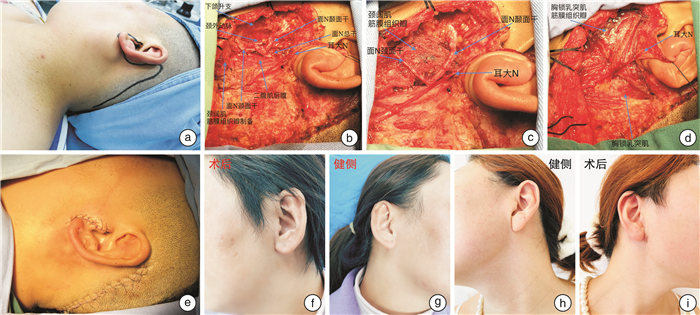
Application of modified Z-shaped cosmetic incision in parotid benign tumor resection
-
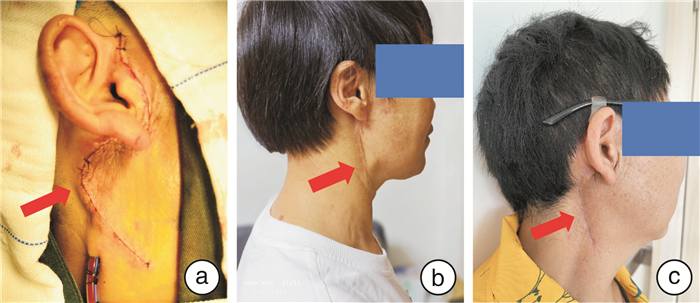
摘要: 目的 探讨改良Z形美容切口在腮腺良性肿瘤切除术中的安全性和美学效果。方法 采用前瞻性研究,将44例行腮腺良性肿瘤切除术的患者随机分为试验组(22例)和对照组(22例)。试验组采用改良Z形美容切口,对照组采用传统S形切口,比较2组在手术时长、住院天数、并发症以及颌面部美观方面的统计学差异。结果 试验组和对照组在性别、年龄、手术方式、病理类型比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);2组对手术持续时间、视觉模拟评分进行比较,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05),但住院天数、手术并发症及温哥华瘢痕量表评分比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。结论 改良Z形美容切口在改善腮腺良性肿瘤切除术后颌面部美观方面的效果更好,且与传统S形切口相比较,安全性一致,因此值得临床推广和应用。Abstract: Objective To explore the safety and aesthetic effect of modified Z-shaped cosmetic incision in parotid benign tumor resection.Methods A prospective study was conducted. A total of 44 patients with benign parotid tumor resection were randomly divided into experimental group(n=22) and control group(n=22). The experimental group underwent modified Z-shaped cosmetic incision, while the control group underwent the traditional S-shaped incision. The surgical duration, hospital stay, complications and maxillofacial aesthetics were compared between the two groups.Results There was no significant difference in gender, age, surgical method, pathological type between the experimental group and the control group(P>0.05). The maxillofacial aesthetics and surgical duration of the two groups was statistically significant(P < 0.05), while there was no statistically significant difference in terms of hospitalization days, surgical complications and Vancouver scar scale score (P>0.05).Conclusion The modified Z-shaped cosmetic incision has a better effect on improving the maxillofacial aesthetics after benign parotid tumor resection, and compared with the traditional S-shaped incision, the safety is consistent, so it is worthy of clinical promotion and application.
-
Key words:
- parotid tumor /
- modified incision /
- cosmetic
-

-
表 1 试验组和对照组基本数据比较
变量 试验组(22例) 对照组(22例) t/χ2 P 性别/例(%) 0.109 0.741 男 7(31.8) 6(27.3) 女 15(68.2) 16(72.7) 年龄/岁 55.04±9.11 47.39±11.22 1.017 0.247 手术方式/例(%) 0.419 0.517 腮腺肿瘤及浅叶切除+胸锁乳突肌瓣修复术 16(72.7) 14(63.6) 腮腺全切+胸锁乳突肌颈阔肌双蒂肌瓣修复术 6(27.3) 8(36.4) 病理类型/例(%) 多形性腺瘤 18(81.8) 16(72.8) 0.518 0.472 腺淋巴瘤 2(9.1) 3(13.6) 0.226 0.635 基底细胞腺瘤 2(9.1) 3(13.6) 0.226 0.635 表 2 试验组和对照组观察指标的比较
X±S 变量 试验组(22例) 对照组(22例) t/χ2 P 手术持续时间/min 140.23±10.69 120.18±5.77 11.044 < 0.001 住院天数/d 7.19±1.33 7.04±1.25 0.280 0.761 并发症/例(%) 暂时性面瘫 7(31.8) 5(22.7) 0.458 0.498 耳垂麻木 4(18.2) 3(13.6) 0.170 0.680 感染 0 0 - - 味觉出汗综合征 0 0 - - VAS/分 9.49±0.01 4.89±1.69 13.939 < 0.001 VSS/分 1.36±0.95 1.41±0.87 0.158 0.875 -
[1] 杨宝琦, 译. 头颈肿瘤学及手术修复[M]. 天津: 天津科技翻译出版有限公司, 2013: 362-363.
[2] 陈杨, 张萌, 张勤修, 等. 改良面部除皱切口在腮腺手术中的应用研究[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2022, 36(12): 940-943. https://lceh.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2022.12.010
[3] Suzuki M, Nakaegawa Y, Kobayashi T, et al. Indications for partial superficial parotidectomy for benign parotid gland tumors using the retrograde approach[J]. Fukushima J Med Sci, 2020, 66(2): 73-77. doi: 10.5387/fms.2020-06
[4] Shi L, Song XB, Wang KT, et al. [Preliminary study on endoscope-assisted resection of superficial benign tumor of parotid gland][J]. Zhonghua Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi, 2019, 54(12): 847-850.
[5] Matsumoto F, Ohba S, Fujimaki M, et al. Efficacy of modified face lift incision for the resection of benign parotid gland tumor located anteriorly or superiorly[J]. Auris Nasus Larynx, 2021, 48(5): 978-982. doi: 10.1016/j.anl.2021.01.014
[6] Ogino A, Onishi K, Nakamichi M, et al. Use of Parotid Gland Fascia in the Prevention of Frey Syndrome After Parotidectomy[J]. J Craniofac Surg, 2019, 30(4): 1009-1011. doi: 10.1097/SCS.0000000000005458
[7] Khafif A, Niddal A, Azoulay O, et al. Parotidectomy via individualized mini-Blair incision[J]. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec, 2020, 82(3): 121-129. doi: 10.1159/000505192
[8] Liu H, Li YS, Dai XM. Modified face-lift approach combined with a superficially anterior and superior-based sternocleidomastoid muscle flap in total parotidectomy[J]. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol, 2012, 113(5): 593-599. doi: 10.1016/j.tripleo.2011.04.042
[9] 石远凯, 孙燕. 临床肿瘤内科手册[M]. 6版. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2015: 147-149.
[10] Flach S, Hey SY, Lim A, et al. Outpatient(same-day discharge)versus inpatient parotidectomy: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Clin Otolaryngol, 2020, 45(4): 529-537. doi: 10.1111/coa.13519
[11] Zhang J, Jiang Q, Na S, et al. Retraction notice to: Minimal Scar Dissection for Partial Parotidectomy via a Modified Cosmetic Incision and an Advanced Wound Closure Method[YJOMS 77(2019)1317. E1-1317. E9][J]. J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2022, 80(5): 967. doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2022.03.001
[12] Lee YC, Liao WC, Yang SW, et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of modified facelift incision versus modified Blair incision in parotidectomy[J]. Sci Rep, 2021, 11(1): 24106. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-03483-6
[13] Bird J, Mirza AH, King E. Caution in the use of TissuePatchDS-PTM in drainless benign superficial parotidectomy, a pilot study: Our experience in three patients[J]. Clin Otolaryngol, 2020, 45(5): 837-840. doi: 10.1111/coa.13594
[14] Colaianni CA, Feng AL, Richmon JD. Partial parotidectomy via periauricular incision: Retrospective cohort study and comparative analysis to alternative incisional approaches[J]. Head Neck, 2021, 43(3): 825-832. doi: 10.1002/hed.26542
[15] Alomar OSK. A new modified limited incision for superficial parotidectomy compared to modified Blair's incision[J]. Ann Med Surg(Lond), 2023, 85(9): 4283-4288. doi: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000001123
[16] Nair S, Aishwarya JG, Jain A, et al. Mini-incision parotidectomy-our technique[J]. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2022, 74(Suppl 3): 6174-6179.
[17] Roh JL. Selective deep lobe parotidectomy via retroauricular hairline(Roh's)incision for deep lobe parotid pleomorphic adenoma[J]. Oral Dis, 2023, 29(1): 188-194. doi: 10.1111/odi.14069
[18] Han P, Liang F, Lin P, et al. Comparison of conventional and endoscope-assisted partial clretain: >superficial parotidectomy for benign neoplasms of the parotid gland: a matched case-control study[J]. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2024, 53(3): 199-204. doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2023.08.002
[19] Zou HW, Gao J, Liu JX, et al. Feasibility and advantages of endoscope-assisted parotidectomy: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2021, 59(5): 503-510. doi: 10.1016/j.bjoms.2020.08.049
[20] Pinar YA, Ikiz ZA, Bilge O. Arterial anatomy of the auricle: its importance for reconstructive surgery[J]. Surg Radiol Anat, 2003, 25(3-4): 175-179. doi: 10.1007/s00276-003-0128-8
-




 下载:
下载: