-
摘要: 药物诱导睡眠内镜(drug-induced sleep endoscopy,DISE)是指使用药物诱导接近于人的生理睡眠状态下进行的一种内镜检查,近年来在临床上的应用日益广泛,本文从儿童DISE适应证、麻醉方案及结果判定等方面的研究进展进行综述,为儿童DISE的拓展应用提供依据。Abstract: Drug-induced sleep endoscopy (DISE) is an endoscopic examination performed under conditions similar to human physiological sleep induced by drugs. In recent years, its clinical application has become increasingly widespread. This article reviews the research progress on the indications, anesthesia, and outcome determination of pediatric DISE, providing a basis for the application of pediatric DISE.
-
Key words:
- drug-induced sleep endoscopy /
- obstructive sleep apnea /
- pediatric
-

-
表 1 常用的5种儿童DISE评分系统比较
评分系统 VOTE Chan SERS Fishman Boudewyns 检查部位/个 4 6 6 5 6 鼻咽 否 是 是 是 是 腭咽 是 是 是 否 是 口咽 是 是 是 是 是 喉咽 是 否 是 否 是 舌根 是 是 否 是 否 声门上 否 是 否 是 否 杓状软骨 否 否 是 否 是 鼻腔 否 是 是 是 是 舌扁桃体 否 可见/不可见 否 否 否 注:“是”表示在评估范围内,“否”表示不在评估范围内。 表 2 阻塞程度分级
VOTE Chan SERS Fishman Boudewyns 静态 动态 0:无 0:无 0:无阻塞 0:无 0:无 0:不存在 1:部分 1:0~50% +1:部分 1:轻度 1:<50% 1:存在 2:完全 2:50%~99% +2:完全 2:中度 2:50%~75% X:不可见 3:完全 3:重度 3:>75% -
[1] Scalzitti NJ, Sarber KM. Diagnosis and perioperative management in pediatric sleep-disordered breathing[J]. Paediatr Anaesth, 2018, 28(11): 940-946. doi: 10.1111/pan.13506
[2] Marcus CL, Brooks LJ, Draper KA, et al. Diagnosis and management of childhood obstructive sleep apnea syndrome[J]. Pediatrics, 2012, 130(3): 576-584. doi: 10.1542/peds.2012-1671
[3] Andersen IG, Holm JC, Homøe P. Obstructive sleep apnea in obese children and adolescents, treatment methods and outcome of treatment-a systematic review[J]. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, 2016, 87: 190-197. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2016.06.017
[4] Wilcox LJ, Bergeron M, Reghunathan S, et al. An updated review of pediatric drug-induced sleep endoscopy[J]. Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol, 2017, 2(6): 423-431. doi: 10.1002/lio2.118
[5] Wang X, Chen YC, Li L, et al. Effects of drug-induced sleep endoscopy in children with conventional obstructive sleep apnea-hypopnea syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Sleep Breath, 2024, 28(2): 935-944. doi: 10.1007/s11325-023-02945-7
[6] Croft CB, Pringle M. Sleep nasendoscopy: a technique of assessment in snoring and obstructive sleep apnoea[J]. Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci, 1991, 16(5): 504-509. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2273.1991.tb01050.x
[7] Croft CB, Thomson HG, Samuels MP, et al. Endoscopic evaluation and treatment of sleep-associated upper airway obstruction in infants and young children[J]. Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci, 1990, 15(3): 209-216. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2273.1990.tb00777.x
[8] Manickam PV, Shott SR, Boss EF, et al. Systematic review of site of obstruction identification and non-CPAP treatment options for children with persistent pediatric obstructive sleep apnea[J]. Laryngoscope, 2016, 126(2): 491-500. doi: 10.1002/lary.25459
[9] Mendes N, Antunes J, Guimarães A, et al. Severe Pediatric Sleep Apnea: Drug-Induced Sleep Endoscopy Based Surgery[J]. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2023, 75(1): 54-59. doi: 10.1007/s12070-022-03245-4
[10] Zalzal HG, Coutras S. Palatine Tonsil Stenting of the Airway as Determined by Drug-Induced Sleep Endoscopy[J]. Case Rep Otolaryngol, 2018, 2018: 2614143.
[11] Collu MA, Esteller E, Lipari F, et al. A case control study of Drug-Induced Sleep Endoscopy(DISE)in pediatric population: a proposal for indications[J]. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, 2018, 108: 113-119. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2018.02.038
[12] Wootten CT, Chinnadurai S, Goudy SL. Beyond adenotonsillectomy: outcomes of sleep endoscopy-directed treatments in pediatric obstructive sleep apnea[J]. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, 2014, 78(7): 1158-1162. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2014.04.041
[13] Esteller E, Villatoro JC, Agüero A, et al. Outcome of drug-induced sleep endoscopy-directed surgery for persistent obstructive sleep apnea after adenotonsillar surgery[J]. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, 2019, 120: 118-122. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2019.02.004
[14] Baldassari CM, Lam DJ, Ishman SL, et al. Expert Consensus Statement: Pediatric Drug-Induced Sleep Endoscopy[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2021, 165(4): 578-591. doi: 10.1177/0194599820985000
[15] Frederick RM 2nd, Brandt J, Sheyn A. Drug-induced sleep endoscopy effect on intraoperative decision making in pediatric sleep surgery: A 2-year follow up[J]. Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol, 2022, 7(6): 2112-2118. doi: 10.1002/lio2.918
[16] Miller C, Kirkham E, Ma CC, et al. Polysomnography outcomes in children with small tonsils undergoing drug-induced sleep endoscopy-directed surgery[J]. Laryngoscope, 2019, 129(12): 2771-2774. doi: 10.1002/lary.27759
[17] Park JS, Chan DK, Parikh SR, et al. Surgical outcomes and sleep endoscopy for children with sleep-disordered breathing and hypotonia[J]. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, 2016, 90: 99-106. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2016.09.004
[18] Lan MC, Hsu YB, Lan MY, et al. Drug-induced sleep endoscopy in children with Prader-Willi syndrome[J]. Sleep Breath, 2016, 20(3): 1029-1034. doi: 10.1007/s11325-016-1338-8
[19] Benoist LB, de Vries N. Organization and logistics of drug-induced sleep endoscopy in a training hospital[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2015, 272(9): 2557-2559. doi: 10.1007/s00405-015-3665-y
[20] Prévost AS, Hylands M, Gervais M, et al. Drug-induced sleep endoscopy compared with systematic adenotonsillectomy in the management of obstructive sleep apnoea in children: a systematic review and meta-analysis protocol[J]. BMJ Open, 2019, 9(9): e028242. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2018-028242
[21] De Vito A, Carrasco Llatas M, Vanni A, et al. European position paper on drug-induced sedation endoscopy(DISE)[J]. Sleep Breath, 2014, 18(3): 453-465. doi: 10.1007/s11325-014-0989-6
[22] Ehsan Z, Mahmoud M, Shott SR, et al. The effects of anesthesia and opioids on the upper airway: A systematic review[J]. Laryngoscope, 2016, 126(1): 270-284. doi: 10.1002/lary.25399
[23] Rabelo FA, Küpper DS, Sander HH, et al. Polysomnographic evaluation of propofol-induced sleep in patients with respiratory sleep disorders and controls[J]. Laryngoscope, 2013, 123(9): 2300-2305. doi: 10.1002/lary.23664
[24] Kandil A, Subramanyam R, Hossain MM, et al. Comparison of the combination of dexmedetomidine and ketamine to propofol or propofol/sevoflurane for drug-induced sleep endoscopy in children[J]. Paediatr Anaesth, 2016, 26(7): 742-751. doi: 10.1111/pan.12931
[25] Williamson A 4th, Ibrahim SR, Coutras SW, et al. Pediatric Drug-Induced Sleep Endoscopy: Technique and Scoring System[J]. Cureus, 2020, 12(10): e10765.
[26] Iannella G, Magliulo G, Greco A, et al. Clinical Application of Pediatric Sleep Endoscopy: An International Survey[J]. Children(Basel), 2024, 11(1): 94.
[27] Kezirian EJ, Hohenhorst W, de Vries N. Drug-induced sleep endoscopy: the VOTE classification[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2011, 268(8): 1233-1236. doi: 10.1007/s00405-011-1633-8
[28] Chan DK, Liming BJ, Horn DL, et al. A new scoring system for upper airway pediatric sleep endoscopy[J]. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2014, 140(7): 595-602. doi: 10.1001/jamaoto.2014.612
[29] 陈勇超, 贾得声, 王一萍, 等. 药物诱导睡眠内镜在儿童阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停低通气综合征中的应用[J]. 国际耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2022, 46(5): 280-284. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-4106.2022.05.007
[30] Arganbright JM, Lee JC, Weatherly RA. Pediatric drug-induced sleep endoscopy: An updated review of the literature[J]. World J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2021, 7(3): 221-227. doi: 10.1016/j.wjorl.2021.05.002
[31] Lam DJ, Krane NA, Mitchell RB. Relationship between Drug-Induced Sleep Endoscopy Findings, Tonsil Size, and Polysomnographic Outcomes of Adenotonsillectomy in Children[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2019, 161(3): 507-513. doi: 10.1177/0194599819860777
[32] Li C, Kou YF, DeMarcantonio MA, et al. Sleep Endoscopy and Cine Magnetic Resonance Imaging Evaluation of Children With Persistent Obstructive Sleep Apnea[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2023, 168(4): 848-855. doi: 10.1177/01945998221097659
-

| 引用本文: | 仇书要, 蔡晓婷, 钟建文, 等. 药物诱导睡眠内镜在儿童OSA中的应用进展[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2025, 39(2): 181-184. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2025.02.017 |
| Citation: | QIU Shuyao, CAI Xiaoting, ZHONG Jianwen, et al. Progress in the application of drug-induced sleep endoscopy in pediatric OSA[J]. J Clin Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2025, 39(2): 181-184. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2025.02.017 |
- Figure 1.



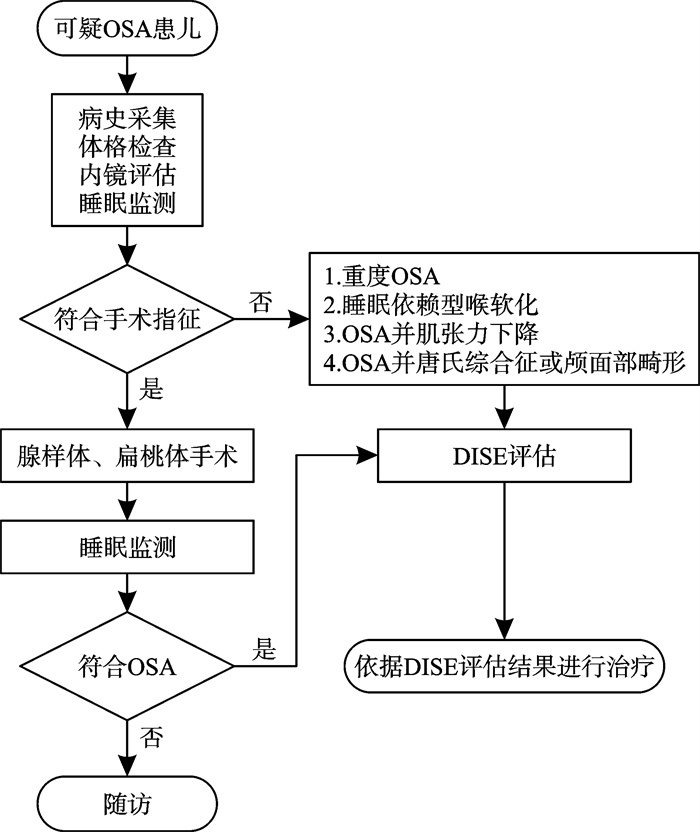
 下载:
下载: