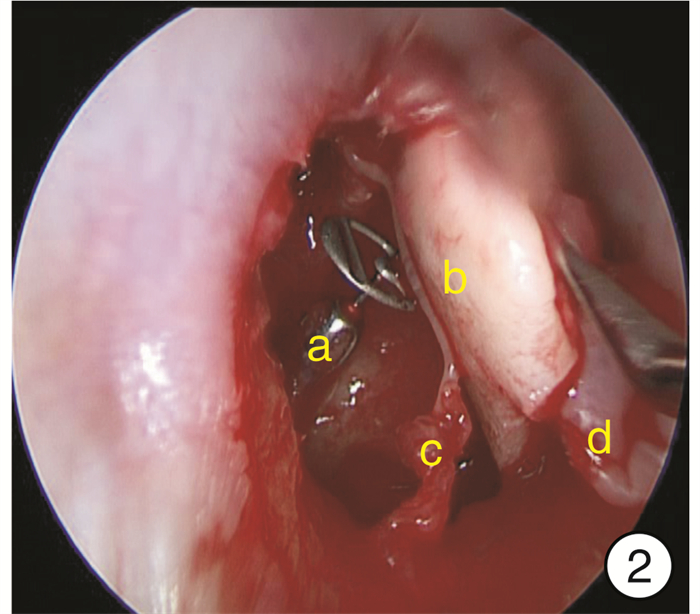
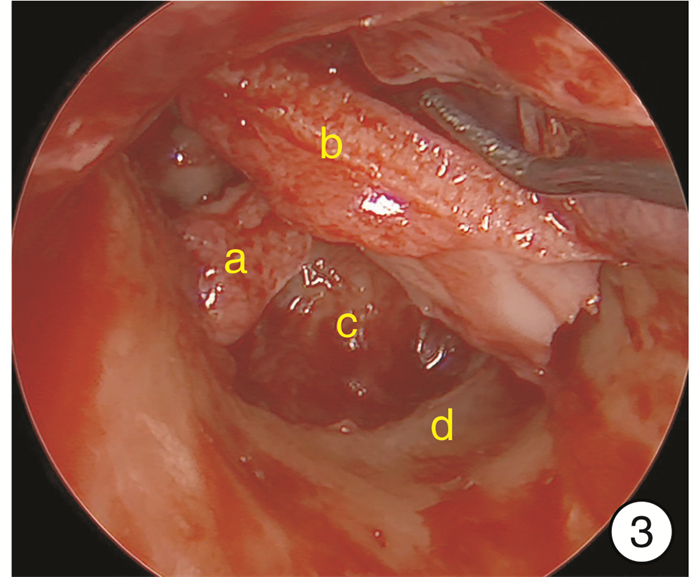
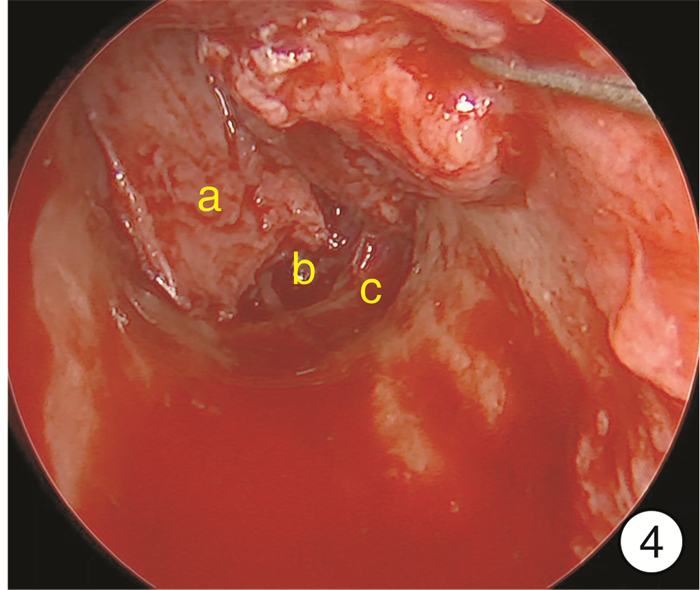
-
摘要: 目的 探讨耳内镜下经耳道处理鼓室硬化的可行性、手术方法和效果。方法 确诊为Ⅱ~Ⅳ型鼓室硬化症患者41例, 均行全耳内镜下手术。清除鼓室硬化灶, 并根据听骨情况行鼓室成形术。分别于术后1、3、6个月复查, 观察鼓膜愈合情况, 并以最后一次测试为最终听力结果, 比较鼓室硬化症不同分型以及不同鼓室成形术式间的术前术后气骨导差(ABG), 评价手术疗效。统计学分析采用SPSS 22.0。结果 术后43耳(97.7%)鼓膜一期完全愈合, 1耳遗留边缘性穿孔。术后均无并发症发生。术前ABG为(36.73±11.68) dB, 术后6个月ABG为(20.55±10.27) dB, 术前术后比较差异有统计学意义(t=20.476, P < 0.05)。鼓室硬化各型之间术前术后ABG比较差异无统计学意义。Ⅲ型的术后听力提高较Ⅱ型、Ⅳ型差, 但差异无统计学意义。Ⅱ型鼓室成形术后听力改善效果与Ⅲ型接近, 差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。结论 耳内镜经外耳道手术处理鼓室硬化症是一种安全有效的手术方法, 近期效果满意, 远期疗效仍需进一步观察。Abstract: Objective To explore the feasibility of transcanal endoscopic ear surgery for tympanosclerosis as well as the surgical method and short-term effect.Method Forty-one patients with type Ⅱ-Ⅳ tympanosclerosis who underwent transcanal endoscopic ear surgery were retrospectively analysed. All the tympanosclerotic lesions were removed with endoscope, then tympanoplasty was performed according to the ossicular involvement. Postoperative examination and audiometry were performed at 1, 3 and 6 months after the operation. Pre-and post-operative(6 months as the final result) pure tone air-bone gap were compared between different types of tympanosclerosis to evaluate the short-term effect, the difference of hearing improvement between different type of tympanoplasties was also compared. SPSS 22.0 was used for statistical analysis.Result Forty-three ears recovered without complications, except one with marginal performation, the graft take rate was 97.7%. The preoperative and 6 months postoperative air-bone gap was (36.73±11.68) dB and (20.55±10.27) dB respectively, with significant difference(t=20.476, P < 0.05). There were no significant differences in hearing improvement among the three types, though the hearing improvement of Type Ⅲ typanosclerosis was worse than that of type Ⅱ and Ⅳ. There was no significant difference in the hearing improvement between type Ⅱ and Ⅲ tympanoplasty(P>0.05).Conclusion Transcanal endoscopic surgery is safe and effective for tympanosclerosis with satisfying short-term effect, though long-term result still needs further investigation.
-
Key words:
- tympanosclerosis /
- endoscopic ear surgery /
- tympanoplasty
-

-
表 1 不同鼓室硬化类型听力效果比较
鼓室硬化类型 耳数 气导阈值/dB HL 骨导阈值/dB HL ABG/dB 听力获益/dB 术前 术后 术前 术后 术前 术后 Ⅱ型 26 50.12±15.24 35.43±13.81 16.67±8.23 17.35±8.43 34.62±11.22 18.32±9.34 14.34±6.02 Ⅲ型 8 52.51±10.43 39.62±12.33 16.78±10.56 14.75±9.85 36.55±12.64 24.24±10.92 10.61±6.99 Ⅳ型 10 54.67±14.62 35.19±12.22 19.74±9.34 18.79±10.25 35.14±12.36 17.59±12.12 14.30±5.81 注:听力获益=术前ABG-术后ABG 表 2 不同手术方式听力效果比较
手术分类 耳数 气导阈值/dB HL 骨导阈值/dB HL ABG/dB 听力获益/dB 术前 术后 术前 术后 术前 术后 Ⅱ型鼓室成形术(PORP) 20 56.32±13.32 37.28±12.78 18.28±11.21 17.45±11.31 38.12±12.33 20.25±11.33 18.68±5.94 Ⅲ型鼓室成形术(软骨片加高) 18 54.17±15.99 35.56±14.33 20.73±12.54 18.14±11.65 34.73±11.45 17.62±10.41 17.34±6.05 -
[1] Gates GA, Klein JO, Lim DJ, et al. Recent advances in otitis media. : Definitions, terminology, and classification of otitis media[J]. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol Suppl, 2002, 188: 8-18.
[2] 杨琼, 张全明, 曾楠, 等. 耳内镜下经耳道入路治疗局限性上鼓室胆脂瘤[J]. 中华耳科学杂志, 2017, 15(4): 416-419. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2922.2017.04.006
[3] 杨海弟, 高敏倩, 郑亿庆. 耳内镜下经耳道入路中耳胆脂瘤手术疗效分析[J]. 中国耳鼻咽喉头颈外科, 2019, 26(7): 346-349. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-EBYT201907002.htm
[4] 张瑾, 汪照炎, 杨琼, 等. 耳内镜下鼓膜成形术临床疗效分析的多中心回顾性研究[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2019, 54(4): 245-250. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-0860.2019.04.002
[5] 刘婷, 谢景华, 何龙. 鼓室硬化全耳内镜手术及近期疗效分析[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2018, 32(10): 732-736. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201810003.htm
[6] Wielinga EW, Kerr AG. Tympanosclerosis[J]. Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci, 1993, 18(5): 341-349. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2273.1993.tb00590.x
[7] Ahmet KOC. The Role of Mastoid Pneumatization in the Pathogenesis of Tympanosclerosis[J]. Int Adv Otol, 2012, 8(3): 426-433.
[8] Albu S, Babighian G, Trabalzini F. Surgical Treatment of Tympanosclerosis[J]. Am J Otol, 2000, 21(5): 631-635.
[9] Bhardwaj A, Anant A, Bharadwaj N, et al. Stapedotomy using a 4 mm endoscope: any advantage over a microscope?[J]. J Laryngol Otol, 2018, 132(9): 807-811. doi: 10.1017/S0022215118001548
[10] Moneir W, Abd El-Fattah AM, Mahmoud E, et al. Endoscopic stapedotomy: Merits and demerits[J]. J Otol, 2018, 13(3): 97-100. doi: 10.1016/j.joto.2017.11.002
[11] Bedri EH, Teferi N, Redleaf M. Stapes release in tympanosclerosis[J]. Otol Neurotol, 2018, 39(2): 184-188. doi: 10.1097/MAO.0000000000001639
[12] 王正敏. 慢性中耳炎功能根治[J]. 中国眼耳鼻喉科杂志, 2010, 10(3): 137-141. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2420.2010.03.001
[13] Yetiser S, Hidir Y, Karatas E, et al. Management of tympanosclerosis with ossicular fixation: review and presentation of long-term results of 30 new cases[J]. J Otolaryngol, 2007, 36(5): 303-308. doi: 10.2310/7070.2007.0048
[14] Bayazit YA, Ozer E, Kara C, et al. An analysis of the single-stage tympanoplasty with over-underlay grafting in tympanosclerosis[J]. Otol Neurotol, 2004, 25(3): 211-214. doi: 10.1097/00129492-200405000-00001
[15] Teufert KB, De La Cruz A. Tympanosclerosis: Long-term hearing results after ossicular reconstruction[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2002, 126(3): 264-272. doi: 10.1067/mhn.2002.122701
[16] Sakalli E, Celikyurt C, Guler B, et al. The effect of stapes fixation on hearing results in tympanosclerosis treated by mobilization[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2015, 272(11): 3271-3275. doi: 10.1007/s00405-014-3414-7
[17] Mutlu F, Iseri M, Erdogan S, et al. An Analysis of Surgical Treatment Results of Patients With Tympanosclerosis[J]. J Craniofac Surg, 2015, 26(8): 2393-2395. doi: 10.1097/SCS.0000000000002152
[18] 张珂, 马芙蓉, 宋为明, 等. 鼓室硬化患者手术前后骨导听力变化的临床研究[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2017, 31(16): 1228-1237. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201716003.htm
-

| 引用本文: | 李希平, 陈志婷, 黄小兵, 等. 耳内镜下鼓室硬化症一期鼓室成形术近期疗效分析[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2020, 34(10): 878-883. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2020.10.004 |
| Citation: | LI Xiping, CHEN Zhiting, HUANG Xiaobing, et al. Short-term effect of endoscopic one-stage tympanoplasty on tympanosclerosis[J]. J Clin Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2020, 34(10): 878-883. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2020.10.004 |
- Figure 1.
- Figure 2.
- Figure 3.
- Figure 4.



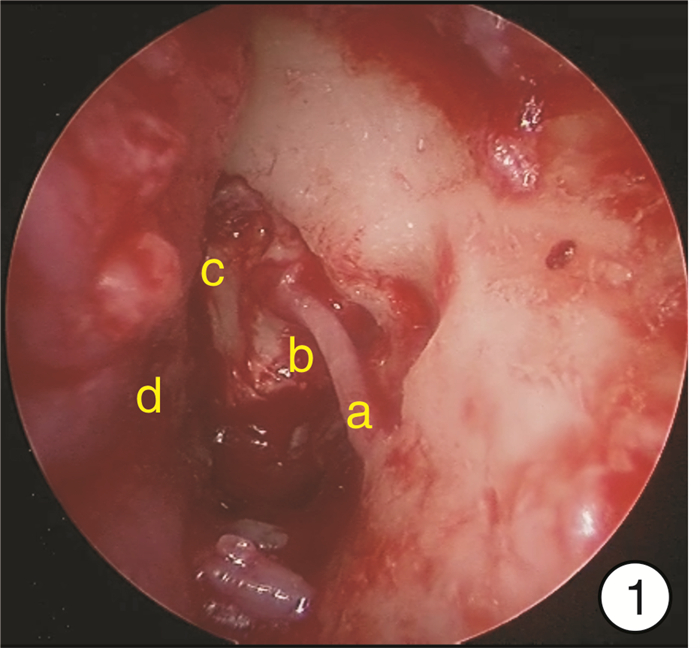
 下载:
下载: