Expression of NFAT5 and IGF1R in nasopharyngeal carcinoma tissues and analysis of clinical characteristics
-
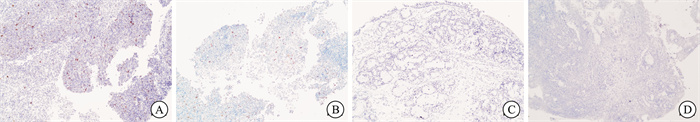
摘要: 目的 探讨在鼻咽癌组织中NFAT5和IGF1R的表达,分析其表达水平及其与临床特征和预后的相关性。 方法 收集2019年1月1日-2019年12月31日由云南省肿瘤医院收治的鼻咽癌组织及癌旁组织标本69例,采用免疫组织化学检测鼻咽癌组织中NFAT5、IGF1R的表达情况,Kaplan-Meier法预测生存时长,Log-Rank法对临床病理学特征展开预后评估。 结果 鼻咽癌组织中NFAT5和IGF1R的阳性表达比例分别为87%和84.5%,相较于癌旁的正常组织,它们在鼻咽癌中的表达显著增高(P<0.05),且二者的表达呈正相关(P<0.05),与T分期、N分期、颅底侵犯及颅神经麻痹相关(P<0.05);NFAT5、IGF1R过表达显著影响鼻咽癌患者的生存率,与预后呈负相关(P<0.05)。 结论 鼻咽癌组织中NFAT5和IGF1R两者过表达,表达水平呈正相关,与临床特征和预后显著相关,可成为判断鼻咽癌预后的肿瘤生物标志物。
-
关键词:
- 鼻咽肿瘤 /
- 活化T细胞核因子5 /
- 胰岛素样生长因子1受体 /
- 预后
Abstract: Objective To investigate the expression of NFAT5 and IGF1R in nasopharyngeal carcinoma tissues and analyze their expression levels in relation to clinical features and prognosis. Methods From January 1, 2019, to December 31, 2019, 69 cases of nasopharyngeal carcinoma tissues and adjacent non-cancerous tissues were collected from patients treated at Yunnan Cancer Hospital. Immunohistochemistry was employed to detect the expression of NFAT5 and IGF1R in nasopharyngeal carcinoma tissues. The Kaplan-Meier method was used to predict survival time, and the clinicopathological features were evaluated using the log-Rank test. Results The positive expression rates of NFAT5 and IGF1R in nasopharyngeal carcinoma tissues were 87.0% and 84.5%, respectively. Compared to adjacent normal tissues, the expression levels of NFAT5 and IGF1R in nasopharyngeal carcinoma tissues were significantly increased (P < 0.05). Furthermore, the expression of NFAT5 and IGF1R was positively correlated with T stage, N stage, skull base invasion, and cranial nerve palsy (P < 0.05). The overexpression of NFAT5 and IGF1R significantly affected the survival rate of patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma and was negatively correlated with prognosis (P < 0.05). Conclusion In nasopharyngeal carcinoma tissues, overexpression of NFAT5 and IGF1R is observed, which is closely linked to clinical features and patient outcomes. These markers may serve as valuable indicators for predicting the prognosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. -

-
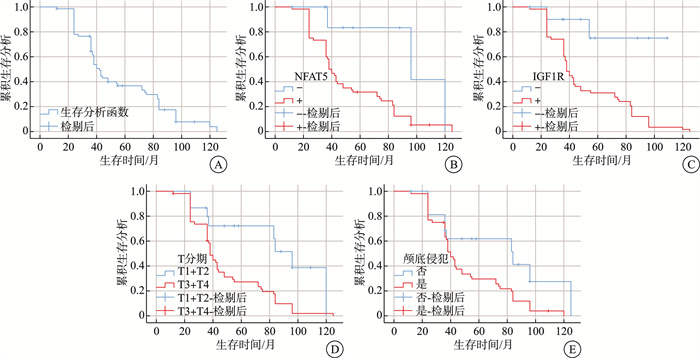
表 1 鼻咽癌组织中NFAT5、IGF1R表达与临床病理特征的关系
例 项目 例数 NFAT5 IGF1R + - 阳性率/% P + - 阳性率/% P 性别 0.177 0.804 男 48 40 8 83.3 40 8 83.3 女 21 20 1 95.2 18 3 85.7 年龄 0.225 0.864 ≤47岁 33 27 6 81.8 28 5 84.8 >47岁 36 33 3 91.7 30 6 83.3 吸烟史 0.093 0.992 否 25 24 1 96.0 21 4 84.0 是 44 36 8 81.8 37 7 84.1 饮酒史 0.433 0.604 否 39 35 4 89.7 32 7 82.1 是 30 25 5 83.3 26 4 86.7 临床分期 0.28 0.040 早期 7 7 0 100.0 4 3 57.1 局部晚期 62 53 9 85.5 54 8 87.1 T分期 <0.001 0.001 T1+T2 15 8 7 53.3 8 7 53.3 T3+T4 54 52 2 96.3 50 4 92.6 N分期 0.029 <0.001 N0 8 5 3 62.5 2 6 25.0 N+ 61 55 6 90.2 56 5 91.8 M分期 0.578 0.532 M0 67 58 9 86.6 56 11 83.6 M1 2 2 0 100.0 2 0 100.0 颅底侵犯 <0.001 0.003 否 17 10 7 58.8 10 7 58.8 是 52 50 2 96.2 48 4 92.3 颅神经麻痹 <0.001 0.002 否 21 13 8 61.9 13 8 61.9 是 69 48 21 69.6 45 3 65.2 表 2 NFAT5和IGF1R及临床病理学特征与预后的关系
项目 例数 3年生存率/% 5年生存率/% P 项目 例数 3年生存率/% 5年生存率/% P NFAT5 0.013 临床分期 0.05 - 9 83.3 41.7 早期 7 71.4 53.6 + 60 60.0 28.1 局部晚期 62 62.0 28.7 IGF1R 0.002 T分期 0.002 - 11 85.0 74.4 T1+T2 15 79.4 61.9 + 58 60.3 27.6 T3+T4 54 60.4 23.4 性别 0.259 N分期 0.089 男 48 66.3 35.1 N0 8 75.7 68.6 女 21 60.0 35.0 N+ 61 62.0 29.5 年龄 0.912 M分期 0.174 ≤47岁 33 66.0 34.3 M0 67 64.9 34.3 >47岁 36 62.9 28.6 M1 2 50.0 0 吸烟史 0.698 颅底侵犯 0.018 否 25 63.3 33.3 否 17 68.8 62.0 是 44 62.2 33.1 是 52 63.2 25.7 饮酒史 0.299 颅神经麻痹 0.093 否 39 61.2 33.1 否 21 59.2 44.4 是 30 69.0 33.4 是 48 66.7 27.1 -
[1] Liu H, Tang L, Li YX, et al. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma: current views on the tumor microenvironment's impact on drug resistance and clinical outcomes[J]. Mol Cancer, 2024, 23(1): 20.
[2] Guo XR, Cui JM, Yuan X, et al. Long-term trends of nasopharyngeal carcinoma mortality in China from 2006 to 2020 by region and sex: an age-period-cohort analysis[J]. BMC Public Health, 2023, 23(1): 2057.
[3] Zhao GZ, Aghakeshmiri S, Chen YT, et al. NFAT5-mediated signalling pathways in viral infection and cardiovascular dysfunction[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(9): 4872.
[4] Cen LS, Xing FL, Xu LY, et al. Potential role of gene regulator NFAT5 in the pathogenesis of diabetes mellitus[J]. J Diabetes Res, 2020, 2020: 6927429.
[5] Werner H. The IGF1 signaling pathway: from basic concepts to therapeutic opportunities[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24(19): 14882.
[6] Zhen HF, Yao YR, Yang HB. SAFB2 inhibits the progression of breast cancer by suppressing the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway via NFAT5[J]. Mol Biotechnol, 2023, 65(9): 1465-1475. doi: 10.1007/s12033-022-00649-z
[7] Baizig NM, Wided BA, El Amine O, et al. The clinical significance of IGF-1R and relationship with Epstein-Barr virus markers: LMP1 and EBERs in Tunisian patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma[J]. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol, 2020, 129(10): 1011-1019. doi: 10.1177/0003489420929362
[8] Xu JW, Wang H, Shi BY, et al. Exosomal MFI2-AS1 sponge miR-107 promotes non-small cell lung cancer progression through NFAT5[J]. Cancer Cell Int, 2023, 23(1): 51. doi: 10.1186/s12935-023-02886-x
[9] Juarez-Vignon Whaley JJ, Afkhami M, Onyshchenko M, et al. Recurrent/metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma treatment from present to future: where are we and where are we heading?[J]. Curr Treat Options Oncol, 2023, 24(9): 1138-1166. doi: 10.1007/s11864-023-01101-3
[10] Lee N, Kim D, Kim WU. Role of NFAT5 in the immune system and pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases[J]. Front Immunol, 2019, 10: 270. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00270
[11] Yoshimoto S, Morita H, Matsuda M, et al. NFAT5 promotes oral squamous cell carcinoma progression in a hyperosmotic environment[J]. Lab Invest, 2021, 101(1): 38-50.
[12] Jiang YS, He RZ, Jiang YH, et al. Transcription factor NFAT5 contributes to the glycolytic phenotype rewiring and pancreatic cancer progression via transcription of PGK1[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2019, 10(12): 948.
[13] Song HJ, Kim YH, Choi HN, et al. TonEBP/NFAT5 expression is associated with cisplatin resistance and migration in macrophage-induced A549 cells[J]. BMC Mol Cell Biol, 2024, 25(1): 6.
[14] Chen BL, Li YC, Xu SJ, et al. NFAT5 regulated by STUB1, facilitates malignant cell survival and p38 MAPK activation by upregulating AQP5 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia[J]. Biochem Genet, 2021, 59(4): 870-883.
[15] Pellegrino M, Secli V, D'Amico S, et al. Manipulating the tumor immune microenvironment to improve cancer immunotherapy: IGF1R, a promising target[J]. Front Immunol, 2024, 15: 1356321.
[16] Tang YF, Liu ZH, Zhang LY, et al. circ_PPAPDC1A promotes Osimertinib resistance by sponging the miR-30a-3p/IGF1R pathway in non-small cell lung cancer(NSCLC)[J]. Mol Cancer, 2024, 23(1): 91.
[17] Roche S, Gaule P, Winrow D, et al. Preclinical evaluation of Insulin-like growth factor receptor 1(IGF1R)and Insulin Receptor(IR)as a therapeutic targets in triple negative breast cancer[J]. PLoS One, 2023, 18(3): e0282512.
[18] Yang KF, Hu YJ, Feng YY, et al. IGF-1R mediates crosstalk between nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells and osteoclasts and promotes tumor bone metastasis[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2024, 43(1): 46.
-

计量
- 文章访问数: 147
- 施引文献: 0



 下载:
下载: