Efficacy analysis of Epley procedure and Semont procedure with different lateral lying angles of the head in posterior semicircular canal BPPV
-
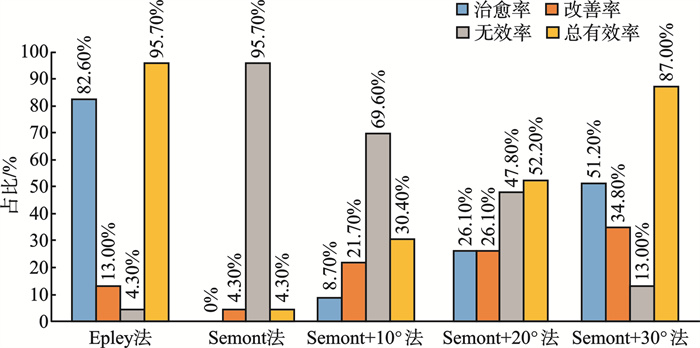
摘要: 目的 探讨应用Epley法及头部不同侧卧角度的Semont法在后半规管良性阵发性位置性眩晕(PC-BPPV)的疗效。 方法 将115例单侧PC-BPPV患者随机分为5组:Epley组、Semont组、Semont+10°组、Semont+20°组、Semont+30°组,每组23例患者,并进行相应的复位治疗,观察2次复位后的即时有效率。 结果 Epley组、Semont组、Semont+10°组、Semont+20°组、Semont+30°组5组患者的总有效率分别为95.7%(22/23)、4.3%(1/23)、30.4%(7/23)、52.2%(12/23)、87.0%(20/23),无效率分别为4.3%(1/23)、95.7%(22/23)、69.6%(16/23)、47.8%(11/23)、13.0%(3/23),5组的总有效率比较差异有统计学意义(χ2=54.11,P<0.01),Semont组、Semont+10°组、Semont+20°组的总有效率与Epley组比较差异有统计学意义(P<0.01),Semont+30°组总有效率与Epley组比较差异无统计学意义(P=0.608>0.012 5)。 结论 在4种不同侧卧角度的Semont法中,随着患侧侧卧角度的增加,复位治疗的总有效率逐渐提高。其中,Semont+30°组在治疗PC-BPPV中的效果与Epley法相当,且显著优于其他3种不同角度的Semont法。因此,在临床实践中,推荐采用Semont+30°复位法治疗PC-BPPV。
-
关键词:
- Semont法 /
- Epley法 /
- 后半规管良性阵发性位置性眩晕
Abstract: Objective To investigate the effects of the Epley and Semont procedures with varying lateral angles of the head on posterior semicircular canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (PC-BPPV). Methods A total of 115 patients with unilateral PC-BPPV were randomly divided into five groups: Epley group, Semont group, Semont+10° group, Semont+20° group, and Semont+30° group, with 23 patients in each group. Corresponding reduction treatments were performed. Results The total effective rates for the Epley group, Semont group, Semont+10° group, Semont+20° group, and Semont+30° group were 95.7% (22/23), 4.3% (1/23), 30.4% (7/23), 52.2% (12/23), and 87.0% (20/23) respectively. The inefficiencies were 4.3% (1/23), 95.7% (22/23), 69.6% (16/23), 47.8% (11/23), and 13.0% (3/23). Statistically significant differences were observed in the total effective rates among the five groups (χ2=54.11, P < 0.01). The total effective rates in the Semont group, Semont+10° group, and Semont+20° group were significantly different from that of the Epley group (P < 0.01), while no statistically significant difference was found between the Semont+30° group and the Epley group (P= 0.608>0.012 5). Conclusion Among the four Semont methods with different lateral lying angles, the total effective rate of reduction treatment increased with the elevation of the lateral lying angle on the affected side. The efficacy of the Semont+30° group in treating PC-BPPV was not significantly different from the Epley group's reduction effect, which was markedly superior to that of the other four Semont methods at different angles. Therefore, the Semont+30° reduction technique is recommended for the treatment of PC-BPPV. -

-
表 1 研究人群的基本特征
特征 复位方法 Epley法 Semont法 Semont+10°法 Semont+20°法 Semont+30°法 年龄/岁 58.1±14.0 44.0±11.2 52.2±10.1 48.7±13.8 46.1±12.9 性别/例(%) 男 5(21.7) 8(34.8) 7(30.4) 3(13.0) 6(26.1) 女 18(78.3) 15(65.2) 16(69.6) 20(87.0) 17(73.9) BPPV侧别/例(%) 左侧 5(21.7) 12(52.2) 10(43.5) 6(26.1) 14(60.9) 右侧 18(78.3) 11(47.8) 13(56.5) 17(73.9) 9(39.1) 病程/d 6.5±12.3 7.5±9.0 5.4±7.4 9.0±9.9 6.4±12.5 -
[1] 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志编辑委员会, 中华医会耳鼻咽喉头颈外科学分会. 良性阵发性位置性眩晕诊断和治疗指南(2017)[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2017, 52(3): 173-177.
[2] von Brevern M, Bertholon P, Brandt T, et al. Benign paroxysmal positional Vertigo: Diagnostic criteria[J]. J Vestib Res, 2015, 25(3-4): 105-117.
[3] Li D, Cheng D, Yang W, et al. Current Therapies in Patients With Posterior Semicircular Canal BPPV, a Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis[J]. Otol Neurotol, 2022, 43(4): 421-428. doi: 10.1097/MAO.0000000000003464
[4] Gan Z, Zhou S, Yang H, et al. Self-Treatment of Posterior Canal Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo: A Preliminary Study[J]. Front Med(Lausanne), 2021, 8: 654637.
[5] Chen X, Mao J, Ye H, et al. The effectiveness of the modified Epley maneuver for the treatment of posterior semicircular canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo[J]. Front Neurol, 2023, 14: 1328896.
[6] Lee HJ, Jeon EJ, Lee DH, et al. Therapeutic Efficacy of the Modified Epley Maneuver With a Pillow Under the Shoulders[J]. Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol, 2020, 13(4): 376-380. doi: 10.21053/ceo.2019.01830
[7] Tang H, Li W. Advances in the diagnosis and treatment of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2017, 14(3): 2424-2430. doi: 10.3892/etm.2017.4837
[8] 时美娟, 孟晴, 吕哲, 等. 良性阵发性位置性眩晕发病率及发病机制新进展[J]. 中华耳科学杂志, 2016, 14(4): 521-525.
[9] Mandalà M, Santoro GP, Asprella Libonati G, et al. Double-blind randomized trial on short-term efficacy of the Semont maneuver for the treatment of posterior canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo[J]. J Neurol, 2012, 259(5): 882-885. doi: 10.1007/s00415-011-6272-x
[10] Thakur B, Raj P, Singh K, et al. To compare the recovery rates of modified Epley's against Semont's manoeuvres in patients with posterior canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: a randomized clinical trial[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2024, 281(9): 4641-4648. doi: 10.1007/s00405-024-08657-2
[11] Oh SY, Kim JS, Choi KD, et al. Switch to Semont maneuver is no better than repetition of Epley maneuver in treating refractory BPPV[J]. J Neurol, 2017, 264(9): 1892-1898. doi: 10.1007/s00415-017-8580-2
[12] Mishra P, Sindhu KLS, Chethana R, et al. Epleys versus semonts manoeuvre in posterior canal benign paroxysmal positional Vertigo[J]. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2023, 75(Suppl 1): 523-527.
[13] Lovato A, Marioni G, Monzani D, et al. Physical Therapy for Benign Positional Vertigo of Posterior Canal: The Role of Alternated Epley and Semont Maneuvers[J]. Ear Nose Throat J, 2023, 102(2): NP60-NP64. doi: 10.1177/0145561320980183
[14] Öztürk Z, Bayar Muluk N, Dündar R, et al. The importance of Epley maneuver in posterior canal benign paroxysmal positional Vertigo[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2024, 28(6): 2155-2160.
[15] Imai T, Uno A, Yamato A, et al. Comparison of the efficacy of the Epley maneuver and repeated Dix-Hallpike tests for eliminating positional nystagmus: A multicenter randomized study[J]. Front Neurol, 2023, 14: 1095041.
[16] AlMohiza MA. Effects of epley procedure on BPPV patients: a systematic review of randomized controlled trails[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2023, 27(16): 7409-7415.
[17] Sinsamutpadung C, Kulthaveesup A. Comparison of outcomes of the Epley and Semont maneuvers in posterior canal BPPV: A randomized controlled trial[J]. Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol, 2021, 6(4): 866-871. doi: 10.1002/lio2.619
[18] Nadagoud SV, Bhat VS, Pragathi BS. Comparative efficacy of epley, semont and gans maneuver in treating posterior canal benign paroxysmal positional Vertigo[J]. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2024, 76(1): 48-54. doi: 10.1007/s12070-023-04071-y
[19] 李阳阳, 刘日钊, 郑锦泉, 等. 后半规管良性阵发性位置性眩晕复位过程中眼震特点及其疗效分析[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2021, 35(9): 821-824.
[20] Scotto di Santillo L, Califano L. Canal switch: a possible complication of physical therapeutic manoeuvers for posterior canal benign paroxysmal positional Vertigo[J]. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital, 2023, 43(1): 49-55.
[21] Hougaard DD, Duch K, Bech MW. Treatment of posterior Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo is efficient and safe with a new Mechanical Rotational Chair[J]. Front Neurol, 2023, 14: 1239959. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1239959
[22] Strupp M, Mandala M, Vinck AS, et al. The semont-plus maneuver or the epley maneuver in posterior canal benign paroxysmal positional Vertigo: a randomized clinical study[J]. JAMA Neurol, 2023, 80(8): 798-804. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2023.1408
[23] 张春雨. 改良Semont手法复位联合甲磺酸倍他司汀治疗后半规管良性阵发性位置性眩晕的疗效分析[J]. 中国医学文摘(耳鼻咽喉科学), 2018, 33(3): 242-244.
[24] 李进让, 邹世桢, 田师宇, 等. 改良Semont方法治疗后半规管良性阵发性位置性眩晕的短期疗效研究[J]. 中国耳鼻咽喉头颈外科, 2017, 24(5): 239-241.
[25] Obrist D, Nienhaus A, Zamaro E, et al. Determinants for a Successful Sémont Maneuver: An In vitro Study with a Semicircular Canal Model[J]. Front Neurol, 2016, 7: 150.
[26] Bhandari A, Kingma H, Bhandari R. BPPV Simulation: A Powerful Tool to Understand and Optimize the Diagnostics and Treatment of all Possible Variants of BPPV[J]. Front Neurol, 2021, 12: 632286.
-

计量
- 文章访问数: 143
- 施引文献: 0



 下载:
下载: