Based on CT imaging, surgical approach selection for frontal and ethmoid sinus osteoma
-
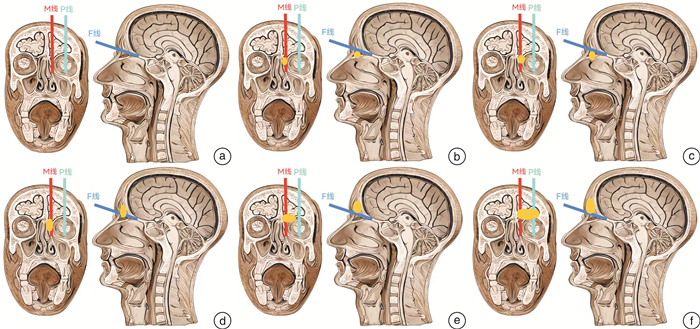
摘要: 目的 探讨在CT影像上不同位置和大小额筛窦骨瘤的手术入路选择标准。方法 分别在鼻窦矢状位和冠状位CT上选择F线(额嘴水平线)、M线(眶内侧壁线)、P线(瞳孔中心垂直线),根据额筛窦骨瘤和F线、P线、M线的关系进行分类,并选择合适的手术入路(包括单纯内镜入路、内镜联合眉弓切口入路及内镜联合冠状切口入路),2020年1月-2023年9月中山大学附属第三医院收治的16例额筛窦骨瘤患者均应用此方法完成额筛窦骨瘤切除手术,其中男9例,女7例;年龄18~69岁,中位年龄48岁。结果 16例患者中,13例单纯内镜下切除骨瘤;3例采用联合入路,其中2例超越M线及F线且未过P线者采用内镜联合眉弓切口入路,余1例超越三线者采用内镜联合冠状切口入路。患者的骨瘤均按照术前设计得到完整切除,术后均未发生明显并发症。结论 额筛窦骨瘤术前建议影像学上仔细评估,根据骨瘤的大小及三线的位置关系,选择合适手术入路,优化诊疗方案。Abstract: Objective To investigate the criteria for selecting surgical approaches for frontal and ethmoid sinus osteomas of different locations and sizes on CT imaging.Methods Using sagittal and coronal CT images, the following lines were delineated: the F-line(a horizontal line passing nasofrontal beak), the M-line(a vertical line passing paries medialis orbitae), and the P-line(a vertical line passing the center of the pupil). Classification of frontal and ethmoid sinus osteomas was based on their relationship with these lines. Appropriate surgical approaches were selected, including pure endoscopic approaches, endoscopic combined with eyebrow incision approach, and endoscopic combined with coronal incision approach. This method was applied to a single center at the Third Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University for endoscopic resection of frontal and ethmoid sinus osteoma. Case Data: Sixteen cases of ethmoid sinus osteomas were treated from January 2020 to September 2023. Among these cases, there were 9 males and 7 females, with ages ranging from 18 to 69 years, and a median age of 48 years.Results Thirteen cases underwent pure endoscopic resection of the osteoma, while in three cases, a combined approach was utilized. Among the combined approach cases, two exceeded both the M-line and the F-line but did not cross the P-line; therefore, they underwent endoscopic combined with eyebrow incision approach. One case exceeded all three lines and thus underwent endoscopic combined with coronal incision. In all cases, complete resection of the osteoma was achieved as per preoperative planning, and none of the patients experienced significant postoperative complications.Conclusion For frontal and ethmoid sinus osteomas, it is advisable to perform a thorough preoperative radiological assessment. Based on the size of the osteoma and its relationship to the three lines, an appropriate surgical approach should be chosen to optimize the diagnostic and treatment plan.
-
Key words:
- osteoma /
- ethmoid sinus /
- frontal sinus /
- endoscopic surgery /
- surgical approaches
-

-
表 1 额筛骨瘤患者的基本资料
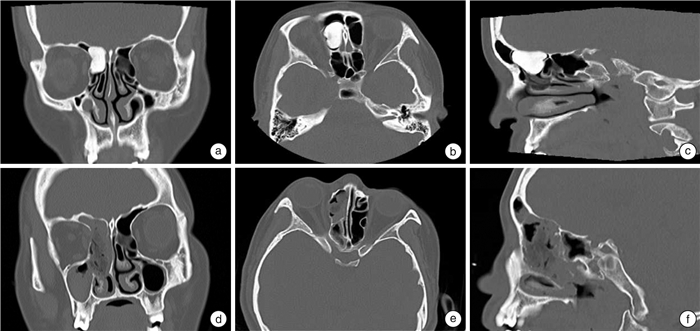
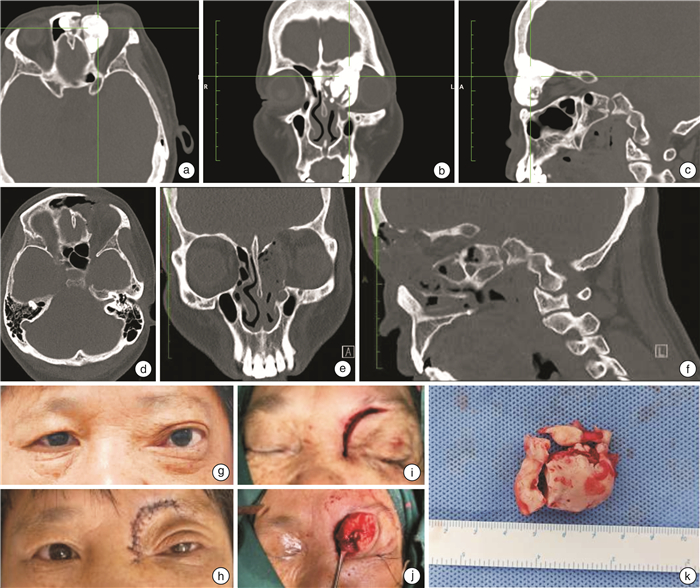
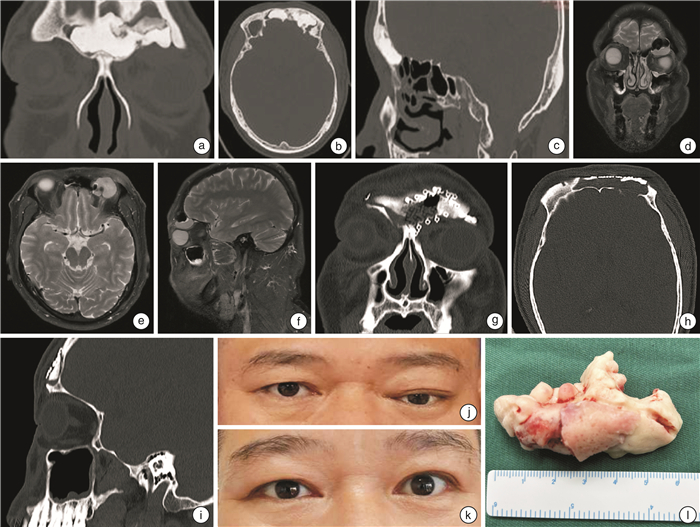
序号 部位 主诉 附着于额窦前壁/后壁 超过F线 超过M线 超过P线 分型 最大径/mm 内镜手术 联合手术入路 筛窦 额窦 1 是 体检发现 否 否 否 Ⅰ型 23 是 2 是 眼球移位 是 否 是 否 Ⅳ型 32 是 3 是 鼻塞、流涕 是 是 是 否 Ⅳ型 25 是 4 是 眼球移位 是 是 是 是 Ⅴ型 60 是 5 是 鼻塞、流涕 否 否 否 Ⅰ型 6 是 6 是 鼻塞、流涕 否 否 否 Ⅰ型 7 是 7 是 鼻塞、流涕 否 否 否 Ⅰ型 11 是 8 是 嗅觉减退 否 否 否 Ⅰ型 9 是 9 是 鼻塞、流涕 否 否 否 Ⅰ型 7 是 10 是 鼻塞、流涕 否 否 是 否 Ⅱ型 8 是 11 是 头痛、流涕 否 否 否 Ⅰ型 9 是 12 是 鼻出血 否 否 否 Ⅰ型 8 是 13 是 鼻塞、流涕 否 否 否 Ⅰ型 17 是 14 是 鼻塞、头痛 是 否 否 Ⅰ型 9 是 15 是 鼻塞、流涕 是 是 否 Ⅲ型 10 是 16 是 视力下降 是 是 否 Ⅲ型 15 是 -
[1] Atallah N, Jay MM. Osteomas of the paranasal sinuses[J]. J Laryngol Otol, 1981, 95(3): 291-304. doi: 10.1017/S0022215100090721
[2] Buyuklu F, Akdogan MV, Ozer C, et al. Growth characteristics and clinical manifestations of the paranasal sinus osteomas[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2011, 145(2): 319-323. doi: 10.1177/0194599811403380
[3] Wolf A, Safran B, Pock J, et al. Surgical Treatment of Paranasal Sinus Osteomas: A Single Center Experience of 58 Cases[J]. Laryngoscope, 2020, 130(9): 2105-2113. doi: 10.1002/lary.28299
[4] Çelenk F, Baysal E, Karata ZA, et al. Paranasal sinus osteomas[J]. J Craniofac Surg, 2012, 23(5): e433-437. doi: 10.1097/SCS.0b013e31825e4b5b
[5] Sofokleous V, Maragoudakis P, Kyrodimos E, et al. Management of paranasal sinus osteomas: A comprehensive narrative review of the literature and an up-to-date grading system[J]. Am J Otolaryngol, 2021, 42(5): 102644. doi: 10.1016/j.amjoto.2020.102644
[6] Stankiewicz JA, Wachter B. The endoscopic modified Lothrop procedure for salvage of chronic frontal sinusitis after osteoplastic flap failure[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2003, 129(6): 678-683. doi: 10.1016/j.otohns.2003.07.011
[7] Gibson T, Walker FM. Large osteoma of the frontal sinus; a method of removal to minimize scarring and prevent deformity[J]. Br J Plast Surg, 1951, 4(3): 210-217.
[8] Selva D, White VA, O'Connell JX, et al. Primary bone tumors of the orbit[J]. Surv Ophthalmol, 2004, 49(3): 328-342. doi: 10.1016/j.survophthal.2004.02.011
[9] Cokkeser Y, Bayarogullari H, Kahraman SS. Our experience with the surgical management of paranasal sinus osteomas[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2013, 270(1): 123-128. doi: 10.1007/s00405-012-1981-z
[10] Muderris T, Sevil E, Bercin S, et al. Giant paranasal sinus osteomas: surgical treatment options[J]. J Craniofac Surg, 2014, 25(4): 1287-1291. doi: 10.1097/SCS.0000000000000588
[11] Nguyen S, Nadeau S. Giant Frontal Sinus Osteomas: Demographic, Clinical Presentation, and Management of 10 Cases[J]. Am J Rhinol Allergy, 2019, 33(1): 36-43. doi: 10.1177/1945892418804911
[12] Dell'Aversana Orabona G, Salzano G, Iaconetta G, et al. Facial osteomas: fourteen cases and a review of literature[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2015, 19(10): 1796-1802.
[13] Kamel SG, Kau CH, Wong ME, et al. The role of Cone beam CT in the evaluation and management of a family with Gardner's syndrome[J]. J Craniomaxillofac Surg, 2009, 37(8): 461-468. doi: 10.1016/j.jcms.2009.06.007
[14] Magboul NA, Al-Ahmari MS, Alzahrani MA, et al. Fibro-Osseous Lesion of the Nose and Paranasal Sinus: A Retrospective Study With Literature Review[J]. Cureus, 2022, 14(7): e27229.
[15] Dedushi K, Hyseni F, Musa J, et al. Importance of MRI in the diagnosis of a rare intracranial mucocele associated with frontal paranasal osteoma: Case report and literature review[J]. Radiol Case Rep, 2021, 16(10): 3094-3098. doi: 10.1016/j.radcr.2021.07.038
[16] 李晴晴, 史亚男, 王巍, 等. 额窦黏液囊肿致失明1例[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2022, 36(1): 59-60. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2022.01.013
[17] Sofokleous V, Maragoudakis P, Kyrodimos E, et al. Management of paranasal sinus osteomas: A comprehensive narrative review of the literature and an up-to-date grading system[J]. Am J Otolaryngol, 2021, 42(5): 102644. doi: 10.1016/j.amjoto.2020.102644
[18] Reale G, Ungari C, Riccardi E, et al. Fronto-ethmoidal osteoma. Open treatment[J]. Ann Ital Chir, 2014, 85(3): 214-218.
[19] Karunaratne YG, Gunaratne DA, Floros P, et al. Frontal Sinus Osteoma: From Direct Excision to Endoscopic Removal[J]. J Craniofac Surg, 2019, 30(6): e494. doi: 10.1097/SCS.0000000000005371
[20] Batra PS, Citardi MJ, Lanza DC. Combined endoscopic trephination and endoscopic frontal sinusotomy for management of complex frontal sinus pathology[J]. Am J Rhinol, 2005, 19(5): 435-441. doi: 10.1177/194589240501900503
[21] Watley DC, Mong ER, Rana NA, et al. Surgical Approach to Frontal Sinus Osteoma: A Systematic Review[J]. Am J Rhinol Allergy, 2019, 33(5): 462-469. doi: 10.1177/1945892419839895
[22] Giotakis E, Sofokleous V, Delides A, et al. Gigantic paranasal sinuses osteomas: clinical features, management considerations, and long-term outcomes[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2021, 278(5): 1429-1441. doi: 10.1007/s00405-020-06420-x
[23] Aburas S, Schneider B, Pfaffeneder-Mantai F, et al. Long-term persistent discomfort due to a giant frontoethmoidal osteoma despite complete surgical removal-A case report[J]. Ann Med Surg(Lond), 2022, 78: 103814.
[24] Gotlib T, Kuÿmiñska M, Ko3odziejczyk P, et al. Osteoma involving the olfactory groove: evaluation of the risk of a CSF leak during endoscopic surgery[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2020, 277(8): 2243-2249. doi: 10.1007/s00405-020-05938-4
-

计量
- 文章访问数: 69
- 施引文献: 0



 下载:
下载: