-
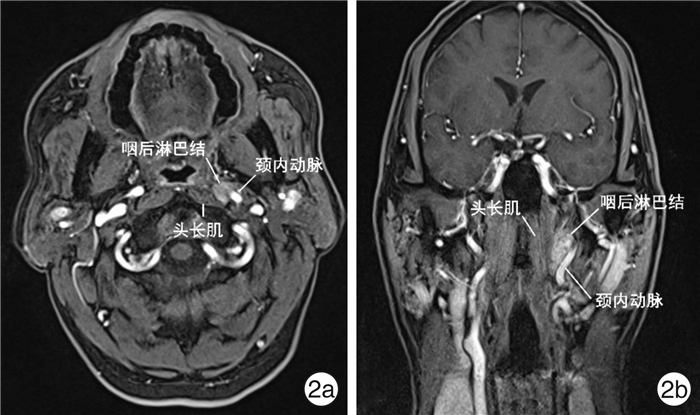
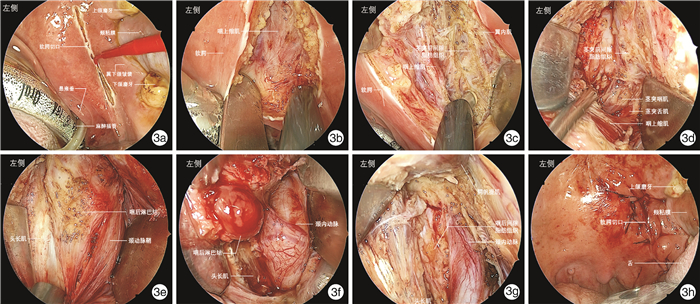
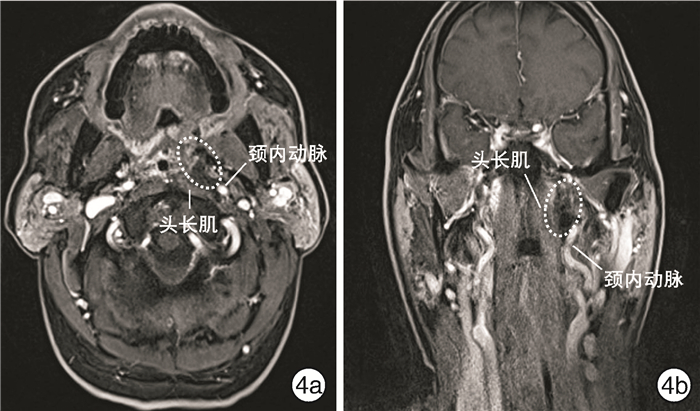
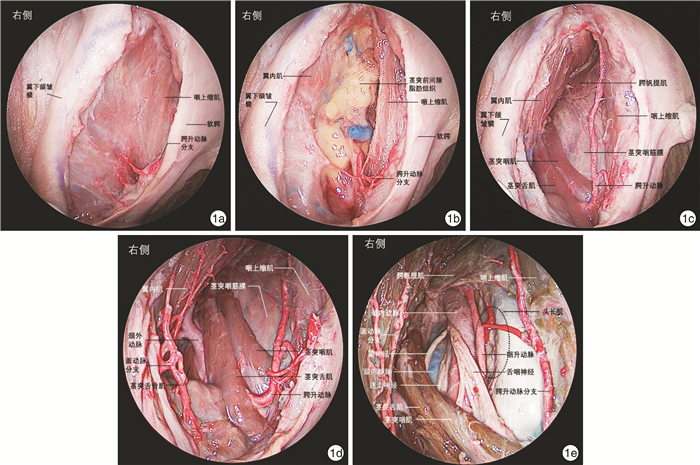
摘要: 目的 探索内镜经口入路咽后淋巴结切除术相关解剖和手术方法。方法 在复旦大学附属眼耳鼻喉科医院解剖实验室对3例(6侧)新鲜冰冻尸头标本进行内镜经口入路咽后间隙解剖学研究,依次显露咽上缩肌、翼内肌、腭帆张肌腱、茎突前间隙脂肪、腭升动脉及其分支、茎突舌肌、茎突咽肌、茎突舌骨肌、颈外动脉、腭帆提肌、颈动脉鞘、咽升动脉以及头长肌。采用0°Karl Storz鼻内镜对上述解剖结构进行拍照并记录毗邻关系。回顾1例转移性咽后淋巴结病例,详细介绍内镜经口入路咽后淋巴结切除术手术方法和技巧。结果 所有标本均通过内镜经口入路显露咽后间隙及相关解剖结构。茎突舌肌、茎突咽肌和腭帆提肌是定位颈内动脉的标志。咽上缩肌、翼内肌、茎突肌群、头长肌及颈动脉鞘是定位咽后淋巴结的标志。腭升动脉、咽升动脉及颈内动脉是内镜经口入路咽后淋巴结切除术中涉及的主要动脉。结论 内镜经口入路是安全、彻底切除咽后淋巴结的新术式。Abstract: Objective The aim of this study is to explore the anatomy and surgical approach of retropharyngeal lymphadenectomy via endoscopic transoral approach.Methods The retropharyngeal spaces were studied with three fresh frozen cadaver head (6 sides) in the anatomical laboratory of Eye, Ear, Nose and Throat Hospital of Fudan University through endoscopic transoral approach. The superior pharyngeal constrictor muscle, medial pterygoid muscle, tendon of tensor veli palatini muscle, fat of prestyloid space, ascending palatine artery and its branches, styloglossus, stylopharyngeus, stylohyoideus, external carotid artery, levator veli palatini, carotid sheath, ascending pharyngeal artery and longus capitis muscle were revealed in order. The above-mentioned structures were photographed with a 0° Karl Storz nasal endoscope and adjacent relationships were recorded. A case of metastatic retropharyngeal lymphadenopathy was reviewed and the surgical methods and techniques of retropharyngeal lymphadenectomy via endoscopic transoral approach were introduced in detail.Results The retropharyngeal space and related anatomical structures were exposed through endoscopic transoral approach in all specimens. The styloglossus, stylopharyngius and levator veli palatini are the markers of locating the internal carotid artery. The superior pharyngeal constrictor muscle, medial pterygoid muscle, styloid muscle group, longus capitis muscle and carotid sheath are the markers that can be used to locate the retropharyngeal lymph nodes. Ascending palatine artery, ascending pharyngeal artery and internal carotid artery are the main arteries involved in retropharyngeal lymphadenectomy via endoscopic transoral approach.Conclusion Endoscopic transoral approach is a new surgical technique to perform retropharyngeal lymphadenectomy safely and completely.
-

-
[1] Coskun HH, Ferlito A, Medina JE, et al. Retropharyngeal lymph node metastases in head and neck malignancies[J]. Head Neck, 2011, 33(10): 1520-1529. doi: 10.1002/hed.21526
[2] Ferlito A, Shaha AR, Rinaldo A. Retropharyngeal lymph node metastasis from cancer of the head and neck[J]. Acta Otolaryngol, 2002, 122(5): 556-560. doi: 10.1080/00016480260092408
[3] Oikawa Y, Michi Y, Tsushima F, et al. Management of retropharyngeal lymph node metastasis in oral cancer[J]. Oral Oncol, 2019, 99(104471).
[4] Lopez F, Suarez C, Vander Poorten V, et al. Contemporary management of primary parapharyngeal space tumors[J]. Head Neck, 2019, 41(2): 522-535.
[5] Guidera AK, Dawes PJ, Fong A, et al. Head and neck fascia and compartments: no space for spaces[J]. Head Neck, 2014, 36(7): 1058-1068. doi: 10.1002/hed.23442
[6] Servian DA, Beer-furlan A, LIMA LR, et al. Pharyngobasilar fascia as a landmark in endoscopic skull base surgery: The triangulation technique[J]. Laryngoscope, 2019, 129(7): 1539-1544. doi: 10.1002/lary.27608
[7] Snosek M, Macchi V, Stecco C, et al. Anatomical and histological study of the alar fascia[J]. Clin Anat, 2021, 34(4): 609-616. doi: 10.1002/ca.23644
[8] Petruzzi G, Zocchi J, Moretto S, et al. Transoral robotic retropharyngeal lymph node dissection in a recurrent head and neck carcinoma[J]. Head Neck, 2019, 41(11): 4051-4053. doi: 10.1002/hed.25874
[9] 孙颖, 马骏, 卢泰祥, 等. 512例鼻咽癌颈淋巴结转移规律的研究[J]. 癌症, 2004, z1: 1523-1527. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-AIZH2004S1036.htm
[10] Kato H, Kanematsu M, Watanabe H, et al. Metastatic retropharyngeal lymph nodes: comparison of CT and MR imaging for diagnostic accuracy[J]. Eur J Radiol, 2014, 83(7): 1157-1162. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2014.02.027
[11] Chen J, Luo J, He X, et al. Evaluation of Contrast-Enhanced Computed Tomography(CT)and Magnetic Resonance Imaging(MRI)in the Detection of Retropharyngeal Lymph Node Metastases in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Patients[J]. Cancer Manag Res, 2020, 12: 1733-1739. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S244034
[12] Li YZ, Xie CM, Wu Y P, et al. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients with retropharyngeal lymph node metastases: a minimum axial diameter of 6 mm is a more accurate prognostic predictor than 5 mm[J]. AJR Am J Roentgenol, 2015, 204(1): 20-23. doi: 10.2214/AJR.14.12936
[13] Lu L, Wei X, Li YH, et al. Sentinel node necrosis is a negative prognostic factor in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a magnetic resonance imaging study of 252 patients[J]. Curr Oncol, 2017, 24(3): e220-e225. doi: 10.3747/co.24.3168
[14] He LJ, Xie C, Li Y, et al. Ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration of retropharyngeal lymph nodes after radiotherapy for nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a novel technique for accurate diagnosis[J]. Cancer Commun(Lond), 2018, 38(1): 20-20.
[15] Liu Y P, Wang S L, ZOU X, et al. Transcervical endoscopic retropharyngeal lymph node(RPLN)dissection in nasopharyngeal carcinoma with RPLN recurrence[J]. Head Neck, 2021, 43(1): 98-107. doi: 10.1002/hed.26459
[16] 龚霄阳, 卫亚楠, 林子萍, 等. 等离子及内镜系统辅助下口内径路治疗咽旁间隙肿瘤疗效分析[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2021, 35(3): 204-208. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH202103003.htm
[17] 何龙, 谢景华, 高雄辉. 内镜辅助下经口径路咽旁间隙肿瘤切除术[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2020, 34(9): 824-827, 835. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH202009013.htm
[18] Ding X, Lin Q G, Zou X, et al. Transoral Robotic Retropharyngeal Lymph Node Dissection in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma With Retropharyngeal Lymph Node Recurrence[J]. Laryngoscope, 2021, 131(6): E1895-E902.
[19] Sun X, Yan B, Truong HQ, et al. A Comparative Analysis of Endoscopic-Assisted Transoral and Transnasal Approaches to Parapharyngeal Space: A Cadaveric Study[J]. J Neurol Surg B Skull Base, 2018, 79(3): 229-240. doi: 10.1055/s-0037-1606551
[20] Liu J, Sun X, Liu Q, et al. A minimally invasive endoscopic transnasal retropterygoid approach to the upper parapharyngeal space: anatomic studies and surgical implications[J]. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol, 2019, 9(11): 1263-1272. doi: 10.1002/alr.22437
[21] Liu Q, Wang H, Zhao W, et al. Endoscopic transnasal transmaxillary approach to the upper parapharyngeal space and the skull base[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2020, 277(3): 801-807. doi: 10.1007/s00405-019-05761-6
[22] Gyanwali B, Li H, Xie L, et al. The role of tensor veli palatini muscle(TVP)and levetor veli palatini[corrected]muscle(LVP)in the opening and closing of pharyngeal orifice of Eustachian tube[J]. Acta Otolaryngol, 2016, 136(3): 249-255. doi: 10.3109/00016489.2015.1107192
[23] Xu X, Ong YK. An endoscopic anatomical study of the levator veli palatini and its relationship to the parapharyngeal internal carotid artery[J]. Head Neck, 2020, 42(8): 1829-36. doi: 10.1002/hed.26101
-

| 引用本文: | 孙希才, 薛凯, 刘强, 等. 内镜经口入路咽后淋巴结切除术[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2022, 36(2): 81-86. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2022.02.001 |
| Citation: | SUN Xicai, XUE Kai, LIU Qiang, et al. Endoscopic transoral retropharyngeal lymphadenectomy[J]. J Clin Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2022, 36(2): 81-86. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2022.02.001 |
- Figure 1.
- Figure 2.
- Figure 3.
- Figure 4.



 下载:
下载: