Clinical significance and expression of periostin in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps
-
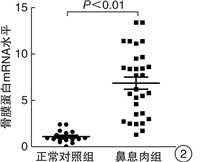
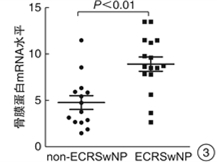
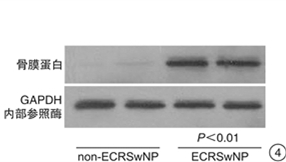
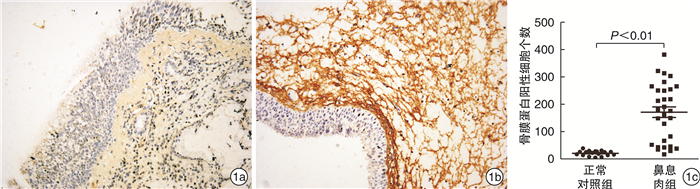
摘要: 目的 探讨骨膜蛋白在鼻息肉发病过程中的作用及可能机制。方法 收集30例CRSwNP患者鼻息肉组织和18例正常对照组的鼻黏膜,免疫组织化学和免疫印迹技术检测骨膜蛋白在各组鼻黏膜中的表达情况;荧光定量PCR法检测各组鼻黏膜组织中骨膜蛋白和IL-5 mRNA表达水平;比较嗜酸粒细胞性和非嗜酸粒细胞性鼻息肉中骨膜蛋白mRNA的表达差异。结果 骨膜蛋白主要表达于鼻黏膜上皮下区域,鼻息肉组织中骨膜蛋白阳性细胞数显著高于正常对照组(P < 0.01);骨膜蛋白mRNA表达水平和蛋白表达水平在嗜酸粒细胞性鼻息肉组织中明显高于非嗜酸粒细胞性鼻息肉组织和正常对照组(均P < 0.01);鼻息肉组织中骨膜蛋白mRNA和IL-5 mRNA表达水平呈正相关(r=0.731 5,P < 0.01)。结论 鼻息肉组织中高表达的骨膜蛋白可能通过趋化和活化嗜酸粒细胞参与鼻息肉的形成过程。Abstract: Objective To investigate the clinical significance and expression of periostin in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps(CRSwNP).Method In this study, we collected 30 CRSwNP patients' nasal polyps(NPs) and 18 control subjects' normal nasal mucosa of uncinate process. The expressions of periostin and IL-5 were examined using immunohistochemistric staining, immunostaining and /or quantitative RT-PCR and the eosinophil infiltration were evaluated as well.Result Periostin was mainly expressed in the subdermal area of nasal mucosa. The number of periostin positive cells in nasal polyps was significantly higher than that in normal control group(P < 0.01). The mRNA and protein expressions of periostin in NPs were significantly higher than that of the control nasal mucosa(all P < 0.01). The expression of priostin mRNA were positively correlated with IL-5 expression in NPs(r=0.731 5, P < 0.01).Conclusion Our findings indicate periostin may participate in the formation of nasal polyps by means of chemostaxis and activation of eosinophils.
-
Key words:
- periostin /
- nasal polyp /
- sinusitis /
- eosinophil /
- IL-5
-

-
[1] Fokkens WJ, Lund VJ, Mullol J, et al. EPOS 2012: European position paper on rhinosinusitis and nasal polyps 2012. A summary for otorhinolaryngologists[J]. Rhinology, 2012, 50(1): 1-12. doi: 10.4193/Rhino12.000
[2] Akidis CA, Bachert C, Cingi C, et al. Endotypes and phenotypes of chronic rhinosinusitis: A PRACTALL document of the European Academy of Allergy and Clinical Immunology and the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma Immunology[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2013, 131(6): 1479-1490. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2013.02.036
[3] Chin D, Harvey RJ. Nasal polyposis: an inflammatory condition requiring effective anti-inflammatory treatment[J]. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2013, 21(1): 23-30. doi: 10.1097/MOO.0b013e32835bc3f9
[4] Izuhara K, Arima K, Ohta S, et al. Periostin in allergic inflammation[J]. Allergol Int, 2014, 63(2): 143-151. doi: 10.2332/allergolint.13-RAI-0663
[5] Izuhara K, Conway SJ, Moore BB, et al. Roles of Periostin in Respiratory Disorders[J]. Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 2016, 193(9): 949-956. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201510-2032PP
[6] Takayama G, Arima K, Kanaji T, et al. Periostin: a novel component of subepithelial fibrosis of bronchial asthma downstream of IL-4 and IL-13 signals[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2006, 118(1): 98-104. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2006.02.046
[7] Masuoka M, Shiraishi H, Ohta S, et al. Periostin promotes chronic allergic inflammation in response to Th2 cytokines[J]. J Clin Invest, 2012, 122(7): 2590-2600. doi: 10.1172/JCI58978
[8] Jia G, Erickson RW, Choy DF, et al. Periostin is a systemic biomarker of eosinophilic airway inflammation in asthmatic patients[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2012, 130(3): 647-654. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2012.06.025
[9] Wang M, Wang X, Zhang N, et al. Association of periostin expression with eosinophilic inflammation in nasal polyps[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2015, 136(6): 1700-1703. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2015.09.005
[10] Wen W, Liu W, Zhang L, et al. Increased neutrophilia in nasal polyps reduces the response to oral corticosteroid therapy[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2012, 129(6): 1522-1528. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2012.01.079
[11] Mullol J, Obando A, Pujols L, et al. Corticosteroid treatment in chronic rhinosinusitis: the possibilities and limits[J]. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am, 2009, 29(4): 657-668. doi: 10.1016/j.iac.2009.07.001
[12] Helling PW, Fokkens WJ, Akdis C, et al. Uncontrolled allergic rhinitis and chronic rhinosinusitis: where do we stand today?[J]. Allergy, 2013, 68(1): 1-7. doi: 10.1111/all.12040
[13] Kudo A. Periostin in fibrillogenesis for tissue regeneration: periostin actions inside and outside the cell[J]. Cell Mol Life Sci, 2011, 68(19): 3201-3207. doi: 10.1007/s00018-011-0784-5
[14] Izuhara K, Nunomura S, Nanri Y, et al. Periostin in inflammation and allergy[J]. Cell Mol Life Sci, 2017, 74(23): 4293-4303. doi: 10.1007/s00018-017-2648-0
[15] Matsusaka M, Kabata H, Fukunaga K, et al. Phenotype of asthma related with high serum periostin levels[J]. Allergol Int, 2015, 64(2): 175-180. doi: 10.1016/j.alit.2014.07.003
[16] Kim MA, Izuhara K, Ohta S, et al. Association of serum periostin with aspirin-exacerbated respiratory disease[J]. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol, 2014, 113(3): 314-320. doi: 10.1016/j.anai.2014.06.014
[17] 李华斌, 冯韶燕, 程岚. 嗜酸粒细胞性慢性鼻窦炎的临床特点和治疗策略[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2016, 30(3): 177-179. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201603001.htm
-




 下载:
下载: