital choanal atresia
-
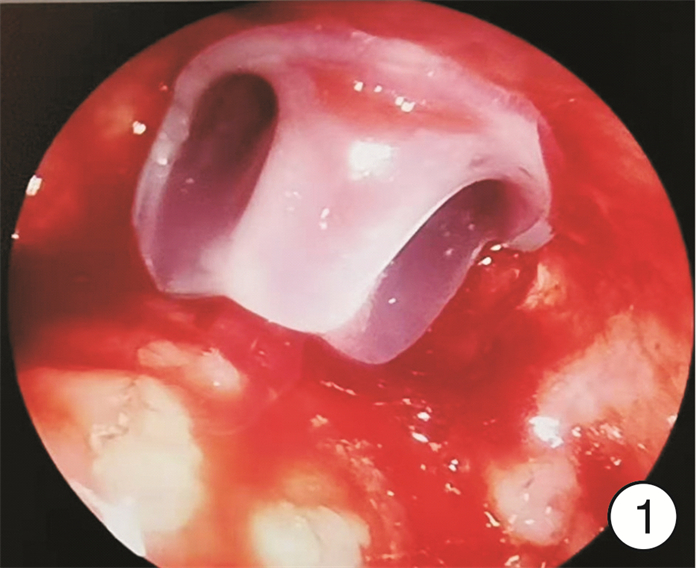
摘要: 目的 探讨内镜下后鼻孔成形术治疗儿童双侧先天性后鼻孔闭锁的临床疗效。方法 回顾性分析经纤维鼻咽镜及鼻窦CT检查确诊为双侧先天性后鼻孔闭锁6例患儿的临床资料, 患儿均行内镜下后鼻孔成形术, 术后放置6个月自制硅胶鼻腔支撑管, 取出支撑管后门诊随访复查评估有无再闭锁。结果 6例双侧先天性后鼻孔闭锁患儿术后鼻腔通气都得到有效改善, 无严重手术相关并发症发生, 5例患儿取管后获得满意疗效, 1例骨性闭锁患儿取出支撑管后复查发现后鼻孔再狭窄。结论 内镜下后鼻孔成形术治疗儿童双侧先天性后鼻孔闭锁临床疗效较为肯定且安全性高, 但仍有较低的再闭锁概率。Abstract: Objective To evaluate the clinical effect of endoscopic repair for the treatment of children with bilateral congenital choanal atresia.Methods A retrospective analysis was conducted in our department that six children who were diagnosed as bilateral congenital choanal atresia by nasopharyngeal endoscopy and nasal CT scanning. All cases underwent endoscopic repair and placed the silicone stent to support the enlarged nostrils for six months, and these patients were followed up to observe re-atresia rate after taking out of the supporting tube.Results Six cases′ nasal ventilation were effectively improved after operation without serious complications, 5 cases showed a satisfactory curative effect after taking out of the supporting tube, only 1 case with bony atresia found choanal re-atresia during follow-up.Conclusion The clinical effect of using endoscopic repair for children with bilateral congenital choanal atresia showed remarkable efficacy with a low re-atresia
-
Key words:
- child /
- choanal atresia /
- endoscopic surgical procedures
-

-
表 1 6例双侧CCA患儿的基本临床资料
例序 性别 年龄/月 闭锁隔性质 闭锁程度 有无合并其他畸形 1 女 44 混合性 完全 无 2 女 1 骨性 完全 先天性心脏病/鼻正中瘘/右眼Adle瞳孔 3 男 48 混合性 部分 先天性心脏病/左眼缺损综合征 4 女 1 膜性 完全 先天性心脏病 5 男 1 膜性 完全 先天性心脏病 6 女 1 混合性 完全 先天性心脏病 -
[1] 江晨艳, 石润杰, 王珮华. 先天性鼻畸形的分类及治疗[J]. 中国中西医结合耳鼻咽喉科杂志, 2018, 26(5): 398-400. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XYJH201805022.htm
[2] Moreddu E, Rossi ME, Nicollas R, et al. Prognostic Factors and Management of Patients with Choanal Atresia[J]. J Pediatr, 2019, 204: 234-239. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2018.08.074
[3] Myers EN. 耳鼻咽喉头颈外科手术学[M]. 倪道凤, 陶泽章, 张秋航, 等. 译. 2版. 天津: 天津翻译出版公司, 2017: 27-32.
[4] Eladl HM, Khafagy YW. Endoscopic bilateral congenital choanal atresia repair of 112 cases, evolving concept and technical experience[J]. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, 2016, 85: 40-45. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2016.03.011
[5] El-Anwar MW, Nofal AA, El-Ahl MA. Endoscopic repair of bilateral choanal atresia, starting with vomer resection: Evaluation study[J]. Am J Rhinol Allergy, 2016, 30(3): 95-99. doi: 10.2500/ajra.2016.30.4321
[6] ŠebováI, VyrvováI, BarkociováJ. Nasal cavity CT imaging contribution to the diagnosis and treatment of choanal atresia[J]. Medicina, 2021, 57(2): 93. doi: 10.3390/medicina57020093
[7] Gulsen S, Baysal E, Celenk F, et al. Treatment of Congenital Choanal Atresia via Transnasal Endoscopic Method[J]. J Craniofac Surg, 2017, 28(2): 338-342. doi: 10.1097/SCS.0000000000003247
[8] Murray S, Luo L, Quimby A, et al. Immediate versus delayed surgery in congenital choanal atresia: A systematic review[J]. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, 2019, 119: 47-53. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2019.01.001
[9] Wolf A, Lang-Loidolt D, Koele W, et al. Are stents beneficial in endoscopic choanal atresia repair of newborns and children? Case series of 11 patients[J]. Clin Otolaryngol, 2016, 41(6): 821-825. doi: 10.1111/coa.12566
[10] 娄凡, 明澄, 马静, 等. 低温等离子射频消融术治疗膜性闭锁为主的先天性后鼻孔闭锁临床分析[J]. 中国耳鼻咽喉头颈外科, 2020, 27(10): 595-597. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-EBYT202010014.htm
[11] Kwong KM. Current updates on choanal atresia[J]. Front Pediatr, 2015, 3: 52.
[12] Strychowsky JE, Kawai K, Moritz E, et al. To stent or not to stent? A meta-analysis of endonasal congenital bilateral choanal atresia repair[J]. Laryngoscope, 2016, 126(1): 218-227. doi: 10.1002/lary.25393
[13] 谢利生, 黄正华, 李琦, 等. 鼻内镜下后鼻孔重建术治疗46例先天性后鼻孔闭锁患儿的疗效观察[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2019, 33(8): 742-745. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201908014.htm
[14] 李泽南, 严尚, 王丽, 等. 鼻中隔后端犁骨切除后鼻孔成形术治疗先天性后鼻孔闭锁五例[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2020, 55(8): 779-782. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115330-20200304-00156
[15] Tatar EÇ, Öcal B, Doǧan E, et al. Stentless endoscopic repair of congenital choanal atresia: is it enough for maintaining choanal patency?[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2017, 274(10): 3673-3678. doi: 10.1007/s00405-017-4702-9
[16] Alice KY, Jacky FW. Surgery for congenital choanal atresia[J]. Oper Tech Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2021, 32(1): 31-38. doi: 10.1016/j.otot.2021.01.006
[17] Yatish Kumar BL, Vibha B. Transnasal endoscopic microdrilling with steroid douching for bony choanal atresia: a novel approach[J]. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2021, 73(2): 193-196. doi: 10.1007/s12070-020-02317-7
-




 下载:
下载: