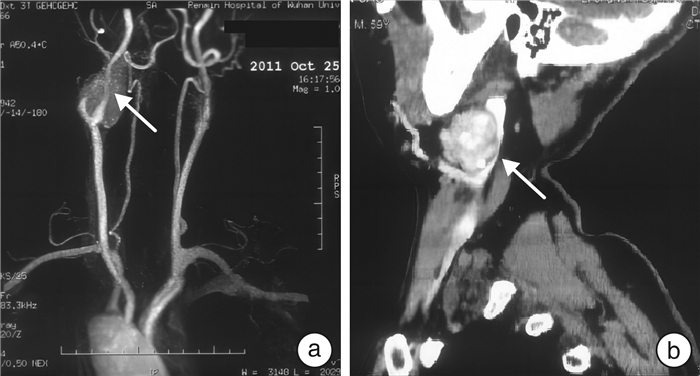
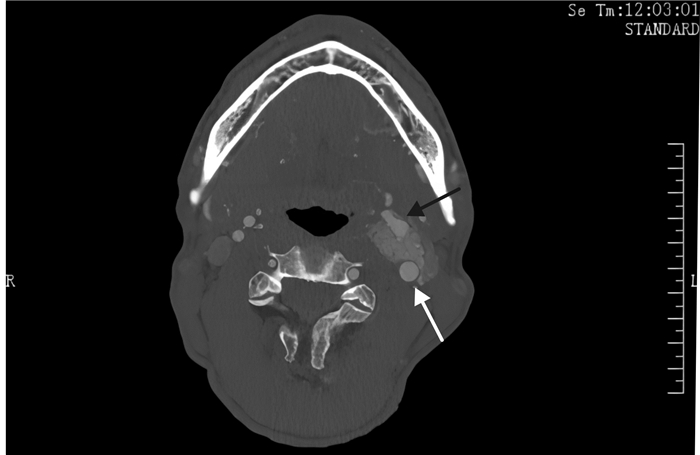
To introduce a new method of resection of carotid body tumor with preservation of the internal carotid artery——microscopic coagulation method
-
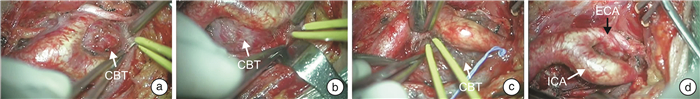
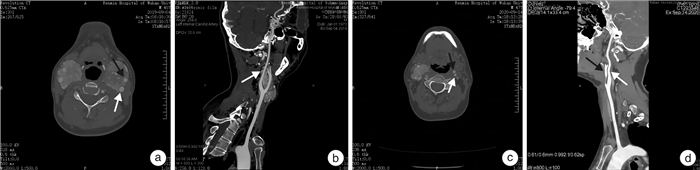
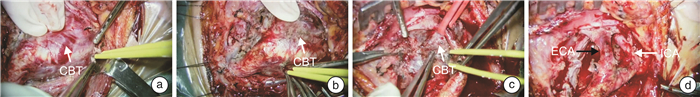
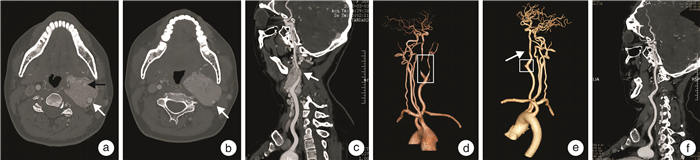
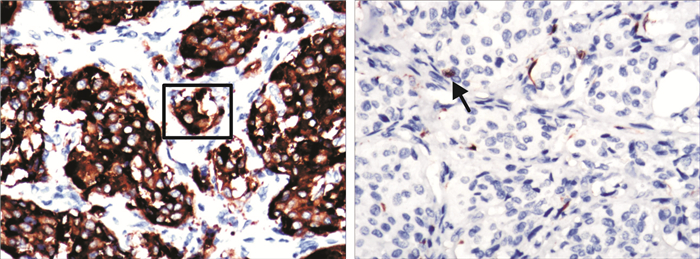
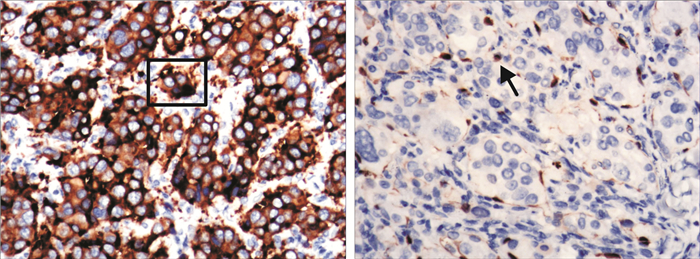
摘要: 目的 介绍保留颈内动脉切除颈动脉体瘤(carotid body tumor,CBT)的手术经验。方法 回顾性分析109例CBT患者的临床资料,总结手术技术要点,综合分析影像学及病理结果,观察患者术后并发症。结果 109例患者中Shamblin Ⅰ型28例,Shamblin Ⅱ型46例,Shamblin Ⅲ型35例。突触素(SYN)和可溶性蛋白-100(S-100)均呈阳性。17例患者病理组织免疫组织化学S-100与SYN平均表达面积百分比存在正相关关系(r=0.48)差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。手术平均时长为(148.4±46.2) min,术中平均出血量为(64.7±22.8) mL,住院平均时间为(15.2±2.6) d。所有患者手术方法均为显微凝切法,其中3例患者切除肿瘤合并颈外动脉结扎术,1例行肿瘤切除合并颈内动脉结扎术,其他患者均行单纯肿瘤切除术。总体术中血管结扎率为3.7%,神经损伤率为6.4%。根据术前CTA、术中情况及术后病理结果,对CBT提出新的分型,直观反映肿瘤与颈动脉的间隙以及肿瘤性质。结论 建议确诊后手术切除CBT。显微镜下寻找肿瘤与血管之间的潜在间隙,运用低能量双极电凝凝闭并切断其间的纤维结缔组织,沿动脉外膜逐渐分离,在完整切除肿瘤同时大部分病例均可做到保留颈动脉,减少术中出血量,降低并发症发生率。术前如何识别手术困难病例尤为重要。Abstract: Objective To introduce the surgical experience of carotid body tumor(CBT) resection with preservation of internal carotid artery.Methods The clinical data of 109 patients with CBT were retrospectively analyzed. The key points of surgical techniques were summarized, the imaging and pathological results were comprehensively analyzed, and the postoperative complications were observed.Results Of the 109 patients, 28 were Shamblin Ⅰ, 46 were Shamblin Ⅱ, and 35 were Shamblin Ⅲ. Synaptophysin(SYN) and soluble protein-100(S-100) were positive in all cases. There was a positive correlation between the average expression area percentage of S-100 and SYN in pathological tissue of 17 patients(r=0.48), and the difference was statistically significant(P < 0.05). The average operation time was(148.4±46.2) minutes, the average intraoperative blood loss was(64.7±22.8) mL, and the average hospital stay was(15.2±2.6) days. Three patients underwent tumor resection combined with external carotid artery ligation, 1 patient underwent tumor resection combined with internal carotid artery ligation, and the remaining patients underwent tumor resection alone. The overall rate of intraoperative vascular ligation was 3.7% and the rate of nerve injury was 6.4%. According to preoperative CTA, intraoperative situation and postoperative pathological results, a new classification of CBT was proposed, which could intuitively reflect the gap between the tumor and the carotid artery and the nature of the tumor.Conclusion Surgical resection of CBT is recommended after diagnosis. The potential gap between the tumor and the blood vessels was found under the microscope. Low energy bipolar electrocoagulation was used to coagulate and cut off the fibrous connective tissue between the tumor and gradually separated along the adventitia of the artery. The carotid artery could be preserved in most cases while the tumor was completely removed, and the amount of intraoperative bleeding and the incidence of complications were reduced. It is particularly important to identify the difficult cases before operation.
-
Key words:
- carotid body tumor /
- surgery /
- bipolar electrocoagulation /
- CT angiography /
- immunohistochemistry
-

-
表 1 患者手术相关情况
X±S 项目 Shamblin Ⅰ、Ⅱ型(n=74) Shamblin Ⅲ型(n=35) P 手术时长/min 143.1±50.0 159.7±34.8 0.080 术中出血量/mL 61.8±21.9 70.9±23.7 0.051 住院时间/d 14.9±2.9 15.8±1.3 0.090 表 2 术中血管结扎及神经损伤情况
% 项目 Shamblin
Ⅰ型(n=28)Shamblin
Ⅱ型(n=46)Shamblin
Ⅲ型(n=35)血管结扎率 0 0 11.4 ECA 0 0 3.0 ICA 0 0 1.0 CCA 0 0 0 颅神经损伤率 0 6.5 11.4 Ⅹ 0 1.0 2.0 Ⅻ 0 2.0 2.0 -
[1] Robertson V, Poli F, Hobson B, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the presentation and surgical management of patients with carotid body tumours[J]. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg, 2019, 57(4): 477-486. doi: 10.1016/j.ejvs.2018.10.038
[2] Zhang W, Liu F, Hou K, et al. Surgical outcomes and factors associated with malignancy in carotid body tumors[J]. J Vasc Surg, 2021, 74(2): 586-591. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2020.12.097
[3] Davila VJ, Chang JM, Stone WM, et al. Current surgical management of carotid body tumors[J]. J Vasc Surg, 2016, 64(6): 1703-1710. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2016.05.076
[4] Zhang JB, Fan XQ, Zhen YN, et al. Impact of preoperative transarterial embolization of carotid body tumor: a single center retrospective cohort experience[J]. Int J Surg, 2018, 54(Pt A): 48-52.
[5] Munakomi S, Chaudhary S, Cherian I. Case Report: Managing a giant, high-grade carotid body tumor in a resource-limited setting[J]. F1000Res, 2017, 6: 1801. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.12726.1
[6] Hua Q, Xu Z, Jiang Y. Diagnosis and surgical treatment of carotid body tumor: a retrospective analysis of 58 patients[J]. Oncol Lett, 2017, 14(3): 3628-3632. doi: 10.3892/ol.2017.6582
[7] Mourad M, Saman M, Stroman D, et al. Evaluating the role of embolization and carotid artery sacrifice and reconstruction in the management of carotid body tumors[J]. Laryngoscope, 2016, 126(10): 2282-2287. doi: 10.1002/lary.26006
[8] Spinelli F, Massara M, la Spada M, et al. A simple technique to achieve bloodless excision of carotid body tumors[J]. J Vasc Surg, 2014, 59(5): 1462-1464. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2013.10.075
[9] 吕海丽, 李谱, 张名霞, 等. 颈动脉体瘤术后16年发生颈部淋巴结转移1例[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2022, 36(6): 475-476. https://lceh.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2022.06.014
[10] Jiang XL, Fang G, Guo DQ, et al. Surgical management of carotid body tumor and risk factors of postoperative cranial nerve injury[J]. World J Surg, 2020, 44(12): 4254-4260. doi: 10.1007/s00268-020-05723-8
[11] 卞策, 汪忠镐. 颈动脉体瘤的诊治要点[J]. 国际外科学杂志, 2014, 41(12): 793-795. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-4203.2014.12.001
[12] Gao LY, Zhang XY, Jiang YX, et al. Assessment of carotid body tumors by superb microvascular imaging of feeding arteries during preoperative evaluation[J]. Front Surg, 2022, 9: 816768. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2022.816768
[13] Hogan AR, Sola JE, Jernigan SC, et al. A pediatric carotid body tumor[J]. J Pediatr Surg, 2018, 53(7): 1432-1436. doi: 10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2018.04.004
[14] 肖泽彬, 曹代荣, 江飞, 等. 320排CT诊断头颈部副神经节瘤[J]. 中国医学影像技术, 2014, 30(11): 1641-1644. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYXX201411015.htm
[15] 谢章弘, 华清泉. 92例颈动脉体瘤患者的诊断与外科治疗经验分析[J]. 中国医师杂志, 2020, 22(8): 1135-1138. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn431274-20200727-01043
[16] 陈婷, 沈暘, 朱江. 颈动脉体瘤的外科治疗及并发症预防与处理[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2018, 32(9): 713-716. https://lceh.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.1001-1781.2018.09.018
[17] Shiga K, Katagiri K, Ikeda A, et al. Challenges of surgical resection of carotid body tumors-multiple feeding arteries and preoperative embolization[J]. Anticancer Res, 2022, 42(2): 645-652. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.15522
[18] Metheetrairut C, Chotikavanich C, Keskool P, et al. Carotid body tumor: a 25-year experience[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2016, 273(8): 2171-2179. doi: 10.1007/s00405-015-3737-z
-




 下载:
下载: