Clinical analysis of 35 cases of adult rhabdomyosarcoma of nasal cavity and sinuses
-
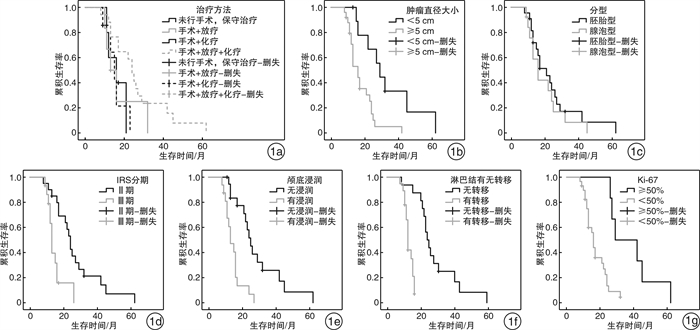
摘要: 目的 探讨成人鼻腔鼻窦横纹肌肉瘤(RMS)的临床特点及影响预后的因素。方法 成人鼻腔鼻窦RMS患者35例, 其中胚胎型22例, 腺泡型13例。手术+放化疗17例, 手术+放疗6例, 手术+化疗7例(手术及化疗后粒子植入4例); 5例未行手术治疗, 仅用抗肿瘤药物治疗。结果 随访9~62个月, 成人鼻腔鼻窦RMS 5年总生存率为2.9%, 其中IRS分期>Ⅱ期、肿瘤颅底浸润、局部淋巴结转移、肿瘤直径≥5 cm、Ki-67≥50%是预后不良因素。结论 成人鼻腔鼻窦RMS以胚胎型多见, 5年总生存率低, 与成人初诊时原发灶肿瘤体积较大、局部淋巴结转移、颅底浸润、Ki-67占比较高等有关。Abstract: Objective To investigate the clinical characteristics and prognostic factors of adult rhabdomyosarcoma(RMS) of nasal cavity and sinus.Method There were 35 adult patients with RMS, including 22 with embryonal type and 13 with acinar type. Surgery + chemoradiotherapy(17 cases), surgery + radiotherapy(6 cases), surgery + chemotherapy(7 cases)(4 cases of seed implantation after surgery and chemotherapy); Five patients were treated with antitumor drugs instead of surgery.Result The study follow-up 9-62 months, adult nasal sinuses RMS total 5 years survival rate was 2.9%, among them the IRS stage>Ⅱ period, the infiltration of the skull base tumor, local lymph node metastasis, tumor diameter of 5 cm or more, 50% or higher Ki-67 are poor prognosis factor. Conclusion RMS in nasal cavity and sinus are mostly embryonal type in adults, and the 5-year overall survival rate is low, which is related to larger primary tumor volume, local lymph node metastasis, skull base infiltration and higher ki-67 ratio at the first diagnosis in adults.
-
Key words:
- rhabdomyosarcoma /
- nasal sinuses /
- adult
-

-
表 1 35例成人鼻腔鼻窦RMS患者的一般资料
项目 例数(%) 项目 例数(%) 性别 首发症状 男 21(60.0) 鼻塞 29(82.9) 女 14(40.0) 鼻出血 15(42.9) 病理组织分型 涕中带血 20(57.1) 胚胎型 22(62.9) 脓涕 8(22.9) 腺泡型 13(37.1) 眼部胀痛 10(28.6) IRS分期 溢泪 6(17.1) Ⅱ期 20(57.1) 视力下降 9(25.7) Ⅲ期 14(40.0) 失明 2(5.7) Ⅳ期 1(2.9) 面部麻木 3(8.6) 初诊病变位置侵及 肿瘤直径/cm 鼻腔及鼻窦 19(54.3) ≥5 20(57.1) 前颅底 16(45.7) < 5 15(42.9) 淋巴结转移 Ki-67/% 有 19(54.3) ≥50 28(80.0) 无 16(45.7) < 50 7(20.0) -
[1] Rudzinski ER, Anderson JR, Hawkins DS, et al. The World Health Organization Classification of Skeletal Muscle Tumors in Pediatric Rhabdomyosarcoma: A Report From the Children's Oncology Group[J]. Arch Pathol Lab Med, 2015, 139(10): 1281-1287. doi: 10.5858/arpa.2014-0475-OA
[2] Joo JH, Han JS, Choi SM, et al. One-year survivor of adult alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma of the maxillary sinus with orbital extension: Case report[J]. Medicine(Baltimore), 2018, 97(35): e11866.
[3] Chen SC, Bee YS, Lin MC, et al. Extensive alveolar-type paranasal sinus and orbit rhabdomyosarcoma with intracranial invasion treated successfully[J]. J Chin Med Assoc, 2011, 74(3): 140-143. doi: 10.1016/j.jcma.2011.01.031
[4] Palacios E, Quiroz-Casian A, Garza Garcia L, et al. Adult case of large sinonasal embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma with intracranial extension[J]. Ear Nose Throat J, 2013, 92(4-5): 177-178.
[5] Ognjanovic S, Linabery AM, Charbonneau B, et al. Trends in childhood rhabdomyosarcoma incidence and survival in the United States, 1975-2005[J]. Cancer, 2009, 115(18): 4218-4226. doi: 10.1002/cncr.24465
[6] 俞其光, 董雪莲, 王海国. 鼻腔胚胎性横纹肌肉瘤一例[J]. 现代实用医学, 2009, 21(4): 368-368. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0800.2009.04.085
[7] Weiss AR, Lyden ER, Anderson JR, et al. Histologic and clinical characteristics can guide staging evaluations for children and adolescents with rhabdomyosarcoma: a report from the Children's Oncology Group Soft Tissue Sarcoma Committee[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2013, 31(26): 3226—3232. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2012.44.6476
[8] Bergamaschi L, Bertulli R, Casanova M, et al. Rhabdomyosarcoma in adults: analysis of treatment modalities in a prospective single-center series[J]. Med Oncol, 2019, 36(7): 59. doi: 10.1007/s12032-019-1282-0
[9] Yerushalmi R, Woods R, Ravdin PM, et al. Ki67 in breast cancer: prognostic and predictive potential[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2010, 11(2): 174-183. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(09)70262-1
[10] Sanghvi S, Misra P, Patel NR, et al. Incidence trends and long-term survival analysis of sinonasal rhabdomyosarcoma[J]. Am J Otolaryngol, 2013, 34(6): 682-689. doi: 10.1016/j.amjoto.2013.04.012
[11] Casey DL, Wolden SL. Rhabdomyosarcoma of the head and Neck: A muhimodal approach[J]. J Neurol Surg B Skull Base, 2018, 79(1): 58-64. doi: 10.1055/s-0037-1617450
[12] Turner JH, Richmon JD. Head and neck rhabdomyosarcoma: a critical analysis of population-based incidence and survival data[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2011, 145(6): 967-973. doi: 10.1177/0194599811417063
[13] Radzikowska J, Kukwa W, Kukwa A, et al. Management of pediatric head and neck rhabdomyosarcoma: A case-series of 36 patients[J]. Oncol Lett, 2016, 12(5): 3555-3562. doi: 10.3892/ol.2016.5072
[14] Wurm J, Constantinidis J, Grabenbauer GG, et al. Rhabdomyosarcomas of the nose and paranasal sinuses: treatment results in 15 cases[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2005, 133(1): 42-50. doi: 10.1016/j.otohns.2005.03.023
[15] Towbin JA, Lowe AM, Colan SD, et al. Incidence, causes, and outcomes of dilated cardiomyopathy in children[J]. JAMA, 2006, 296(15): 1867-1876. doi: 10.1001/jama.296.15.1867
[16] 高军茂, 许卫东, 陈点点, 等. 调强适形放疗治疗成人脑膜旁横纹肌肉瘤[J]. 现代肿瘤医学, 2018, 26(7): 1024-1028. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4992.2018.07.011
[17] 刘江华, 毛彦娜, 李彦格, 等. 36例儿童横纹肌肉瘤疗效分析[J]. 现代肿瘤医学, 2019, 27(9): 1598-1601. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4992.2019.09.031
[18] 张谊, 张伟令, 黄东生, 等. 儿童头颈部横纹肌肉瘤98例生存情况分析[J]. 中华全科医师杂志, 2019, 18(7): 663-667. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1671-7368.2019.07.010
[19] 段超, 王生才, 金眉, 等. 多学科联合诊治儿童头颈部横纹肌肉瘤48例临床研究[J]. 中华实用临床杂志, 2019, 34(7): 529-533.
[20] 赵丹, 郑磊, 吕晓鸣, 等. 125Ⅰ放射性粒子植入近距离放疗在儿童口腔颌面-头颈部肉瘤治疗中的应用[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2017, 97(1): 33-37.
[21] 李克鹏, 刘柱, 金红军, 等. 鼻部横纹肌肉瘤诊疗分析[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2017, 31(18): 1398-1401, 1407. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201718008.htm
-




 下载:
下载: