-
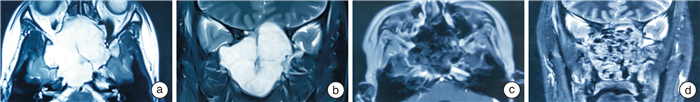
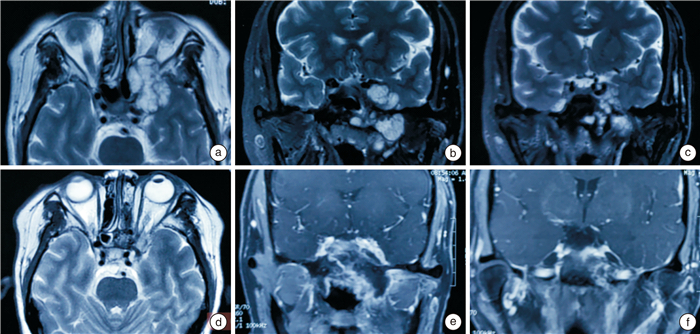
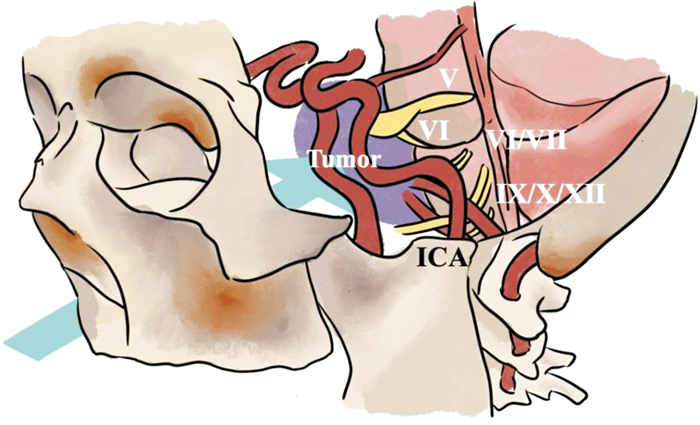
摘要: 目的 探讨内镜经鼻入路处理颅底软骨肉瘤的手术技术及临床效果。方法 收集2013—2022年在首都医科大学宣武医院耳鼻咽喉头颈外科诊断为颅底软骨肉瘤并接受内镜经鼻手术的患者资料。回顾性分析患者的临床表现、病理学分级、累及部位和范围及内镜经鼻手术治疗后的并发症情况,并采用Kaplan-Meier法统计其无病生存率。结果 资料完整的31例患者中,主体位于岩斜区27例(87%),累及前颅底4例(13%)。病理分级Ⅰ级(12例),Ⅱ级(16例),Ⅲ(3例)。其中,25例实现了影像学全切,6例术后残留。术后平均随访时间为35.7个月(6~120个月),在全切病例中有5例复发(5/25),5年的无瘤生存率为80%。6例患者在术后出现一过性外展神经麻痹,4例出现脑脊液鼻漏。无死亡病例和永久的颅神经麻痹。全切率(P=0.001)和累及桥小脑角、颈静脉孔(P=0.037)是影响软骨肉瘤残留、复发的独立危险因素。结论 内镜经鼻入路手术是处理颅底软骨肉瘤较为安全、可行的治疗方式。Abstract: Objective To explore the surgical techniques and clinical outcomes of endoscopic transnasal approaches in the treatment of skull base chondrosarcomas.Methods Data from patients diagnosed with skull base chondrosarcomas and treated via endoscopic transnasal surgery at the Department of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery, Xuanwu Hospital, Capital Medical University, from 2013 to 2022 were collected. This retrospective study analyzed the patients' clinical presentations, histopathological grading, involved sites and extents, and complications following the endoscopic transnasal surgery. Disease-free survival rates were calculated using the Kaplan-Meier method.Results Complete data from 31 patients showed that the primary tumor site was in the petroclival region in 27 cases(87%), and the anterior skull base in 4 cases(13%). Pathological grades were Grade Ⅰ(12 cases), Grade Ⅱ(16 cases), and Grade Ⅲ(3 cases). Total resection was achieved in 25 cases, with residual disease post-surgery in 6 cases. The average follow-up duration was 35.7 months(ranging from 6 to 120 months). Among those who achieved complete resection, recurrence occurred in 5 cases(5/25), with a five-year disease-free survival rate of 80%. Postoperative complications included transient abducens nerve palsy in 6 patients and cerebrospinal fluid rhinorrhea in 4 patients. There were no cases of death or permanent cranial nerve palsy. Total resection rate(P=0.001) and involvement of the cerebellopontine angle and jugular foramen(P=0.037) were identified as independent risk factors for residual disease and recurrence of chondrosarcoma.Conclusion The endoscopic transnasal approach is a safe and feasible treatment option for skull base chondrosarcomas.
-
Key words:
- endoscopic approach /
- surgery /
- skull base /
- chondrosarcoma /
- complications
-

-
表 1 31例颅底软骨肉瘤病例特点
例序 性别 年龄/岁 病理分级 临床表现 肿瘤主要累及部位 1 男 47 Ⅰ 头痛 斜坡、蝶窦 2 女 31 Ⅱ 复视、视力减退 斜坡、鞍区、海绵窦、前颅底、眶尖、眶内 3 女 71 Ⅰ 无 斜坡、颞下窝 4 男 49 Ⅱ 复视 岩尖、斜坡、海绵窦 5 女 36 Ⅰ 头痛、鼻塞 前颅底、鼻腔、鼻窦 6 女 62 Ⅱ 复视、头痛、脑水肿 斜坡、颞下窝、颈静脉孔 7 女 32 Ⅰ 鼻塞、鼻出血 鼻中隔、鼻窦 8 女 64 Ⅱ 头痛、面部麻木 斜坡、颞下窝 9 女 43 Ⅱ 复视、面部麻木、头痛 斜坡、颞下窝、岩尖 10 女 37 Ⅱ 复视 斜坡 11 女 37 Ⅱ 复视 斜坡、海绵窦 12 男 67 Ⅲ 鼻出血、分泌性中耳炎 斜坡、鼻咽 13 女 36 Ⅰ 面部麻木、头痛 斜坡、颞下窝 14 女 44 Ⅰ 头痛 斜坡 15 女 49 Ⅱ 头痛、动眼神经麻痹、面瘫 斜坡、岩尖、桥小脑角、颈静脉孔 16 女 28 Ⅰ 复视 斜坡、颞下窝 17 男 45 Ⅱ 鼻塞、鼻出血 前颅底、鼻腔、鼻窦 18 女 49 Ⅰ 头痛 斜坡 19 女 54 Ⅲ 鼻出血、复视、分泌性中耳炎 蝶窦、斜坡、鼻咽 20 女 59 Ⅱ 复视、头痛 斜坡 21 男 45 Ⅱ 复视、视力减退、面部麻木 斜坡、岩尖、桥小脑角、颈静脉孔 22 女 27 Ⅰ 鼻塞、鼻出血、眼球突出,头痛 前颅底、斜坡 23 女 46 Ⅰ 复视、视力减退、面部麻木 斜坡、岩尖、海绵窦 24 男 54 Ⅱ 头痛、视力减退 蝶窦、斜坡 25 男 42 Ⅱ 头痛、复视 斜坡、鞍区、海绵窦、眶尖 26 男 75 Ⅲ 头痛、面部麻木 斜坡、眶尖、翼腭窝和颞下窝 27 女 41 Ⅱ 复视 蝶窦、岩尖、斜坡、海绵窦 28 女 38 Ⅱ 头痛 蝶窦、斜坡 29 男 56 Ⅰ 复视、头痛 斜坡、蝶窦、颞下窝 30 女 32 Ⅰ 头痛 蝶窦、斜坡 31 女 63 Ⅱ 鼻塞、头痛 鼻腔、鼻窦、斜坡 表 2 31例颅底软骨肉瘤临床结局
例序 手术切除率 并发症 随访时间/月 复发情况 术后复发时间/月 1 STR 无 24 残留 - 2 PR 脑脊液漏,失明 120 残留 - 3 STR 无 15 残留 - 4 GTR 一过性外展麻痹 24 无 无 5 GTR 无 110 复发 24 6 PR 脑脊液漏 12 残留 - 7 GTR 无 48 复发 6 8 GTR 上颌神经损伤 36 无 无 9 GTR 无 36 无 无 10 GTR 一过性外展麻痹 24 无 无 11 GTR 一过性外展麻痹 48 复发 6 12 GTR 无 36 无 无 13 GTR 上颌神经损伤 48 无 无 14 GTR 脑脊液漏 24 无 无 15 STR 脑脊液漏 36 残留 - 16 GTR 一过性外展麻痹 12 无 无 17 GTR 无 36 复发 16 18 GTR 无 24 无 无 19 GTR 一过性外展麻痹 24 无 无 20 GTR 无 24 无 无 21 STR 分泌性中耳炎 24 残留 - 22 GTR 无 10 无 无 23 GTR 一过性外展麻痹 6 无 无 24 GTR 无 38 无 无 25 GTR 无 45 复发 12 26 GTR 无 21 无 无 27 GTR 无 26 无 无 28 GTR 无 78 无 无 29 GTR 上颌神经损伤 38 无 无 30 GTR 无 19 无 无 31 GTR 无 42 无 无 表 3 软骨肉瘤残留/复发的单因素分析
组别 例数 χ2 P 全切率 13.527 0.001 未全切 6 全切 25 前颅底 1.565 0.226 无 26 受累 5 眶尖,海绵窦 0.215 0.484 无 24 受累 7 翼腭窝,颞下窝 0.015 0.646 无 25 受累 6 桥小脑角,颈静脉孔 6.039 0.037 无 28 受累 3 斜坡岩尖蝶窦鼻咽 1.411 0.281 无 3 受累 28 病理分级 0.040 0.577 Ⅰ级 12 Ⅱ/Ⅲ级 19 -
[1] Awad M, Gogos AJ, Kaye AH. Skull base chondrosarcoma[J]. J Clin Neurosci, 2016, 24: 1-5. doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2015.10.029
[2] Bloch OG, Jian BJ, Yang I, et al. Cranial chondrosarcoma and recurrence[J]. Skull Base, 2010, 20(3): 149-156. doi: 10.1055/s-0029-1246218
[3] Samii A, Gerganov V, Herold C, et al. Surgical treatment of skull base chondrosarcomas[J]. Neurosurg Rev, 2009, 32(1): 67-75. doi: 10.1007/s10143-008-0170-4
[4] Sekhar LN, Pranatartiharan R, Chanda A, et al. Chordomas and chondrosarcomas of the skull base: results and complications of surgical management[J]. Neurosurg Focus, 2001, 10(3): E2.
[5] Mesquita Filho PM, Ditzel Filho LF, Prevedello DM, et al. Endoscopic endonasal surgical management of chondrosarcomas with cerebellopontine angle extension[J]. Neurosurg Focus, 2014, 37(4): E13. doi: 10.3171/2014.7.FOCUS14349
[6] Hofstetter CP, Singh A, Anand VK, et al. The endoscopic, endonasal, transmaxillary transpterygoid approach to the pterygopalatine fossa, infratemporal fossa, petrous apex, and the Meckel cave[J]. J Neurosurg, 2010, 113(5): 967-974. doi: 10.3171/2009.10.JNS09157
[7] Zhang Q, Kong F, Yan B, et al. Endoscopic endonasal surgery for clival chordoma and chondrosarcoma[J]. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec, 2008, 70(2): 124-129. doi: 10.1159/000114536
[8] Moussazadeh N, Kulwin C, Anand VK, et al. Endoscopic endonasal resection of skull base chondrosarcomas: technique and early results[J]. J Neurosurg, 2015, 122(4): 735-742. doi: 10.3171/2014.11.JNS14827
[9] Crockard HA, Cheeseman A, Steel T, et al. A multidisciplinary team approach to skull base chondrosarcomas[J]. J Neurosurg, 2001, 95(2): 184-189. doi: 10.3171/jns.2001.95.2.0184
[10] Brackmann DE, Teufert KB. Chondrosarcoma of the skull base: long-term follow-up[J]. Otol Neurotol, 2006, 27(7): 981-991. doi: 10.1097/01.mao.0000233812.48800.b4
[11] Almefty K, Pravdenkova S, Colli BO, et al. Chordoma and chondrosarcoma: similar, but quite different, skull base tumors[J]. Cancer, 2007, 110(11): 2457-2467.
[12] Zanation AM, Snyderman CH, Carrau RL, et al. Endoscopic endonasal surgery for petrous apex lesions[J]. Laryngoscope, 2009, 119(1): 19-25. doi: 10.1002/lary.20027
[13] 曾宪海, 徐敏, 李娟娟, 等. 内镜下经鼻至岩尖区的临床应用解剖学研究[J]. 中华耳科学杂志, 2019, 17(4): 541-545.
[14] Hasegawa H, Shin M, Kondo K, et al. Role of endoscopic transnasal surgery for skull base chondrosarcoma: a retrospective analysis of 19 cases at a single institution[J]. J Neurosurg, 2018, 128(5): 1438-1447. doi: 10.3171/2017.1.JNS162000
[15] 李万鹏, 卢涵宇, 王欢, 等. 鼻腔鼻窦软骨肉瘤47例临床分析[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2020, 55(1): 14-20.
[16] Mangussi-Gomes J, Alves-Belo JT, Truong HQ, et al. Anatomical Limits of the Endoscopic Contralateral Transmaxillary Approach to the Petrous Apex and Petroclival Region[J]. J Neurol Surg B Skull Base, 2020, 83(1): 44-52.
[17] Solares CA, Fakhri S, Batra PS, et al. Transnasal endoscopic resection of lesions of the clivus: a preliminary report[J]. Laryngoscope, 2005, 115(11): 1917-1922. doi: 10.1097/01.mlg.0000172070.93173.92
[18] 丁樾, 孟庆国. 内镜经鼻入路咽旁段颈内动脉临床解剖研究进展[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2024, 38(4): 354-358. https://lceh.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2024.04.018
[19] 周涛, 魏少波, 孟祥辉, 等. 单纯神经内镜下经鼻蝶入路垂体瘤切除术[J]. 中华外科杂志, 2010, 48(19): 1443-1446.
[20] 张林, 谢宝树, 姚文益, 等. 神经内镜下经鼻-蝶窦入路术中、术后脑脊液鼻漏的处理[J]. 中国微侵袭神经外科杂志, 2016, 21(9): 385-388.
[21] Bloch OG, Jian BJ, Yang I, et al. A systematic review of intracranial chondrosarcoma and survival[J]. J Clin Neurosci, 2009, 16(12): 1547-1551. doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2009.05.003
[22] Bohman LE, Koch M, Bailey RL, et al. Skull base chordoma and chondrosarcoma: influence of clinical and demographic factors on prognosis: a SEER analysis[J]. World Neurosurg, 2014, 82(5): 806-814. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2014.07.005
[23] Abbas K, Siddiqui AT. Evaluation of different treatment and management options for chondrosarcoma; the prognostic factors determining the outcome of the disease[J]. IJS oncology, 2018, 3(3): e58. doi: 10.1097/IJ9.0000000000000058
[24] Weber DC, Badiyan S, Malyapa R, et al. Long-term outcomes and prognostic factors of skull-base chondrosarcoma patients treated with pencil-beam scanning proton therapy at the Paul Scherrer Institute[J]. Neuro Oncol, 2016, 18(2): 236-243. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/nov154
-

| 引用本文: | 杨晓彤, 严波, 危维, 等. 内镜经鼻入路切除颅底软骨肉瘤的临床分析[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2024, 38(12): 1127-1133. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2024.12.007 |
| Citation: | YANG Xiaotong, YAN Bo, WEI Wei, et al. Clinical analysis of endoscopic transnasal resection of skull base chondrosarcoma[J]. J Clin Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2024, 38(12): 1127-1133. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2024.12.007 |
- Figure 1.
- Figure 2.
- Figure 3.
- Figure 4.



 下载:
下载: