A case report of giant neurofibromatosis of maxillofacial, neck and chest was treated by multidisciplinary cooperation
-
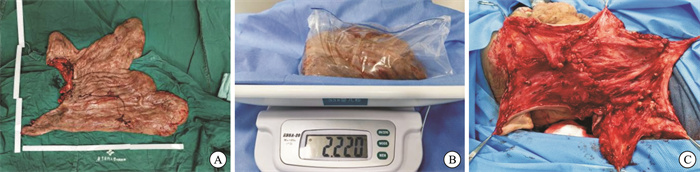
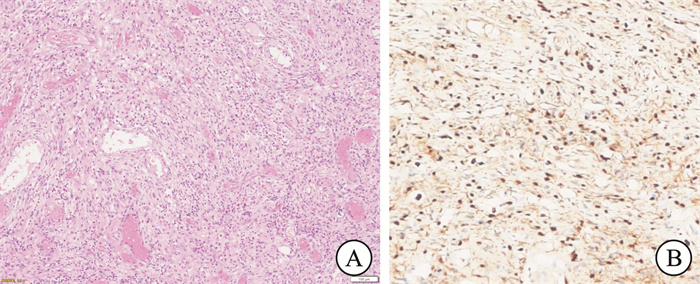
摘要: 1型神经纤维瘤病(neurofibromatosis type 1,NF1)是一种常染色体显性遗传性神经系统疾病。神经纤维瘤作为NF1中一种典型表现,体积可逐渐发展,当面积大于100 cm2时称为巨大NF1,是神经纤维鞘中施万细胞的瘤样增生。广东医科大学附属医院耳鼻咽喉中心收治了1例少见的颌面颈胸部巨大神经纤维瘤病患者,并在不同学科的协助下为其成功开展了手术治疗。Abstract: Neurofibromatosis Type 1 (NF1) is an autosomal dominant hereditary neurological disorder. One of the typical manifestations of NF1 is neurofibroma, which can develop gradually over time. When the volume exceeds 100 cm2, it is referred to as giant neurofibroma, representing a tumor-like proliferation of Schwann cells within the nerve fiber sheath. The Department of Otolaryngology at the Affiliated Hospital of Guangdong Medical University received a rare case involving a patient with giant neurofibromatosis affecting the maxillofacial region, neck, and chest. The patient underwent successful surgical treatment with the collaboration of various medical disciplines.
-
Key words:
- neurofibromatosis type 1 /
- cutaneous neurofibroma /
- surgical treatment
-

-
[1] 王生才, 李艳珍, 张杰, 等. 儿童丛状神经纤维瘤的诊治进展[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2022, 36(6): 477-482.
[2] Tamura R. Current understanding of neurofibromatosis type 1, 2, and schwannomatosis[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(11): 5850. doi: 10.3390/ijms22115850
[3] Farschtschi S, Mautner VF, McLean ACL, et al. The neurofibromatoses[J]. Dtsch Arztebl Int, 2020, 117(20): 354-360.
[4] Foiadelli T, Naso M, Licari A, et al. Advanced pharmacological therapies for neurofibromatosis type 1-related tumors[J]. Acta Biomed, 2020, 91(7-S): 101-114.
[5] Legius E, Messiaen L, Wolkenstein P, et al. Revised diagnostic criteria for neurofibromatosis type 1 and Legius syndrome: an international consensus recommendation[J]. Genet Med, 2021, 23(8): 1506-1513. doi: 10.1038/s41436-021-01170-5
[6] 朱以诚. Ⅰ型神经纤维瘤病多学科诊治指南(2023版)[J]. 罕见病研究, 2023, 2(2): 210-230.
[7] Blakeley JO, Plotkin SR. Therapeutic advances for the tumors associated with neurofibromatosis type 1, type 2, and schwannomatosis[J]. Neuro Oncol, 2016, 18(5): 624-638.
[8] Karaconji T, Whist E, Jamieson RV, et al. Neurofibromatosis type 1: review and update on emerging therapies[J]. Asia Pac J Ophthalmol(Phila), 2019, 8(1): 62-72.
[9] Cutruzzolà A, Irace C, Frazzetto M, et al. Functional and morphological cardiovascular alterations associated with neurofibromatosis 1[J]. Sci Rep, 2020, 10(1): 12070.
[10] Nopajaroonsri C, Lurie AA. Venous aneurysm, arterial dysplasia, and near-fatal hemorrhages in neurofibromatosis type 1[J]. Hum Pathol, 1996, 27(9): 982-985.
[11] 阮潜瑛, 张彬, 李素梅, 等. 躯干巨大神经纤维瘤患者联合预存自体全血及成分血的输血效果案例报道1例[J]. 检验医学与临床, 2023, 20(10): 1497-1499.
[12] Geube M, Sale S, Bakdash S, et al. Prepump autologous blood collection is associated with reduced intraoperative transfusions in aortic surgery with circulatory arrest: a propensity score-matched analysis[J]. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg, 2022, 164(5): 1572-1580.
[13] 高阳, 胡晓洁, 林晓曦. Ⅰ型神经纤维瘤病中血管病变的研究进展[J]. 组织工程与重建外科杂志, 2014, 10(4): 218-221.
[14] Chamseddin BH, Le LQ. Management of cutaneous neurofibroma: current therapy and future directions[J]. Neurooncol Adv, 2020, 2(Suppl 1): i107-i116.
[15] 朱倍瑶, 魏澄江, 王薇, 等. 皮肤型神经纤维瘤的治疗方案及研究进展[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志, 2022, 36(9): 1064-1071.
[16] Mukhopadhyay S, Maitra A, Choudhury S. Selumetinib: the first ever approved drug for neurofibromatosis-1 related inoperable plexiform neurofibroma[J]. Curr Med Res Opin, 2021, 37(5): 789-794.
-

计量
- 文章访问数: 100
- 施引文献: 0




 下载:
下载: