Tinnitus and depression after cochlear implantation in adult sensorineural deafness
-
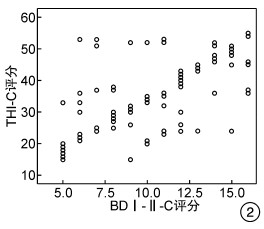
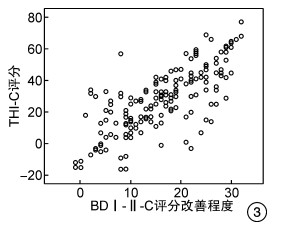
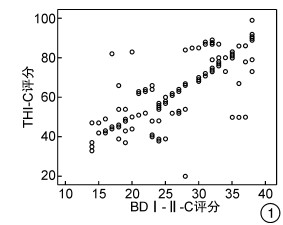
摘要: 目的 探讨成人重度、极重度耳聋患者耳蜗植入术(CI)后耳鸣和抑郁状态的变化及其相关性。方法 回顾性选择166例行CI的成人患者作为研究对象,所有患者手术前后均接受中文版耳鸣残疾评估量表(THI-C)调查和贝克抑郁量表第2版中文版(BDI-Ⅱ-C)调查,观察患者术后耳鸣改善情况、手术前后THI-C和BDI-Ⅱ-C得分情况以及两者之间的相关性。结果 CI术后6个月复查,患者手术前后耳鸣残疾评估等级显著下降(Z=-9.478,P < 0.001),THI-C评分(t=69.128,P < 0.001)、BDI-Ⅱ-C评分(t=58.531,P < 0.01)均显著降低。Spearman相关性分析显示,手术前、后THI-C和BDI-Ⅱ-C评分之间以及THI-C评分改善程度和BDI-Ⅱ-C评分改善程度之间均具有显著正相关性(r术前=0.763、r术后=0.741、r差值=0.741,均P < 0.001)。结论 CI能显著改善成人感音神经性聋患者的耳鸣和抑郁程度。随着耳鸣程度的改善,患者抑郁状态也得以相应缓解。
-
关键词:
- 听觉丧失,感音神经性 /
- 耳蜗植入术 /
- 耳鸣 /
- 抑郁
Abstract: Objective The aim of this study is to investigate the changes and correlation of tinnitus and depression in adult patients with severe deafness after cochlear implantation.Methods A total of 166 adult patients who underwent cochlear implantation(CI) were retrospectively selected as the research objects. All patients were investigated by Chinese Version of the Tinnitus Handicap Inventory(THI-C) and Chinese Version of the Beck Depression Inventory-Ⅱ(BDI-Ⅱ-C) before and after operation, and the improvement of tinnitus after operation was observed THI-C and BDI-Ⅱ-C scores before and after operation and the correlation between them.Results Re-examination at 6 months after CI showed that the evaluation grade of tinnitus disability before and after the operation decreased significantly(Z=-9.478, P < 0.001), and the THI-C score (t=69.128, P < 0.001), and BDI-Ⅱ-C score (t=58.531, P < 0.01)were significantly reduced. Spearman correlation analysis showed that there was a significant positive correlation between THI-C and BDI-Ⅱ-C scores before and after operation, aswell as the improvement of THI-C score and BDI-Ⅱ-C score(rpreoperative=0.763, rpostoperative=0.741, rdifference=0.741, all P < 0.001).Conclusion Cochlear implantation can significantly improve tinnitus and depression in adult patients with sensorineural hearing loss. With the improvement of tinnitus, the depressive state of patients can be alleviated accordingly.-
Key words:
- hearing loss, sensorineural /
- cochlear implantation /
- tinnitus /
- depression
-

-
表 1 CI手术前后患者耳鸣等级、评分及抑郁评分情况
时间 THI-C等级 THI-C评分 BDI-Ⅱ-C评分 1级 2级 3级 4级 术前(n=166) 8 62 85 21 63.5±16.5 26.5±7.0 术后(n=166) 115 29 15 7 35.6±11.3 10.6±3.5 Z/t值 -9.478 69.128 58.531 P值 < 0.001 < 0.001 < 0.001 -
[1] 夏红艳, 赵立东, 王秋菊, 等. 《日本慢性耳鸣诊治临床实践指南》摘译[J]. 听力学及言语疾病杂志, 2021, 29(1): 114-116. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TLXJ202101032.htm
[2] 陈艳, 韩淼, 王咪, 等. 耳鸣诊疗进展[J]. 临床误诊误治, 2019, 32(1): 109-113. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCWZ201901026.htm
[3] 靳卫红, 刘涛. 耳鸣声治疗临床研究进展[J]. 中国耳鼻咽喉颅底外科杂志, 2020, 26(05): 590-593. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZEBY202005027.htm
[4] Deep NL, Dowling EM, Jethanamest D, et al. Cochlear Implantation: an Overview[J]. J Neurol Surg B Skull Base. 2019, 80(2): 169-177. doi: 10.1055/s-0038-1669411
[5] 钟零珠, 林智, 孙丽霞. 人工耳蜗植入患者耳鸣临床特征和相关因素调查研究[J]. 中华耳科学杂志, 2020, 18(6): 1072-1076. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHER202006014.htm
[6] Kloostra FJ, Arnold R, Hofman R, Van Dijk P. Changes in tinnitus after cochlear implantation and its relation with psychological functioning[J]. Audiol Neurotol. 2015, 20(2): 81-89. doi: 10.1159/000365959
[7] Sullivan CB, Al-Qurayshi Z, Zhu V, et al. Long-term audiologic outcomes after cochlear implantation for single-sided deafness[J]. Laryngoscope, 2019, 130(7): 1805-1811.
[8] Ketterer MC, Knopke S, Häußler SM, Hildenbrand T, Becker C, Gräbel S, et al. Asymmetric hearing loss and the benefit of cochlear implantation regarding speech perception, tinnitus burden and psychological comorbidities: a prospective follow-up study[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2018, 275(11): 2683-2693. doi: 10.1007/s00405-018-5135-9
[9] 李琦. 2019版美国听力学学会《人工耳蜗植入临床实践指南》解读: 患者选择和适应证[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2021, 35(6): 491-494. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH202106003.htm
[10] 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志编辑委员会, 中华医学会耳鼻咽喉头颈外科学分会, 中国残疾人康复协会听力语言康复专业委员会. 人工耳蜗植入工作指南(2013)[J]. 中华耳鼻喉头颈外科杂志, 2014, 49(2): 89-95. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHEB200402001.htm
[11] 吴迪, 郑芸, 陈知己. 中文版耳鸣残疾量表用于患者自评的适应度评估[J]. 四川大学学报(医学版), 2018, 49(6): 985-988. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXYK201806035.htm
[12] 蒋水琳, 杨文辉. 贝克抑郁量表第2版中文版在我国大学生中的因子结构[J]. 中国临床心理学杂志, 2020, 28(2): 299-305. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZLCY202002017.htm
[13] Shore SE, Wu C. Mechanisms of Noise-Induced Tinnitus: Insights from Cellular Studies[J]. Neuron, 2019, 103(1): 8-20. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2019.05.008
[14] Peter N, Liyanage N, Pfiffner F, et al. The influence of cochlear implantation on tinnitus in patients with single-sided deafness: a systematic review[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2019: 853368380.
[15] Szyfter W, Karlik M, Sekula A, et al. Current indications for cochlear implantation in adults and children[J]. Otolaryngol Pol, 2019, 73(3): 1-5.
[16] Pierzycki RH, Corner C, Fielden C A, et al. Effects of tinnitus oncochlear implantprogramming[J]. Trends Hear, 2019, 23: 1534118960.
[17] 王智超, 黄琦, 陈兵, 等. 人工耳蜗术后耳鸣疗效及耳鸣改变模式分析[J]. 临床耳鼻喉头颈外科杂志, 2020, 34(11): 966-971. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH202011002.htm
[18] Kloostra FJ, Verbist J, Hofman R, et al. A Prospective Study of the Effect of Cochlear Implantation on Tinnitus[J]. Audiol Neurotol. 2018, 23(6): 356-363. doi: 10.1159/000495132
[19] Kloostra FJ, Arnold R, Hofman R, et al. Models to predict positive and negative effects of cochlear implantation on tinnitus[J]. Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol, 2018, 4(1): 138-142.
[20] Ivansic D, Besteher B, Gantner J, Guntinas-Lichius O, et al. Psychometric assessment of mental health in tinnitus patients, depressive and healthy controls[J]. Psychiatry Res, 2019, 281: 112582. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2019.112582
[21] Brueggemann P, Seydel C, Schaefer C, et al. ICD-10 Symptom Rating questionnaire for assessment of psychological comorbidities in patients with chronic tinnitus[J]. HNO, 2019, 67(Suppl 2): 46-50.
[22] 丁云童, 徐亚运, 陈龙, 等. 耳鸣致残等级与老年抑郁症患者抑郁程度的相关性研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2020, 23(32): 4047-4052. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QKYX202032025.htm
[23] Pierzycki RH, Corner C, Fielden CA, et al. Effects of tinnitus on cochlear implant programming[J]. Trends Hear, 2019, 23: 2331216519836624.
-




 下载:
下载: