Effects of cochlear implantation on tinnitus in patients with single-sided deafness and asymmetrical hearing loss
-
摘要: 目的 评估人工耳蜗对单侧聋(single-sided deafness,SSD)及不对称性听力损失(asymmetrical hearing loss,AHL)患者耳鸣的影响,并讨论不同因素对耳鸣的影响。方法 本研究前瞻性入组17例母语为汉语普通话的成人SSD/AHL人工耳蜗使用者。采用耳鸣致残量表(THI)和视觉模拟量表(VAS)评分评估患者在术前、术后1个月、开机1个月、开机3个月、开机6个月、开机12个月和开机24个月各时间点耳鸣困扰和耳鸣响度的变化情况。结果 SSD/AHL患者人工耳蜗开机后THI总分及3个维度得分均较术前降低,且耳蜗开机后各时间点得分与术前比较均差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。耳鸣VAS评分也较术前降低,且同一随访时间点佩戴耳蜗(CI-on)时VAS评分比不佩戴耳蜗(CI-off)时VAS评分更低,差异有统计学意义。结论 人工耳蜗可帮助多数SSD/AHL患者减轻耳鸣困扰和耳鸣响度,但临床上不应单纯为治疗耳鸣而植入耳蜗。Abstract: Objective To evaluate the effects of cochlear implantation in patients with single-sided deafness(SSD) and asymmetrical hearing loss(AHL).Methods Seventeen Mandarin-speaking CI patients diagnosed as SSD/AHL were recruited in our study. The Tinnitus Handicap Inventory(THI) and the Visual Analogue Scale(VAS) were used to assess changes in tinnitus distress and tinnitus loudness in SSD patients at each time point(pre-operation and post-operation).Results The THI score and all 3 dimensions were significant decreased with CI-on than pre-operation(P < 0.05). Tinnitus VAS scores were also decreased, and VAS scores were lower with CI-on than with CI-off, and were both significantly different at each time point after CI switch-on(P < 0.05).Conclusion CI could help SSD/AHL patients to suppress tinnitus and reduce the loudness of tinnitus. However, CI should not be a treatment of tinnitus.
-
Key words:
- cochlear implant /
- single-sided deafness /
- asymmetric hearing loss /
- tinnitus
-

-
表 1 17例受试者基本信息
编号 性别 年龄/岁 侧别 听力损失原因 听力损失
时间/年非植入耳
平均听阈/dB HL每日佩戴
时间/h耳鸣治疗效果 SSD1 男 50 右 骨化性迷路炎 3.00 21.25 15~16 有效 SSD2 女 38 左 梅尼埃病 20.00 6.25 10~12 有效 SSD3 女 34 右 突聋 7.00 2.50 12~13 有效 SSD4 女 38 右 听神经瘤 4.00 7.50 10~12 有效 SSD5 男 36 右 突聋 3.00 1.25 10~11 有效 SSD6 男 36 右 突聋 0.50 1.25 8~9 无效 SSD7 女 41 右 突聋 6.00 6.25 10~11 有效 SSD8 男 42 左 骨化性迷路炎 1.00 18.75 13~14 有效 SSD9 男 35 右 突聋 0.50 10.00 10~11 有效 SSD10 男 24 右 突聋 0.25 13.75 13~14 有效 SSD11 女 40 左 未知 9.00 13.75 13~14 无效 SSD12 男 31 右 突聋 0.83 6.25 15~16 有效 SSD13 女 37 左 骨化性迷路炎 0.33 10.00 12~13 有效 AHL1 女 33 右 未知 20.00 50.00 12~14 有效 AHL2 男 42 左 未知 8.00 52.50 13~14 有效 AHL3 男 32 右 未知 20.00 42.50 12~13 有效 AHL4 女 30 右 骨化性迷路炎 0.33 32.50 13~14 有效 表 2 不同随访时间THI问卷总分和各维度得分比较
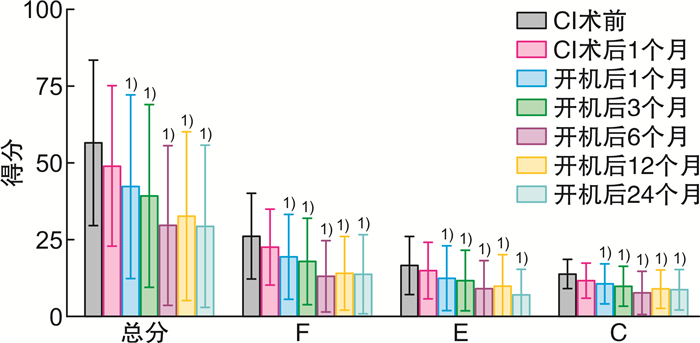
M(P25,P75) 时间 THI问卷总分 Za Pa F Zb Pb 术前 51.0(31.0,84.5) 26.0(12.0,39.5) CI术后1个月 44.0(29.0,72.0) -1.820 0.066 20.0(12.5,33.0) -1.450 0.153 开机1个月 38.0(18.0,68.0) -2.930 0.002 20.0(8.0,28.0) -2.874 0.002 开机3个月 38.0(14.0,66.0) -2.513 0.008 20.0(6.0,30.0) -2.649 0.005 开机6个月 34.0(16.0,69.5) -2.611 0.004 19.0(5.0,31.0) -2.611 0.004 开机12个月 36.0(7.0,52.0) -2.765 0.003 14.0(2.0,21.0) -2.947 0.001 开机24个月 29.0(5.0,45.0) -2.946 0.001 13.0(2.0,20.0) -2.897 0.001 时间 E Zc Pc C Zd Pd 术前 16.0(8.0,27.5) 13.0(10.5,19.5) CI术后1个月 14.0(10.0,22.0) -1.341 0.196 14.0(4.5,16.0) -1.900 0.055 开机1个月 10.0(4.0,24.0) -1.935 0.048 10.0(6.0,16.0) -2.768 0.002 开机3个月 12.0(2.0,20.0) -2.037 0.037 10.0(6.0,16.0) -2.724 0.004 开机6个月 10.0(3.0,22.5) -2.557 0.008 7.0(3.5,15.0) -2.620 0.004 开机12个月 10.0(0,17.0) -2.137 0.028 10.0(3.0,12.0) -2.367 0.015 开机24个月 5.0(0,11.5) -2.787 0.003 8.0(3.0,11.5) -2.211 0.023 F、E、C分别代表THI问卷评分的3个维度,功能性评价、情感性评价和严重性评价。a各随访时间与术前THI总分比较;b各随访时间与术前F维度得分比较;c各随访时间与术前E维度得分比较;d各随访时间与术前C维度得分比较。 表 3 不同随访时间耳鸣VAS得分比较
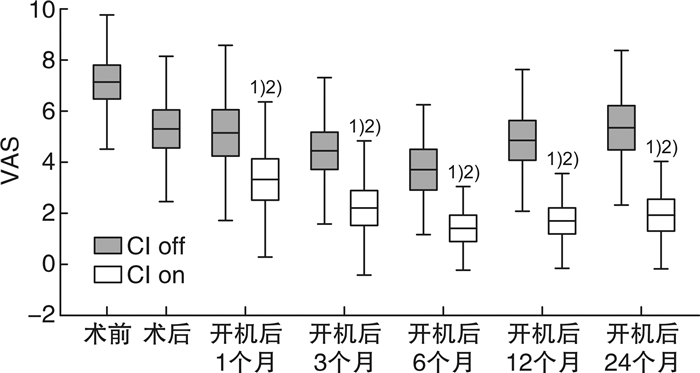
M(P25,P75) 随访时间 CI-on CI-off Za Pa Zb Pb Zc Pc 术前 8.00(5.00,8.50) CI术后1个月 5.00(3.75,8.00) -2.362 0.014 开机1个月 2.25(0.75,6.25) 5.25(1.75,8.00) -2.280 0.017 -2.213 0.021 -3.047 0.001 开机3个月 2.00(0,3.00) 4.00(2.00,6.00) -2.650 0.005 -2.919 0.001 -3.268 0.001 开机6个月 1.00(0,2.25) 3.50(1.00,6.13) -1.840 0.059 -2.457 0.008 -2.756 0.002 开机12个月 1.00(0,3.00) 5.00(3.50,6.00) -2.302 0.018 -2.907 0.001 -2.897 0.001 开机24个月 2.00(0,3.50) 6.00(3.00,8.00) -1.230 0.224 -2.723 0.004 -2.897 0.001 a各随访时间关闭耳蜗时与术前VAS得分比较;b各随访时间耳蜗工作和关闭耳蜗VAS得分比较;c各随访时间耳蜗工作时与术前VAS得分比较。 -
[1] Tyler RS, Baker LJ. Difficulties experienced by tinnitus sufferers[J]. J Speech Hear Disord, 1983, 48(2): 150-154. doi: 10.1044/jshd.4802.150
[2] Dhanasingh A, Hochmair I. CI in single-sided deafness[J]. Acta Otolaryngol, 2021, 141(sup1): 82-105. doi: 10.1080/00016489.2021.1888496
[3] Vermeire K, Van de Heyning P. Binaural hearing after cochlear implantation in subjects with unilateral sensorineural deafness and tinnitus[J]. Audiol Neurootol, 2009, 14(3): 163-171. doi: 10.1159/000171478
[4] Van de Heyning P, Vermeire K, Diebl M, et al. Incapacitating unilateral tinnitus in single-sided deafness treated by cochlear implantation[J]. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol, 2008, 117(9): 645-652. doi: 10.1177/000348940811700903
[5] Jacob R, Stelzig Y, Nopp P, et al. Audiological results with cochlear implants for single-sided deafness[J]. HNO, 2011, 59(5): 453-460. doi: 10.1007/s00106-011-2321-0
[6] Van de Heyning P, Távora-Vieira D, Mertens G, et al. Towards a unified testing framework for single-sided deafness studies: a consensus paper[J]. Audiol Neurootol, 2016, 21(6): 391-398. doi: 10.1159/000455058
[7] Newman CW, Jacobson GP, Spitzer JB. Development of the tinnitus handicap inventory[J]. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 1996, 122(2): 143-148. doi: 10.1001/archotol.1996.01890140029007
[8] Meng Z, Zheng Y, Liu S, et al. Reliability and validity of the Chinese(mandarin)tinnitus handicap inventory[J]. Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol, 2012, 5(1): 10-16. doi: 10.3342/ceo.2012.5.1.10
[9] 石秋兰, 卜行宽, 王俊国, 等. 耳鸣致残量表中文版的研译与临床应用[J]. 南京医科大学学报(自然科学版), 2007, 27(5): 476-479. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-4368.2007.05.018
[10] 明静, 胡金旺, 韦冰雪. 成人感音神经性聋患者人工耳蜗植入后耳鸣和抑郁状态的研究[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2022, 36(2): 86-89. https://lceh.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2022.02.002
[11] 郭晓会, 王斌, 曹克利, 等. 伴耳鸣患者人工耳蜗植入术中电刺激听觉脑干诱发电位特点及术后疗效分析[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2022, 36(6): 423-428. https://lceh.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2022.06.004
[12] Mertens G, De Bodt M, Van de Heyning P. Cochlear implantation as a long-term treatment for ipsilateral incapacitating tinnitus in subjects with unilateral hearing loss up to 10 years[J]. Hear Res, 2016, 331: 1-6. doi: 10.1016/j.heares.2015.09.016
[13] Punte AK, Vermeire K, Hofkens A, et al. Cochlear implantation as a durable tinnitus treatment in single-sided deafness[J]. Cochlear Implants Int, 2011, 12(Suppl 1): S26-S29.
[14] Arndt S, Aschendorff A, Laszig R, et al. Comparison of pseudobinaural hearing to real binaural hearing rehabilitation after cochlear implantation in patients with unilateral deafness and tinnitus[J]. Otol Neurotol, 2011, 32(1): 39-47. doi: 10.1097/MAO.0b013e3181fcf271
[15] Dillon MT, Buss E, Rooth MA, et al. Effect of cochlear implantation on quality of life in adults with unilateral hearing loss[J]. Audiol Neurootol, 2017, 22(4-5): 259-271. doi: 10.1159/000484079
[16] Deep NL, Spitzer ER, Shapiro WH, et al. Cochlear implantation in adults with single-sided deafness: outcomes and device use[J]. Otol Neurotol, 2021, 42(3): 414-423. doi: 10.1097/MAO.0000000000002955
[17] Morelli L, Fancello V, Gaino F, et al. Cochlear implantation in single-sided deafness: a single-center experience of 138 cases[J]. Eur Arch Oto Rhino Laryngol, 2023, 280(10): 4427-4432. doi: 10.1007/s00405-023-07959-1
[18] Finke M, Bönitz H, Lyxell B, et al. Cochlear implant effectiveness in postlingual single-sided deaf individuals: what's the point?[J]. Int J Audiol, 2017, 56(6): 417-423. doi: 10.1080/14992027.2017.1296595
[19] Arts RA, Netz T, Janssen AM, et al. The occurrence of tinnitus after CI surgery in patients with severe hearing loss: a retrospective study[J]. Int J Audiol, 2015, 54(12): 910-917. doi: 10.3109/14992027.2015.1079930
[20] Sladen DP, Frisch CD, Carlson ML, et al. Cochlear implantation for single-sided deafness: a multicenter study[J]. Laryngoscope, 2017, 127(1): 223-228. doi: 10.1002/lary.26102
[21] Souliere CR, Kileny PR, Zwolan TA, et al. Tinnitus suppression following cochlear implantation. A multifactorial investigation[J]. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 1992, 118(12): 1291-1297. doi: 10.1001/archotol.1992.01880120017004
[22] Levy DA, Lee JA, Nguyen SA, et al. Cochlear implantation for treatment of tinnitus in single-sided deafness: a systematic review and Meta-analysis[J]. Otol Neurotol, 2020, 41(8): e1004-e1012. doi: 10.1097/MAO.0000000000002711
[23] Kloostra FJJ, Verbist J, Hofman R, et al. A prospective study of the effect of cochlear implantation on tinnitus[J]. Audiol Neurootol, 2018, 23(6): 356-363. doi: 10.1159/000495132
[24] Demajumdar R, Stoddart R, Donaldson I, et al. Tinnitus, cochlear implants and how they affect patients[J]. J Laryngol Otol Suppl, 1999, 24: 24-26.
[25] Miyamoto RT, Bichey BG. Cochlear implantation for tinnitus suppression[J]. Otolaryngol Clin North Am, 2003, 36(2): 345-352. doi: 10.1016/S0030-6665(02)00165-2
[26] Borges ALF, Duarte PLES, Almeida RBS, et al. Cochlear implant and tinnitus-a meta-analysis[J]. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol, 2021, 87(3): 353-365. doi: 10.1016/j.bjorl.2020.11.006
[27] Punte AK, De Ridder D, Van de Heyning P. On the necessity of full length electrical cochlear stimulation to suppress severe tinnitus in single-sided deafness[J]. Hear Res, 2013, 295: 24-29. doi: 10.1016/j.heares.2012.08.003
[28] Di Nardo W, Cantore I, Cianfrone F, et al. Tinnitus modifications after cochlear implantation[J]. Eur Arch Oto Rhino Laryngol, 2007, 264(10): 1145-1149. doi: 10.1007/s00405-007-0352-7
[29] Arts RA, George EL, Janssen M, et al. Tinnitus suppression by intracochlear electrical stimulation in single sided deafness-A prospective clinical trial: follow-up[J]. PLoS One, 2016, 11(4): e0153131. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0153131
[30] Perreau A, Tyler R, Mancini PC. Programming a cochlear implant for tinnitus suppression[J]. J Am Acad Audiol, 2020, 31(4): 302-308. doi: 10.3766/jaaa.18086
[31] Arts RA, George EL, Chenault MN, et al. Optimizing intracochlear electrical stimulation to suppress tinnitus[J]. Ear Hear, 2015, 36(1): 125-135. doi: 10.1097/AUD.0000000000000090
-

计量
- 文章访问数: 274
- 施引文献: 0



 下载:
下载: