Exploration of technique for preservation of external-middle ear structure in surgery of jugular foramen paraganglioma (appended 2 case reports)
-
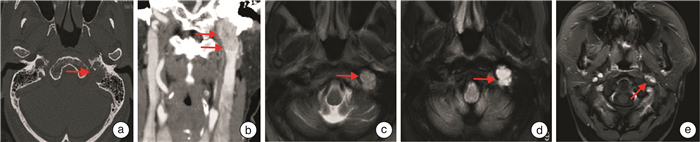
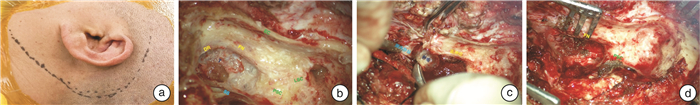
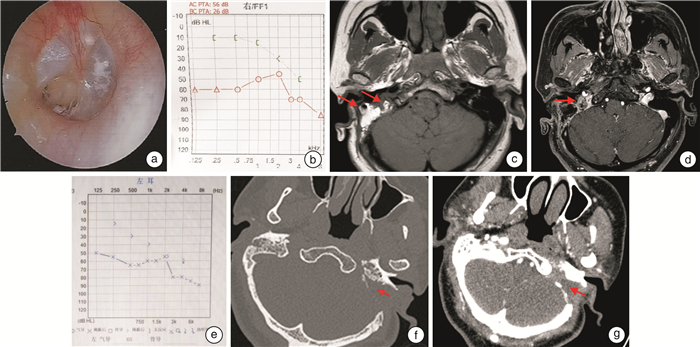
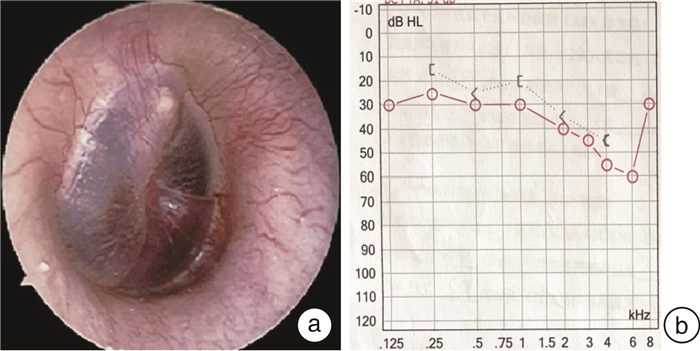
摘要: 目的 探讨对经典颞下窝A型入路进行技术改良,保留外中耳结构,对于颈静脉孔区副神经节瘤手术治疗的可行性及效果。方法 回顾性分析2例接受经迷路下经乳突-上颈部联合入路手术治疗的颈静脉孔区副神经节瘤患者的病例资料,分析患者颈静脉孔区副神经节瘤病变的临床特征,肿瘤切除程度,术后面神经功能及听力保留情况,及术后并发症的发生等。结果 2例患者均为女性,术后病理均确定为副神经节瘤。患者肿瘤分期分别为:病例1 C2De1,病例2 C1De1;2例患者肿瘤均得到完全切除,术后病例1发生感染,遗留鼓膜穿孔及混合性耳聋。病例2术后出现左侧轻度面瘫(Ⅱ级),予以对症治疗后恢复。随访半年均未见肿瘤残留或复发。结论 对于部分颈静脉孔区副神经节瘤采用迷路下经乳突-上颈部联合入路进行手术治疗,可实现切除肿瘤的同时保留外中耳结构和功能,从而提高患者的生活质量。该术式适用于病变局限于颈静脉孔区,不累及或仅累及颈内动脉垂直段(C1或C2),不伴有明显听力下降的副神经节瘤患者。Abstract: Objective To investigate the feasibility and effect of the modified surgery of the classic infratemporal fossa type A approach for the surgical treatment of jugular foramen paraganglioma with preservation of the external and middle ear structures.Methods The medical data of 2 patients with jugular foraminal paraganglioma treated by sublabyrinthic-transmastoid approach were retrospectively analyzed. The clinical feature, degree of tumor resection, postoperative facial nerve function and hearing retention, and the incidence of postoperative complications were evaluated.Results Two patients were both female, and were pathologically confirmed as paraganglioma. The tumor of case 1 was staged as C2De1, and case 2 as C1De1. Tumors were completely resected in both patients. Case 1 suffered infection after surgery, with residual tympanic membrane perforation and mixed deafness. Case 2 developed mild facial paralysis(grade Ⅱ) after surgery, and recovered after symptomatic treatment. There was no tumor residue or recurrence during half a year of follow-up.Conclusion Surgical treatment of certain paragangliomas in the jugular foramen with a combined sublabyrinthic-transmastoid and upper neck approach might achieve both complete resection of the tumor and preserving the structure and function of the outer-middle ear. This procedure is suitable for paragangliomas restricted in the jugular foramen area, with no or limited involvement of the internal carotid artery(C1 or C2), and with no or mild hearing loss.
-

-
[1] Fisch U. Infratemporal fossa approach to tumours of the temporal bone and base of the skull[J]. J Laryngol Otol, 1978, 92(11): 949-967. doi: 10.1017/S0022215100086382
[2] Kong DD, Zhang YB, Li FT, et al. Tension-free anterior rerouting of the facial nerve in management of jugular foramen paragangliomas[J]. Laryngoscope, 2021, 131(12): 2684-2687. doi: 10.1002/lary.29658
[3] Cokkeser Y, Brackmann D, Fayad J. Conservative facial nerve management in jugular foramen schwannomas[J]. Am J Otolaryngol, 2000, 21(2): 270-274. doi: 10.1016/S0196-0709(00)80021-6
[4] Chen JQ, Tan HY, Wang ZY, et al. Strategy for facial nerve management during surgical removal of benign jugular foramen tumors: Outcomes and indications[J]. Eur Ann Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Dis, 2019, 136(3): S21-S25. doi: 10.1016/j.anorl.2018.08.016
[5] Jackson CG. The infratympanic extended facial recess approach for anteriorly extensive middle ear disease: a conservation technique[J]. Laryngoscope, 1993, 103(4 Pt 1): 451-454.
[6] Odat H, Shin SH, Odat MA, et al. Facial nerve management in jugular paraganglioma surgery: a literature review[J]. J Laryngol Otol, 2016, 130(3): 219-224. doi: 10.1017/S0022215115003394
[7] Jang M, Liu H, Dai C. The application of sigmoid sinus tunnel-packing or push-packing of the inferior petrous sinus in the microsurgical management of jugular paragangliomas[J]. Otol Neurotol, 2018, 39(2): e166-e172. doi: 10.1097/MAO.0000000000001683
[8] Fayad JN, Keles B, Brackmann DE. Jugular foramen tumors: clinical characteristics and treatment outcomes[J]. Otol Neurotol, 2010, 31(2): 299-305. doi: 10.1097/MAO.0b013e3181be6495
[9] 李伟, 冯奕思, 戴春富. 颈静脉孔区副神经节瘤的临床表现及干预策略[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈杂志, 2022, 57(7): 895-900.
[10] 殷悦, 赵杨, 田旭, 等. 不同面神经处理方式应用于颈静脉孔区肿瘤切除术效果分析[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2024, 38(5): 368-371, 375. https://lceh.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2024.05.003
[11] 孔德弟, 戴春富. 颞下窝A型径路中面神经无张前移位的手术技巧[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2022, 36(7): 549-552. https://lceh.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2022.07.014
[12] Feng GD, Wei XM, Sun HY, et al. Tympanum reconstruction using a sternocleidomastoid flap in patients with lateral skull base lesions: surgical technique and clinical report[J]. Head Neck, 2020, 42(10): 2821-2829. doi: 10.1002/hed.26323
[13] Maniglia AJ, Sprecher RC, Megerian CA, et al. Inferior mastoidectomy-hypotympanic approach for surgical removal of glomus jugulare tumors: an anatomical and radiologic study emphasizing distances between critical structures[J]. Laryngoscope, 1992, 102(4): 407-414. doi: 10.1288/00005537-199204000-00007
[14] Cinibulak Z, Krauss JK, Nakamura M. Navigated minimally invasive presigmoidal suprabulbar infralabyrinthine approach to the jugular foramen without rerouting of the facial nerve[J]. Neurosurgery, 2013, 73(1 suppl operative): ons3-ons15.
[15] Cinibulak Z, Al-Afif S, Nakamura M, et al. Surgical treatment of selected tumors via the navigated minimally invasive presigmoidal suprabulbar infralabyrinthine approach without rerouting of the facial nerve[J]. Neurosurg Rev, 2022, 45(5): 3219-3229. doi: 10.1007/s10143-022-01825-0
[16] 张明山, 张宏伟, 谷春雨, 等. 经岩骨入路切除颈静脉孔区肿瘤的临床分析[J]. 中华神经外科杂志, 2021, 37(11): 1097-1101.
[17] Borba LA, Ale-Bark S, London C. Surgical treatment of glomus jugulare tumors without rerouting of the facial nerve: an infralabyrinthine approach[J]. Neurosurg Focus, 2004, 17(2): E8.
[18] Gjuric M, Bilic M. Transmastoid-infralabyrinthine tailored surgery of jugular paragangliomas[J]. Skull Base, 2009, 19(1): 75-82. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1103128
-




 下载:
下载: