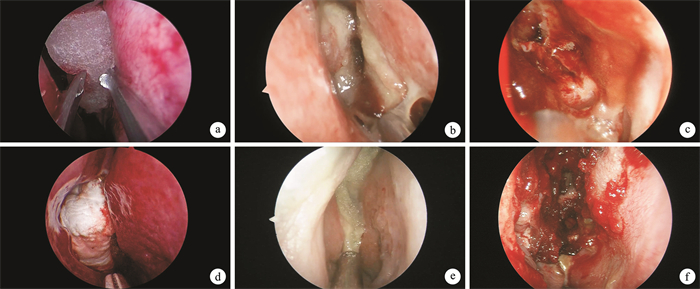
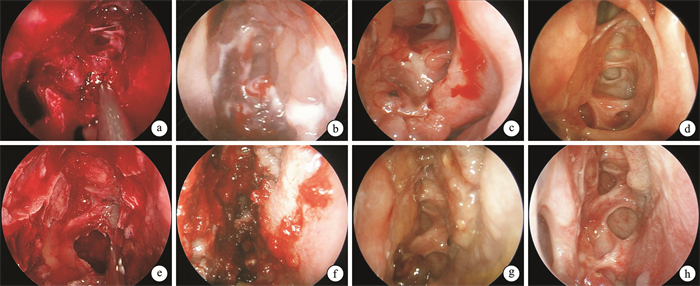
A clinical comparative study of domestic nasal packing sponge and imported nasopore sponge in post-sinusotomy care
-
摘要: 目的 本研究旨在探讨创新型国产可降解鼻腔填充海绵与纳吸绵在鼻内镜手术后止血效果及患者舒适度方面的差异。方法 采用前瞻性随机对照试验设计,研究共纳入患者30例,按随机分组原则分为2组,分别使用2种海绵进行鼻腔填塞。通过比较2组患者填塞后24 h内无出血率、填塞后48 h无出血率、头鼻部位疼痛评级、鼻眼症状视觉模拟量表评分及安全性指标,评估2种材料的止血效果、舒适度及安全性。结果 试验组与对照组受试者填塞后24 h无出血率均为73.33%,填塞后48 h无出血率均为0(100%),试验组与对照组受试者填塞后不同时间段头鼻部位疼痛评级均为Ⅰ级(100%),试验组与对照组差异无统计学意义(P=1.000)。填塞当天试验组“喷嚏”评分为(0.73±1.03)分,低于对照组的(2.27±1.67)分,(P=0.007);填塞后48 h的试验组“喷嚏”评分为(0.67±0.98),低于对照组的(1.67±1.18)分,(P=0.019)。试验组与对照组受试者在筛选期、填塞后7 d、填塞后1个月、填塞后3个月进行鼻内镜检查量化评分(Lund-Kennedy评分),2组差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。试验组和对照组受试者之间实验室其他检查指标均正常。结论 创新型国产可降解鼻腔填充海绵在鼻内镜手术后的鼻腔填塞中,不仅提供了与进口材料相当的止血效果,还能显著提高患者的术后舒适度,是一种经济实惠且有效的鼻腔填塞材料选择。Abstract: Objective This study aims to investigate the differences in hemostatic efficacy and patient comfort between an innovative domestically produced biodegradable nasal packing sponge and a traditional absorbent sponge following endoscopic nasal surgery.Methods A prospective, randomized controlled trial design was utilized, including 30 patients who were divided into two groups according to random allocation, each receiving one of the two types of nasal packing. The study assessed the hemostatic efficacy, comfort, and safety of the materials by comparing the rates of no bleeding within 24 hours after packing, re-bleeding rates after 48 hours, pain ratings in the head and nasal areas, scores on a visual analog scale for nasal ocular symptoms, and safety indicators between the two groups.Results The rates of no bleeding within 24 hours post-packing were 73.33% for both the experimental and control groups, with a no-bleeding rate of 100% after 48 hours in both groups. The pain rating in the head and nasal areas at various times post-packing was Grade Ⅰ(100%) in both groups, with no statistically significant difference(P=1.000). The experimental group's sneezing score on the day of packing was(0.73±1.03), lower than the control group's(2.27±1.67), (P=0.007); after 48 hours, the experimental group's sneezing score was(0.67±0.98), also lower than the control group's(1.67±1.18), (P=0.019). There was no significant difference between the two groups in the Lund-Kennedy scoring during endoscopic examinations at the screening period, 7 days, 1 month, and 3 months post-packing(P>0.05). Laboratory tests for other examination indicators were normal in both groups.Conclusion The innovative domestically produced biodegradable nasal packing sponge not only provides hemostatic efficacy comparable to imported materials but also significantly improves patient comfort after surgery. It represents an economical and effective choice for nasal packing materials.
-
Key words:
- nasal packing /
- endoscopic nasal surgery /
- absorbent sponge /
- hemostatic efficacy /
- patient comfort
-

-
表 1 试验组对照组人口统计学和临床特征
项目 试验组(n=15) 对照组(n=15) 合计 年龄/岁 44.53± 10.01 42.73± 13.83 43.63± 11.90 性别/例 女 6 7 13 男 9 8 17 BMI 25.05 24.27 24.67 息肉/例 单侧 1 2 3 双侧 5 5 10 鼻窦手术/例 单侧 6 3 9 双侧 9 12 21 表 2 鼻眼症状评分
X±S 症状 试验组 对照组 t P 填塞当天 嗅觉障碍 9.00±0.00 9.00±0.00 <0.001 1.000 鼻塞 9.07±0.26 9.00±0.00 0.933 0.351 鼻痒 0.20±0.56 0.33±0.90 -0.070 0.944 喷嚏 0.73±1.03 2.27±1.67 -2.682 0.007 流涕 1.53±1.85 2.60±2.41 -1.230 0.219 流泪 1.80±1.26 1.87±1.46 -0.192 0.847 眼痒/异物感/眼红肿 1.87±2.39 2.80±2.43 -1.280 0.201 填塞后24 h 嗅觉障碍 9.00±0.00 9.00±0.00 <0.001 1.000 鼻塞 9.07±0.26 9.00±0.00 0.933 0.351 鼻痒 0.20±0.56 0.33±0.90 -0.070 0.944 喷嚏 1.20±1.15 2.13±1.51 -1.681 0.093 流涕 2.07±1.91 2.40±2.35 -0.258 0.797 流泪 1.60±0.99 1.47±1.13 0.306 0.759 眼痒/异物感/眼红肿 1.73±2.37 2.33±2.02 -1.107 0.268 填塞后48 h 嗅觉障碍 7.00±2.78 7.47±2.07 -0.282 0.778 鼻塞 3.67±2.64 4.20±2.54 -0.697 0.486 鼻痒 0.20±0.41 0.07±0.26 1.021 0.307 喷嚏 0.67±0.98 1.67±1.18 -2.346 0.019 流涕 1.47±1.25 1.53±1.55 <0.001 1.000 流泪 0.73±0.88 0.53±0.74 0.557 0.577 眼痒/异物感/眼红肿 1.33±1.63 1.40±1.35 -0.412 0.681 填塞后7 d 嗅觉障碍 5.67±4.05 5.60±3.07 0.495 0.621 鼻塞 2.00±2.30 1.00±1.13 0.828 0.407 鼻痒 0.13±0.35 0.13±0.35 <0.001 1.000 喷嚏 0.60±1.06 0.93±0.59 -1.949 0.051 流涕 1.40±1.24 1.13±0.99 0.588 0.557 流泪 0.27±0.46 0.27±0.46 <0.001 1.000 眼痒/异物感/眼红肿 0.53±0.92 0.73±0.88 -0.886 0.376 表 3 Lund-Kennedy评分
X±S 评分时间 试验组 对照组 t P 筛选期左侧评分 1.93±1.49 1.87±1.60 0.118 0.907 筛选期右侧评分 1.87±1.41 1.60±1.59 0.486 0.631 筛选期总分 3.80±2.51 3.47±3.02 0.329 0.745 填塞后7 d左侧评分 0.87±0.64 0.73±0.59 0.592 0.559 填塞后7 d右侧评分 0.80±0.86 0.67±0.72 0.459 0.650 填塞后7 d总分 1.67±1.40 1.40±1.06 0.590 0.560 填塞后1个月左侧评分 0.53±0.64 0.53±0.52 <0.001 1.000 填塞后1个月右侧评分 0.47±0.64 0.40±0.51 0.316 0.754 填塞后1个月总分 1.00±1.25 0.93±0.96 0.163 0.871 填塞后3个月左侧评分 0.08±0.29 0.23±0.44 -0.984 0.336 填塞后3个月右侧评分 0.08±0.29 0.23±0.44 -0.984 0.336 填塞后3个月总分 0.17±0.58 0.46±0.88 -0.984 0.336 注:填塞后3个月试验组12例,对照组13例。 -
[1] Valentine R, Wormald PJ. Nasal dressings after endoscopic sinus surgery: what and why?[J]. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2010, 18(1): 44-48. doi: 10.1097/MOO.0b013e3283346f36
[2] Orlandi RR, Kingdom TT, Hwang PH. International consensus statement on allergy and rhinology: rhinosinusitis executive summary[J]. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol, 2016, 6(Suppl 1): S3-S21.
[3] Jeong HS, Lee HK, Kim HS, et al. A case-controlled, retrospective, comparative study on the use of biodegradable synthetic polyurethane foam versus polyvinyl acetate sponge after nasal fracture reduction[J]. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2014, 43(6): 717-721. doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2013.12.008
[4] Luo PF, Liu LL, Xu WY, et al. Preparation and characterization of aminated hyaluronic acid/oxidized hydroxyethyl cellulose hydrogel[J]. Carbohydr Polym, 2018, 199: 170-177. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.06.065
[5] Massey CJ, Singh A. Advances in absorbable biomaterials and nasal packing[J]. Otolaryngol Clin North Am, 2017, 50(3): 545-563. doi: 10.1016/j.otc.2017.01.006
[6] Burduk PK, Wierzchowska M, Grzesśkowiak B, et al. Clinical outcome and patient satisfaction using biodegradable(NasoPore)and non-biodegradable packing, a double-blind, prospective, randomized study[J]. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol, 2017, 83(1): 23-28. doi: 10.1016/j.bjorl.2016.01.001
[7] Kastl KG, Reichert M, Scheithauer MO, et al. Patient comfort following FESS and NasoporeⓇ packing, a double blind, prospective, randomized trial[J]. Rhinology, 2014, 52(1): 60-65. doi: 10.4193/Rhino13.020
[8] 史丽, 于鹏, 陈爱平. 鼻出血诊疗策略暨MasterPillar临床应用指导意见[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2023, 37(7): 519-523. https://lceh.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2023.07.003
[9] 杨国慧, 韩德民. 鼻腔填塞材料研究进展[J]. 国际耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2017, 41(1): 47-51.
[10] Abbas K, Amin M, Hussain MA, et al. Designing novel bioconjugates of hydroxyethyl cellulose and salicylates for potential pharmaceutical and pharmacological applications[J]. Int J Biol Macromol, 2017, 103: 441-450. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.05.061
-




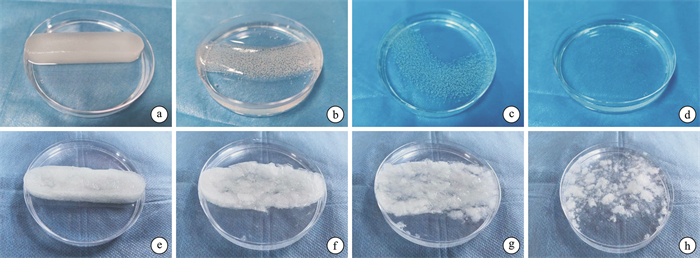
 下载:
下载: