Effect of phosphorylated HSP27 on the proliferation and metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma and its mechanism
-
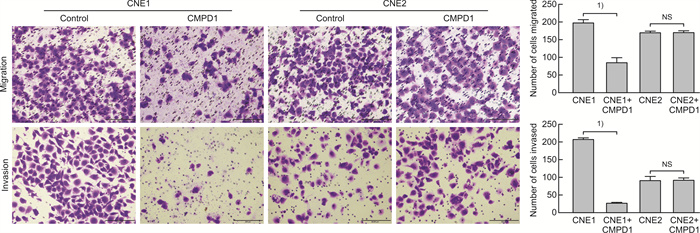
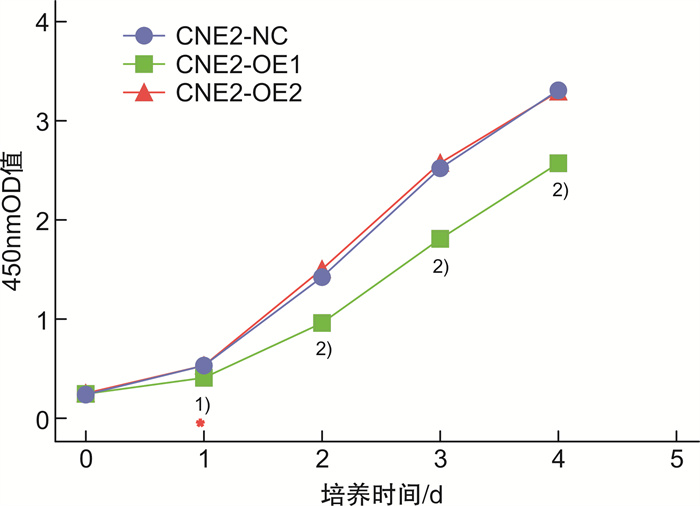
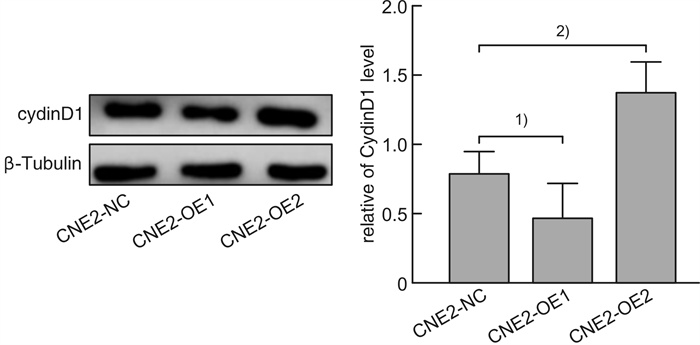
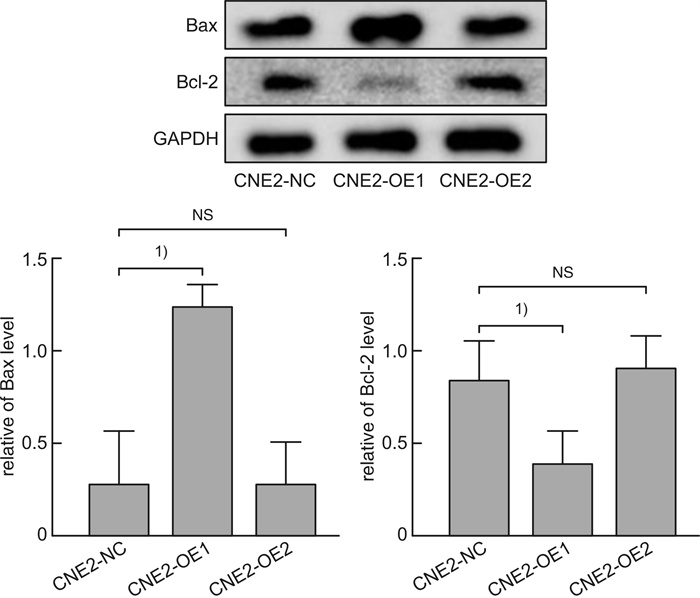
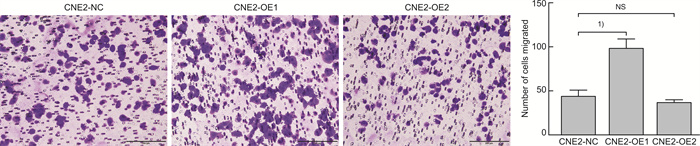
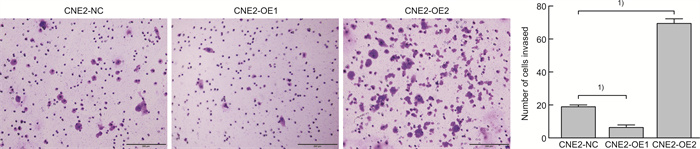
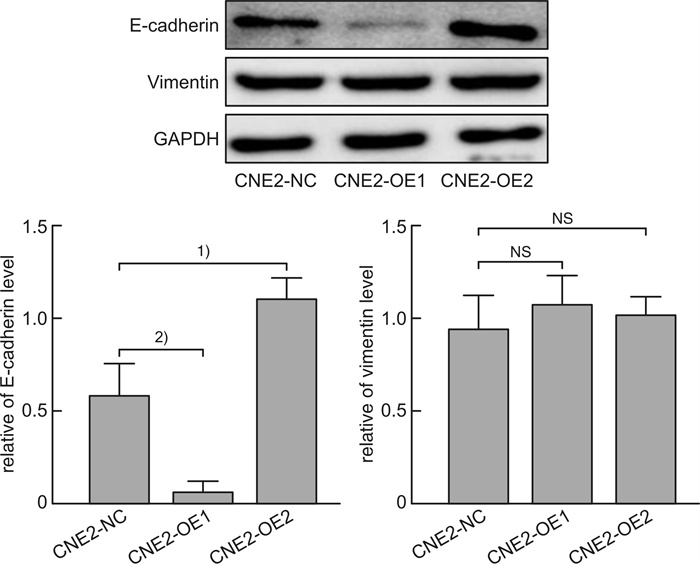
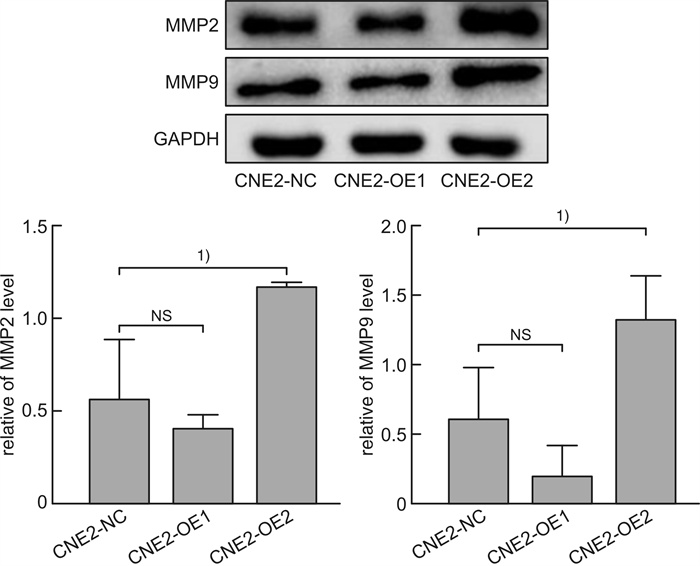
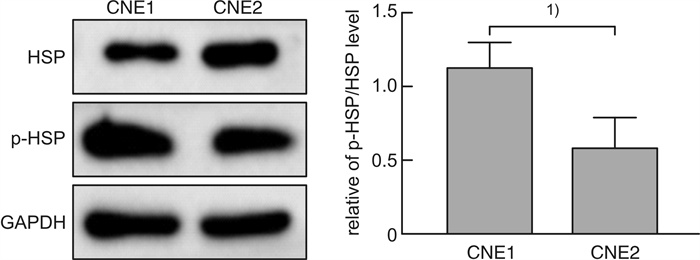
摘要: 目的 探讨磷酸化HSP27(p-HSP27)对鼻咽癌增殖和转移的影响及其分子机制。 方法 ① Western blot检测鼻咽癌CNE1、CNE2细胞中HSP27和p-HSP27的表达水平;抑制HSP27磷酸化,Transwell检测细胞的迁移、侵袭能力。②合成过表达HSP27磷酸化和去磷酸化突变体的鼻咽癌细胞株(CNE2-OE1和CNE2-OE2),以转染空载体的CNE2细胞(CNE2-NC)为对照:CCK8检测3组细胞的增殖能力,Western blot检测CyclinD1、Bax和Bcl-2的表达水平;Transwell检测细胞的迁移、侵袭能力,Western blot检测E-cadherin、Vimentin、MMP2、MMP9的表达水平。 结果 ① HSP27在CNE2中的表达高于CNE1,p-HSP27的表达则相反;抑制HSP27磷酸化以后,CNE1的侵袭、迁移能力显著降低,CNE2无明显变化。②与CNE2-NC比较:CNE2-OE1生长速度降低,CNE2-OE2生长速度加快;CyclinD1在CNE2-OE1中表达下调,在CNE2-OE2中表达较高;CNE2-OE1中Bax的表达升高,Bcl-2的表达降低,两者在CNE2-OE2中的表达无明显变化。③与CNE2-NC比较:CNE2-OE1的迁移能力增强、侵袭能力减弱,CNE2-OE2的迁移能力减弱而侵袭能力增强;E-cadherin在CNE2-OE1中表达减少、在CNE2-OE2中表达增加,Vimentin在3组细胞中的表达差异无统计学意义;MMP2和MMP9在CNE2-OE2中表达上调,在CNE2-OE1中表达略下调。 结论 ① HSP27和p-HSP27在不同鼻咽癌细胞中呈差异性表达,鼻咽癌的转移能力不仅与HSP27、也与p-HSP27的表达水平有关。②p-HSP27可抑制CNE2细胞增殖,促进其凋亡。③p-HSP27在鼻咽癌转移的不同环节发挥不同作用,其可增加CNE2细胞的迁移能力、降低其侵袭能力;p-HSP27可能通过下调E-cadherin使CNE2细胞发生EMT改变进而促进CNE2细胞迁移,通过下调MMPs的表达抑制CNE2细胞侵袭。Abstract: Objective To investigate the effect of phosphorylated HSP27 on the proliferation and metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma and its molecular mechanism. Methods ① Western blot assay was used to detect the expression levels of HSP27 and p-HSP27 in CNE1 and CNE2 cells of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Inhibited the phosphorylation of HSP27, Transwell assay detected the metastasis ability of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. ②Nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell lines(CNE2-OE1 and CNE2-OE2) overexpressing phosphorylated and dephosphorylated mutants of HSP27 were synthesized, empty vector transfected CNE2 cells(CNE2-NC) were used as controls. The proliferation ability of the three groups of cells was detected by CCK8, and the expression levels of CyclinD1, Bax and Bcl-2 were detected by Western blot. Transwell was used to detect the migration and invasion ability of cells, and Western blot was used to detect the expression levels of E-cadherin, Vimentin, MMP2 and MMP9. Results The expression level of HSP27 in CNE2 was higher than that of CNE1 cells, while the expression level of p-HSP27 was opposite. After inhibition of HSP27 phosphorylation, the invasion and migration ability of CNE1 cells decreased significantly, with no significant change in CNE2 cells. Compared with CNE2-NC, the growth rate of CNE2-OE1 decreased, and the growth rate of CNE2-OE2 increased. The expression level of CyclinD1 was down-regulated in CNE2-OE1 and higher in CNE2-OE2. The expression level of Bax in CNE2-OE1 was increased, while the expression of Bcl-2 was decreased. There was no significant change in the expression of Bax and Bcl-2 in CNE2-OE2. Compared with CNE2-NC, the migration ability of CNE2-OE1 was enhanced and the invasion ability was weakened, while the migration ability of CNE2-OE2 was weakened and the invasion ability was enhanced. There was no significant difference in the expression levels of E-cadherin was decreased in CNE2-OE1 and increased in CNE2-OE2. There was no significant difference in the expression levels of Vimentin among the three groups. The expression levels of MMP2 and MMP9 were up-regulated in CNE2-OE2, and slightly down-regulated in CNE2-OE1. Conclusion HSP27 and p-HSP27 were differentially expressed in different nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells, and the metastasis ability of nasopharyngeal carcinoma was not only related to the expression level of HSP27, but also related to the level of p-HSP27. The p-HSP27 inhibited CNE 2 cell proliferation and promoted their apoptosis. As p-HSP27 plays different roles in different stages of nasopharyngeal carcinoma metastasis, it can increase the migration ability of CNE2 cells and reduce its invasion ability. p-HSP27 may induce EMT changes in CNE2 by down-regulating E-cadherin, thus promoting CNE2 migration, and may inhibit CNE2 invasion by down-regulating MMPs expression.
-
Key words:
- nasopharyngeal carcinoma /
- HSP27 /
- phosphorylation /
- proliferation /
- metastasis
-

-
[1] Chen YP, Chan ATC, Le QT, et al. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma[J]. Lancet, 2019, 394: 64-80. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)30956-0
[2] 何引, 殷海, 吴家森, 等. 鼻内镜下复发性鼻咽癌手术治疗的临床研究[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2023, 37(10): 771-777. https://lceh.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2023.10.002
[3] Hwang SY, Choi SK, Seo SH, et al. Specific roles of HSP27 S15 phosphorylation augmenting the nuclear function of HER2 to promote trastuzumab resistance[J]. Cancers, 2020, 12(6): 1540. doi: 10.3390/cancers12061540
[4] Yin CF, Kao SC, Hsu CL, et al. Phosphoproteome analysis reveals dynamic heat shock protein 27 phosphorylation in tanshinone ⅡA-induced cell death[J]. J Proteome Res, 2020, 19(4): 1620-1634. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.9b00836
[5] Bi XW, Zhang M, Zhou JY, et al. Phosphorylated Hsp27 promotes adriamycin resistance in breast cancer cells through regulating dual phosphorylation of c-Myc[J]. Cell Signal, 2023, 112: 110913. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2023.110913
[6] Liu ZY, Liu Y, Long YP, et al. Role of HSP27 in the multidrug sensitivity and resistance of colon cancer cells[J]. Oncol Lett, 2020, 19(3): 2021-2027.
[7] Huang CY, Wei PL, Chen WY, et al. Silencing heat shock protein 27 inhibits the progression and metastasis of colorectal cancer(CRC)by maintaining the stability of stromal interaction molecule 1(STIM1) proteins[J]. Cells, 2018, 7(12): E262. doi: 10.3390/cells7120262
[8] Liu XZ, Feng CY, Liu JJ, et al. Androgen receptor and heat shock protein 27 co-regulate the malignant potential of molecular apocrine breast cancer[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2018, 37(1): 90. doi: 10.1186/s13046-018-0762-y
[9] Tian L, Zhao ZF, Xie L, et al. Taurine up-regulated 1 accelerates tumorigenesis of colon cancer by regulating miR-26a-5p/MMP14/p38 MAPK/Hsp27 axis in vitro and in vivo[J]. Life Sci, 2019, 239: 117035. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.117035
[10] Shi DB, Ma RR, Zhang H, et al. GAGE7B promotes tumor metastasis and growth via activating the p38δ/pMAPKAPK2/pHSP27 pathway in gastric cancer[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2019, 38(1): 124. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1125-z
[11] Peng X, Zhou Y, Chen Y, et al. Reduced LINC00551 expression promotes proliferation and invasion of esophageal squamous cancer by increase in HSP27 phosphorylation[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2021, 236(2): 1418-1431. doi: 10.1002/jcp.29947
[12] Karademir D, Özgür A. Small molecule heat shock protein 27 inhibitor J2 decreases ovarian cancer cell proliferation via induction of apoptotic pathways[J]. Med Oncol, 2023, 40(9): 250. doi: 10.1007/s12032-023-02126-2
[13] Neo SP, Alli-Shaik A, Wee S, et al. Englerin A rewires phosphosignaling via Hsp27 hyperphosphorylation to induce cytotoxicity in renal cancer cells[J]. J Proteome Res, 2022, 21(8): 1948-1960. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.2c00248
[14] Ernst BP, Wiesmann N, Gieringer R, et al. HSP27 regulates viability and migration of cancer cell lines following irradiation[J]. J Proteomics, 2020, 226: 103886. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2020.103886
[15] Ju HY, Hu ZR, Wei DL, et al. A novel intronic circular RNA, circGNG7, inhibits head and neck squamous cell carcinoma progression by blocking the phosphorylation of heat shock protein 27 at Ser78 and Ser82[J]. Cancer Commun, 2021, 41(11): 1152-1172. doi: 10.1002/cac2.12213
[16] Zhang BH, Xie F, Aziz AUR, et al. Heat shock protein 27 phosphorylation regulates tumor cell migration under shear stress[J]. Biomolecules, 2019, 9(2): 50. doi: 10.3390/biom9020050
[17] Ke JR, Wu GR, Zhang J, et al. Melanoma migration is promoted by prion protein via Akt-hsp27 signaling axis[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2020, 523(2): 375-381. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.12.042
[18] Li ZQ, Tang XF, Duan S. Interference from LncRNA SPRY4-IT1 restrains the proliferation, migration, and invasion of melanoma cells through inactivating MAPK pathway by up-regulating miR-22-3p[J]. Int J Clin Exp Pathol, 2019, 12(2): 477-487.
[19] Wang J, Wang GW, Cheng DM, et al. Her2 promotes early dissemination of breast cancer by suppressing the p38-MK2-Hsp27 pathway that is targetable by Wip1 inhibition[J]. Oncogene, 2020, 39(40): 6313-6326. doi: 10.1038/s41388-020-01437-2
[20] Drexler R, Wagner KC, Küchler M, et al. Significance of unphosphorylated and phosphorylated heat shock protein 27 as a prognostic biomarker in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma[J]. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol, 2020, 146(5): 1125-1137. doi: 10.1007/s00432-020-03175-0
-




 下载:
下载: