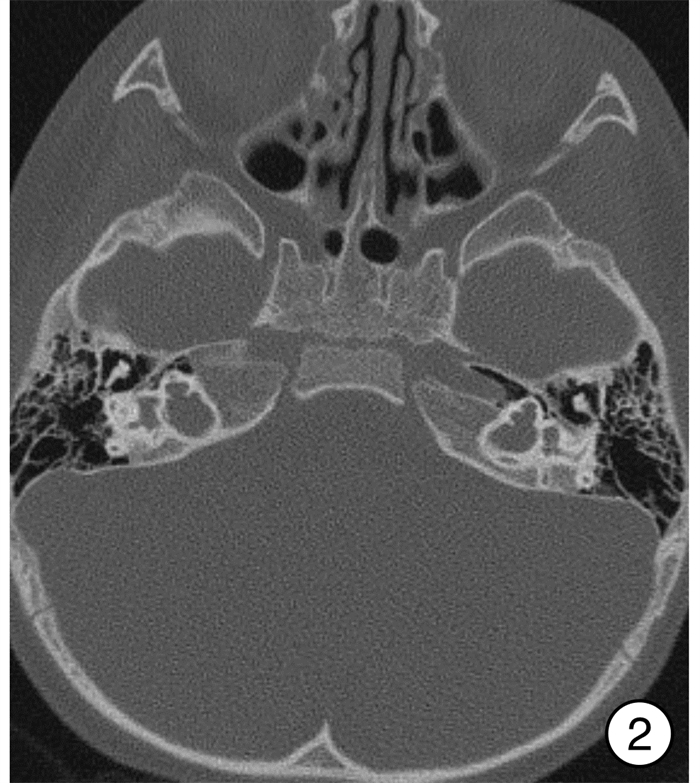
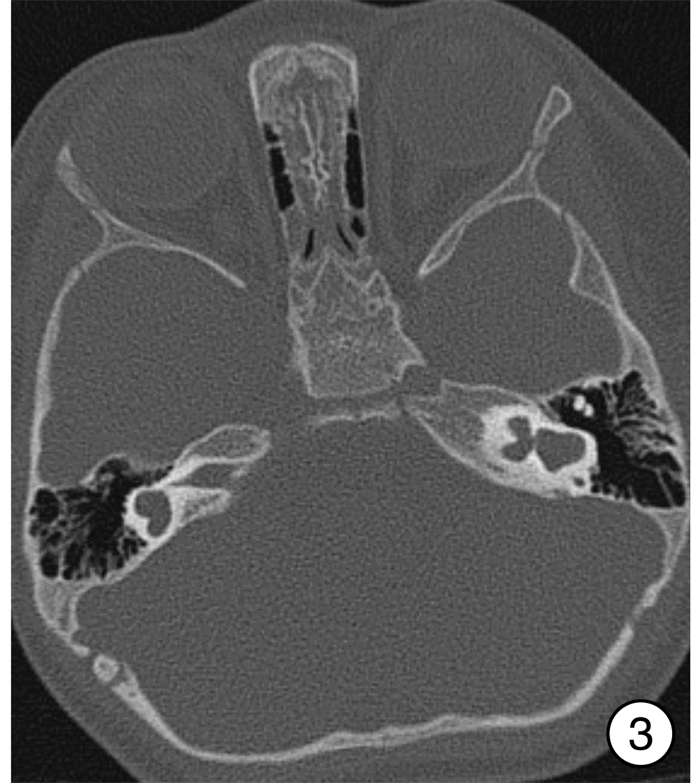
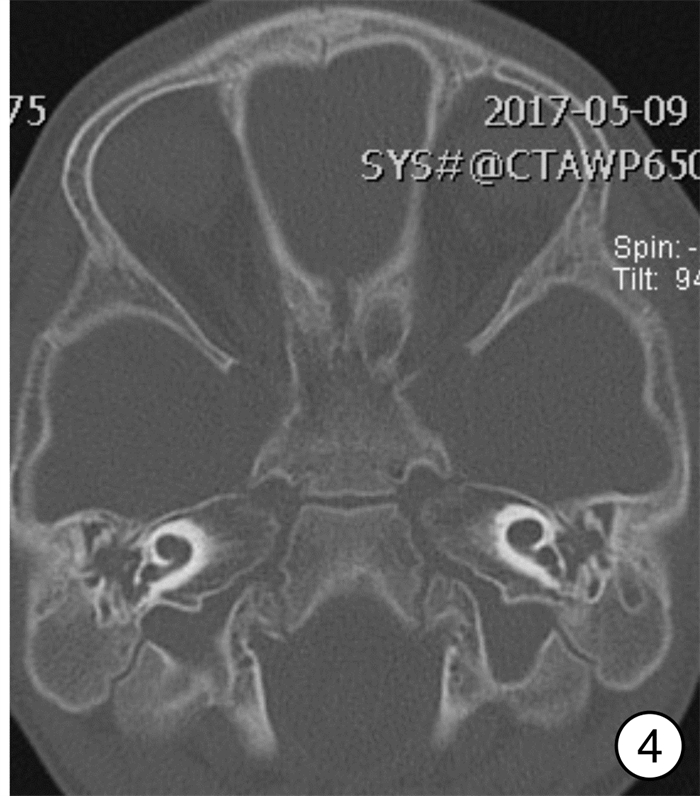
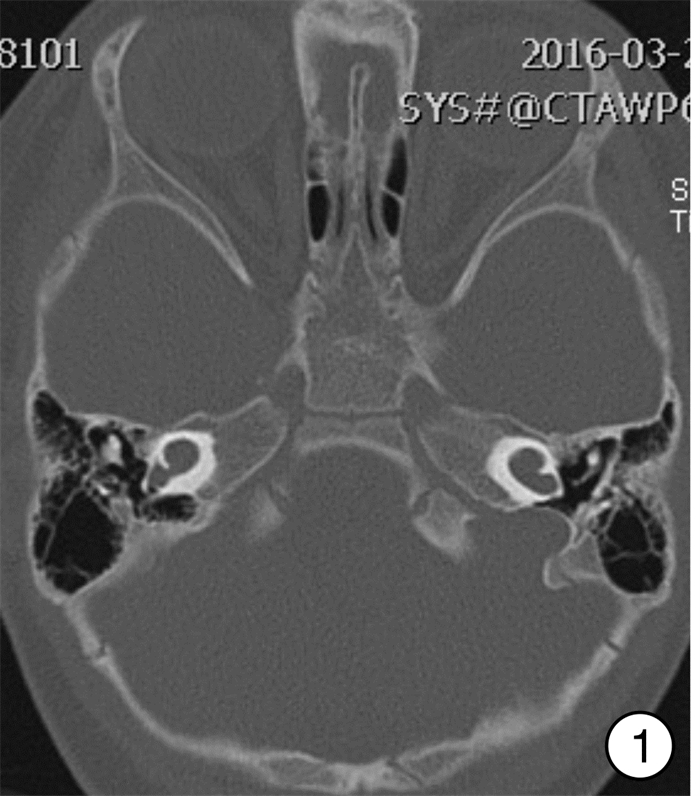
An analysis of surgical management of difficulties during cochlear implant with inner ear anomalies
-
摘要: 目的 探讨内耳畸形患儿行人工耳蜗植入手术的难点及其处理方法。方法 186例内耳畸形行人工耳蜗植入术的患儿(内耳畸形组)中, 孤立的半规管发育不良6例(3.23%), 孤立的大前庭导水管综合征137例(73.66%), Mondini畸形26例(13.98%), 不全分隔Ⅲ型6例(3.23%), 不全分隔Ⅰ型1例(0.54%), 内听道狭窄3例(1.61%), 耳蜗发育不良7例(3.76%); 随机抽取200例内耳结构正常的人工耳蜗植入患儿为对照组。所收集的资料包括内耳异常的类型、术中表现和临床处理策略以及术后言语康复情况。结果 内耳畸形组中, 148例次(77.49%)手术顺利, 6例次(3.14%)电极插入不完整, 29例次(15.18%)术中出现脑脊液井喷, 8例次(4.19%)内耳畸形患儿手术中因为圆窗结构异常而开窗位置定位困难。内耳畸形组术中均采用面隐窝入路, 17.8%的患儿存在明显的面神经结构异常, 明显多于对照组, 仅1例患儿在术后1周出现面神经延迟麻痹, 治疗后恢复良好; 6.81%的内耳畸形患儿采用扩大圆窗入路进行电极插入, 明显少于对照组(28%)。内耳畸形组和对照组行人工耳蜗植入的术后言语康复效果比较差异无统计学意义。结论 内耳畸形患儿行人工耳蜗植入术安全可行且效果显著。内耳畸形患儿发生面神经及圆窗等中耳结构异常的概率更高, 因此术前应特别注意阅读影像学结果, 以预测术中可能发生的风险。术前制定最安全的手术计划, 包括电极的类型和开窗的方式, 并且手术必须由经验丰富的外科医生实施或者指导, 以根据术中所见调整最优的手术方案。Abstract: Objective The purpose of this study is to review the difficulties that can occur during cochlear implant surgery in patients with inner ear abnormalities and the management.Method A retrospective analysis was made on 186 cases of cochlear implant with inner ear malformation, the types of inner ear malformations included 6 cases(3.23%) of isolated semicircular dysplasia, 137 cases(73.66%) of isolated large vestibular aqueducts, 26 cases(13.98%) of Mondini malformations, 6 cases(3.23%) of incomplete septal type Ⅲ, 3 cases(1.61%) of internal auditory stenosis, 7 cases(3.76%) of cochlear dysplasia and 1 case(0.54%) of incomplete septal typeⅠ. Two hundred patients with normal inner ear structures were randomly selected as the control group. The data collected included the types of inner ear abnormalities, intraoperative manifestations, clinical management strategies, and postoperative speech rehabilitation, and the literature was reviewed.Result 148 patients(77.49%) with inner ear malformation underwent successful surgery, electrode insertion was incomplete in 6 patients(3.14%), and cerebrospinal fluid blowout occurred in 29 patients(15.18%), it was difficult to locate the window because of the abnormal structure of the window in 8 cases(4.19%). In 191 patients, the facial recess approach was adopted intraoperatively, and 17.8% of the patients had significant structural abnormalities of the facial nerve, significantly more than the group with normal inner ear structure. Only 1 patient showed delayed facial nerve paralysis 1 week after surgery, and recovered well after treatment. 6.81% of the patients adopted the expanded round window approach, which was significantly lower than that of the group with normal inner ear structure(28%). There was no significant difference between patients with inner ear malformation and patients with extremely severe deafness with normal inner ear structure who received cochlear implant in speech rehabilitation.Conclusion Cochlear implant is safe, feasible and effective for patients with inner ear malformation. For patients with inner ear malformation, special attention should be paid to the preoperative imaging reading to predict the possible risks during the operation. The safest surgical plan, including the type of electrode and the manner in which the window is opened, must be prepared before the operation, and the operation must be performed or directed by an experienced surgeon who can adjust the optimal surgical plan according to what is seen during the operation.
-
Key words:
- cochlear implantation /
- inner ear malformation /
- surgical difficulties /
- surgical risks
-

-
表 1 2组患儿不同康复阶段的CAP和SIR评分结果比较
x±s 测试项目及时间 对照组
(200例)内耳畸形组(186例) LVAS
(137例)Mondini畸形
(26例)IP-Ⅲ畸形
(6例)IP-Ⅰ畸形
(1例)内听道狭窄
(3例)半规管发育不良
(6例)CAP 术前 0.730±0.528 0.723±0.449 0.783±0.736 0.500±0.548 0 0.667±0.577 0.667±0.516 术后3个月 1.880±0.7541) 1.898±0.8771) 1.913±0.2881) 1.833±0.7531) 1 1.667±0.577 1.833±0.4081) 术后6个月 2.860±0.7641)2) 2.883±0.8321)2) 2.870±0.6261)2) 2.833±0.7531)2) 2 2.667±0.5771) 3.000±0.6321)2) 术后9个月 3.875±0.9071)2)3) 3.832±0.9281)2)3) 4.043±0.9761)2)3) 4.333±1.3661)2)3) 4 4.333±0.5771)2)3) 4.500±0.5481)2)3) 术后12个月 4.990±1.0941)2)3)4) 5.022±1.1721)2)3)4) 5.130±1.0141)2)3)4) 5.167±1.3291)2)3) 6 5.000±1.0001)2)3) 5.833±0.9831)2)3)4) SIR 术前 1.205±0.405 1.270±0.446 1.261±0.449 1.167±0.408 1 1.000±0.000 1.333±0.516 术后3个月 2.060±0.6851) 2.080±0.6871) 2.304±0.5591) 1.833±0.7531) 2 1.667±0.577 2.167±0.7531) 术后6个月 2.700±0.7301)2) 2.672±0.7291)2) 2.957±0.7671)2) 2.667±0.5161)2) 2 2.667±1.155 3.000±0.6321)2) 术后9个月 3.270±0.9391)2)3) 3.241±0.9891)2)3) 3.652±0.9351)2)3) 3.333±0.5161)2)3) 3 3.333±0.5771)2) 3.667±0.8161)2)3) 术后12个月 3.940±0.7811)2)3)4) 3.818±0.7501)2)3)4) 4.130±0.7571)2)3)4) 4.167±0.7531)2)3)4) 3 3.667±1.1551)2) 4.333±0.5161)2)3)4) 与术前比较,1)P < 0.05;与术后3个月比较,2)P < 0.05;与术后6个月比较,3)P < 0.05;与术后9个月比较,4)P < 0.05。 -
[1] 许庆庆, 翟所强, 韩东一, 等. 伴内耳畸形聋病患者人工耳蜗植入效果的Meta分析[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2015, 29(8): 743-747. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201508020.htm
[2] Gheorghe DC, Zamfir-Chiru-Anton A. Complications in cochlear implant surgery[J]. J Med Life, 2015, 8(3): 329-332.
[3] Sennaroglu L, Bajin MD. Classification and current management of inner ear malformations[J]. Balkan Med J, 2017, 34(5): 397-411. doi: 10.4274/balkanmedj.2017.0367
[4] Lu L, Wang M, Dong J, et al. Active and adequate exposure of the facial nerve and chorda tympani nerve to improve the safety of cochlear implantation[J]. Ear Nose Throat J, 2019, Online ahead of print.
[5] Bruijnzeel H, Draaisma K, van Grootel R, et al. Systematic review on surgical outcomes and hearing preservation for cochlear implantation in children and adults[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2016, 154(4): 586-596. doi: 10.1177/0194599815627146
[6] Bae SC, Shin YR, Chun YM. Cochlear implant surgery through round window approach is always possible[J]. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol, 2019, 128(6_suppl): 38S-44S. doi: 10.1177/0003489419834311
[7] Aldhafeeri AM, Alsanosi AA. Management of surgical difficulties during cochlear implant with inner ear anomalies[J]. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, 2017, 92: 45-49. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2016.11.001
[8] Cabbarzade C, Sennaroglu L, Süslü N. CSF gusher in cochlear implantation: The risk of missing CT evidence of a cochlear base defect in the presence of otherwise normal cochlear anatomy[J]. Cochlear Implants Int, 2015, 16(4): 233-236. doi: 10.1179/1754762813Y.0000000048
[9] Ketterer MC, Aschendorff A, Arndt S, et al. The of influence cochlear morphology on the final electrode array position[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2018, 275(2): 385-394. doi: 10.1007/s00405-017-4842-y
[10] Shi Y, Li Y, Gong Y, et al. Cochlear implants for patients with inner ear malformation: Experience in a cohort of 877 surgeries[J]. Clin Otolaryngol, 2019, 44(4): 702-706. doi: 10.1111/coa.13360
[11] 黄金聪, 陈平. 人工耳蜗电极位置与电极阻抗关系的研究进展[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2019, 33(12): 1221-1224. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201912030.htm
-




 下载:
下载: