Strategy of the diagnosis and treatment for epistaxis and guideline for clinical application of MasterPillar
-
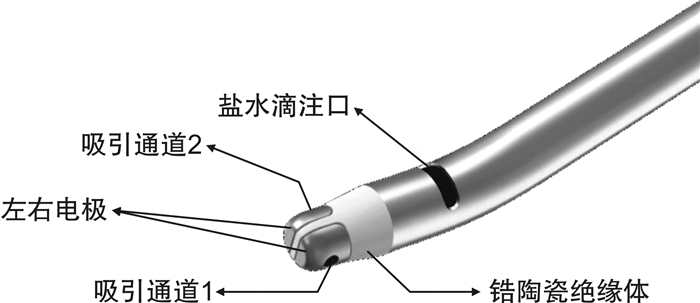
摘要: 鼻出血是耳鼻咽喉科常见急症,病因复杂,表现多样,及时明确诊断并充分止血是临床处理的关键。电凝止血是鼻出血的一种安全、可靠、有效的治疗方法,目前常用的止血设备普遍存在一些不足,本文介绍了一款新型等离子止血刀头,将滴注、冲洗、止血、吸引动态循环功能融合于一体,以期在鼻出血或鼻腔、鼻窦手术中实现微创、高效、精准止血。Abstract: Epistaxis is a common otorhinolaryngological emergency with complex etiological factors and varied clinical manifestations. The key to epistaxis treatment is accurate diagnosis and adequate hemostasis. Electrocoagulation is a reliable, safe and effective treatment for epistaxis. However, there are still several deficiencies in application of the commonly used electrocoagulation surgical products. This paper introduces a new type of radiofrequency head incorporating the dynamic circulatory functions of drip, irrigation, hemostasis and aspiration. We aim to achieve noninvasive, effective and accurate hemostasis in the treatment of epistaxis or nasal sinus surgery.
-
Key words:
- epistaxis /
- hemostasis method /
- new type of radiofrequency
-

-
[1] Tomkinson A, Roblin DG, Flanagan P, et al. Patterns of hospital attendance with epistaxis[J]. Rhinology, 1997, 35(3): 129-131.
[2] 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志编辑委员会鼻科组, 中华医学会耳鼻咽喉头颈外科学分会鼻科学组. 鼻出血诊断及治疗指南(草案)[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2015, 50(4): 265-267. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-0860.2015.04.001
[3] 谷庆隆, 高兴强, 罗征秀, 等. 儿童鼻出血诊断与治疗—临床实践指南(2021年)[J]. 中国实用儿科杂志, 2021, 36(10): 721-724. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZSEK202110001.htm
[4] Clancy MS, Palmer S, Olitsky S, et al. Second International Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia[J]. Ann Intern Med, 2021, 174(7): 1036.
[5] 杨钦泰, 邓慧仪, 王玮豪, 等. 难治性鼻出血隐匿出血部位的分布和治疗[J]. 中国耳鼻咽喉头颈外科, 2016, 23(10): 602-605. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-EBYT201610014.htm
[6] 时光刚, 姚寿国, 王昭迪, 等. 创伤性迟发性鼻出血与假性动脉瘤关系的临床研究[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2008, 43(6): 414-418. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1673-0860.2008.06.004
[7] Snyderman CH, Goldman SA, Carrau RL, et al. Endoscopic sphenopalatine artery ligation is an effective method of treatment for posterior epistaxis[J]. Am J Rhinol, 1999, 13: 137-140. doi: 10.2500/105065899782106805
[8] Wormald PJ, Wee DT, van Hasselt CA. Endoscopic ligation of the sphenopalatine artery for refractory posterior epistaxis[J]. Am J Rhinol, 2000, 14(4): 261-264. doi: 10.2500/105065800779954455
[9] 谷庆隆, 高兴强, 罗征秀, 等. 儿童鼻出血诊断与治疗—临床实践指南(2021年)[J]. 中国实用儿科杂志, 2021, 36(10): 721-724. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZSEK202110001.htm
[10] 黄选兆, 汪吉宝, 孔维佳. 实用耳鼻咽喉头颈外科学[M]. 2版. 北京人民卫生出版社, 2010: 124-125.
[11] Chitsuthipakorn W, Seresirikachorn K, Kanjanawasee D, et al. Endoscopic sphenopalatine foramen cauterization is an effective treatment modification of endoscopic sphenopalatine artery ligation for intractable posterior epistaxis[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2020, 277(9): 2463-2467.
[12] Hill M, Farrell N, Verma R, et al. Management of epistaxis secondary to extracranial anterior ethmoid artery pseudoaneurysm[J]. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol, 2020, 10(12): 1343-1344.
[13] 李勇, 陆忠琪. 筛动脉的临床应用解剖[J]. 中国临床解剖学杂志, 1991, 9(2): 93-95, 126. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZLJZ199102013.htm
-




 下载:
下载: