Preliminary study of medialization thyroplasty for unilateral vocal fold immobility
-
摘要: 目的 初步探讨甲状软骨成形声带内移术治疗单侧声带运动不良的可行性及其疗效。方法 8例单侧声带运动不良患者, 局部麻醉下在甲状软骨开窗, 置入预成型的硅酮支架, 将麻痹的声带向内侧移位, 改善声门闭合状态。手术前后均采用纤维喉镜录像、嗓音主观分析及喉部薄层CT检查, 评估声门闭合、嗓音改善及植入物位置。结果 8例患者嗓音障碍指数术前为91.5(64.5, 97.5), 术后为22.5(5.0, 47.5), 术后显著小于术前(P < 0.05)。GRBAS结果: G、R、B、A术后均显著小于术前(P < 0.05);S术前术后均为0。声门关闭不全评分术前为1.0(1.0, 1.0), 术后为4.0(2.5, 5.0), 术后显著高于术前(P < 0.05)。术后喉部CT检查患侧声带明显内移。术前有误吸的4例患者术后症状明显改善。8例患者随访5~48个月, 无一例出现并发症。结论 甲状软骨成形声带内移术有效地改善了单侧声带运动不良患者的发声和生活质量。
-
关键词:
- 甲状软骨成形声带内移术 /
- 声带运动不良 /
- 声带麻痹 /
- 嗓音
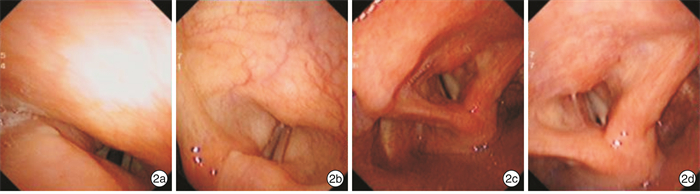
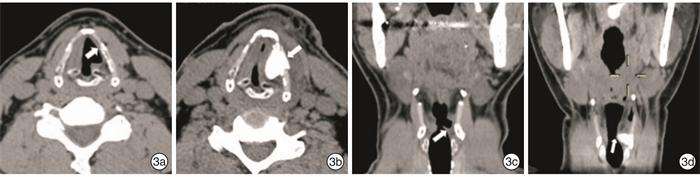
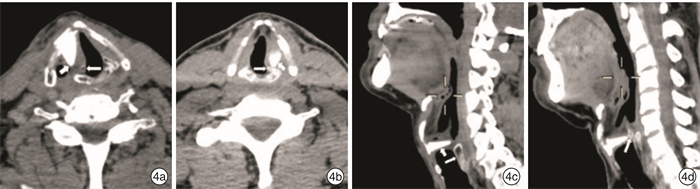
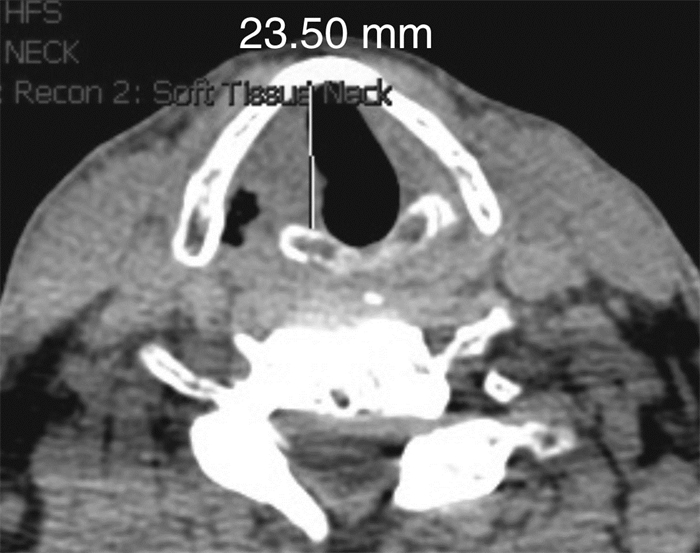
Abstract: Objective To explore the feasibility and effectiveness of medialization thyroplasty for the treatment of unilateral vocal fold immobility (UVFI).Method Eight UVFI patients were performed medialization thyroplasty under local anesthesia. We made a window in the thyroid cartilage under local anesthesia, then insert the preformed silicone implant. The paralyzed vocal fold was medialized to make the glottis closed. Fibrolaryngoscope video recording, subjective voice analysis and CT thin slice scan of larynx were done before and after surgery to evaluate closure of vocal cords, improvement of voice and position of implantation.Result The preoperative and postoperative voice handicap index 30(VHI-30) of the 8 patients were 91.5(64.5, 97.5) and 22.5(5.0, 47.5) respectively, which showed statistical difference(P < 0.05). GRBAS results: The postoperative G, R, B, A were all smaller than preoperative ones, which showed statistical difference(P < 0.05); the pre and postoperative S was both 0. The fibrolaryhgoscope recording showed the preoperative and postoperative score of incomplete glottis closure was 1.0(1.0, 1.0) and 4.0(2.5, 5.0) respectively, which showed statistical difference(P < 0.05). Postoperative laryngeal CT showed significant vocal cord medialization on the affected side. Aspiration was significantly improved in 4 patients who were suffered from this symptom before the surgery. No complication occurred with the 8 patients during 5 to 48 months follow up.Conclusion Medialization thyroplasty can effectively improve vocalization and quality of life in patients with UVFI.-
Key words:
- medialization thyroplasty /
- vocal fold immobility /
- vocal cord paralysis /
- voice
-

-
表 1 8例UVFI患者的临床资料
例序 性别 年龄/岁 侧别 病因 病程/月 随访时间/月 误吸 1 女 65 右 甲状腺手术 18 48 有 2 男 36 左 胸腔手术 6 42 无 3 女 50 右 咽旁间隙神经鞘瘤切除术后 24 42 有 4 男 49 右 甲状腺术后 50 36 无 5 男 34 左 甲状腺术后 108 28 无 6 男 73 右 甲状腺术后 17 26 有 7 男 59 左 肺叶切除术 204 24 有 8 男 53 右 肺癌术后 16 5 无 表 2 8例患者手术前后VHI-30、GRBAS、声门关闭不全评分结果
分 例序 VHI-30评分 G R B A S 声门关闭不全评分 术前 术后 术前 术后 术前 术后 术前 术后 术前 术后 术前 术后 术前 术后 1 98 8 2.5 0.8 1.5 0.8 2.5 0.2 1.0 0 0 0 1 5 2 75 10 2.2 0 1.0 0 2.2 0 1.0 0 0 0 1 4 3 95 4 3.0 1.2 2.0 1.0 3.0 1.2 1.5 0.5 0 0 1 5 4 96 55 2.0 0.8 1.0 0.8 2.0 0 0.5 0 0 0 1 4 5 88 40 1.2 1.0 1.2 1.0 0.8 0 0 0 0 0 2 4 6 104 45 2.5 1.2 1.2 1.0 2.5 1.2 1.5 0.8 0 0 1 2 7 41 3 2.5 0.5 1.0 0.5 2.5 0 1.2 0 0 0 1 5 8 61 35 3.0 1.2 2.0 1.0 3.0 1.2 1.5 0 0 0 1 2 注:例3、例8术前均为近耳语。 表 3 VHI-30、GRBAS、声门关闭不全评分非参数配对检验统计结果(n=8)
中位数 四分位距 P VHI-30 术前 91.5 64.5,97.5 0.012 术后 22.5 5.0,47.5 GRBAS G术前 2.50 2.05,2.88 0.012 G术后 0.90 0.58,1.20 R术前 1.20 1.00,1.90 0.011 R术后 0.90 0.58,1.00 B术前 2.50 2.05,2.88 0.012 B术后 0.10 0,1.20 A术前 1.10 0.63,1.50 0.017 A术后 0 0,0.38 S术前 0 0 S术后 0 0 声门关闭不全 术前 1.0 1.0,1.0 0.011 术后 4.0 2.5,5.0 -
[1] Cohen SM, Dupont WD, Courey MS. Quality-of-life impact of nonneoplastic voice disorders: a meta-analysis[J]. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol, 2006, 115(2): 128-134. doi: 10.1177/000348940611500209
[2] 徐文, 李红艳, 胡蓉, 等. 嗓音障碍指数量表中文版信度和效度评价[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2008, 43(9): 670-675. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1673-0860.2008.09.008
[3] Hirano M, Arnold GE, Winckel F, et al. Clinical examination of voice in disorders of human communication[M]. New York: Springer, 1981: 81-84.
[4] Chhetri DK, Gerratt BR, Kreiman J, et al. Combined arytenoid adduction and laryngeal reinnervation in the treatment of vocal fold paralysis[J]. Laryngoscope, 1999, 109(12): 1928-1936. doi: 10.1097/00005537-199912000-00006
[5] Dejonckere PH, Bradley P, Clemente P, et al. A basic protocol for functional assessment of voice pathology, especially for investigating the efficacy of(phonosurgical)treatments and evaluating new assessment techniques. Guidelines elaborated by the Committee on Phoniatrics of the European Laryngological Society(ELS)[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2001, 258(2): 77-82. doi: 10.1007/s004050000299
[6] Montgomery WW, Blaugrund SM, Varvares MA. Thyroplasty: a new approach[J]. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol, 1993, 102(8 Pt 1): 571-579.
[7] Kelchner LN, Stemple JC, Gerdeman E, et al. Etiology, pathophysiology, treatment choices, and voice results for unilateral adductor vocal fold paralysis: a 3-year retrospective[J]. J Voice, 1999, 13(4): 592-601. doi: 10.1016/S0892-1997(99)80013-7
[8] Rosen CA. Complications of phonosurgery: results of a national survey[J]. Laryngoscope, 1998, 108(11 Pt 1): 1697-1703.
[9] 高颖娜, 陈世彩, 陈东辉, 等. 颈襻前根修复单侧喉返神经损伤的疗效分析[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2018, 53(9): 655-659. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-0860.2018.09.004
[10] Friedrich G, de Jong F, Mahieu HF, et al. Laryngeal framework surgery: a proposal for classification and nomenclature by the Phonosurgery Committee of the European Laryngological Society[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2001, 258(8): 389-396. doi: 10.1007/s004050100375
[11] Ramacle M, Lawson G, Hedayat A, et al. Medialization framework surgery for voice improvement after endoscopic cordectomy[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2001, 258(6): 267-271. doi: 10.1007/s004050100350
[12] Zeitels SM, Jarboe J, Franco RA. Phonosurgical reconstruction of early glottic cancer[J]. Laryngoscope, 2001, 111(10): 1862-1865. doi: 10.1097/00005537-200110000-00036
[13] Young VN, Zullo TG, Rosen CA. Analysis of laryngeal framework surgery: 10-year follow-up to a national survey[J]. Laryngoscope, 2010, 120(8): 1602-1608. doi: 10.1002/lary.21004
-





 下载:
下载: