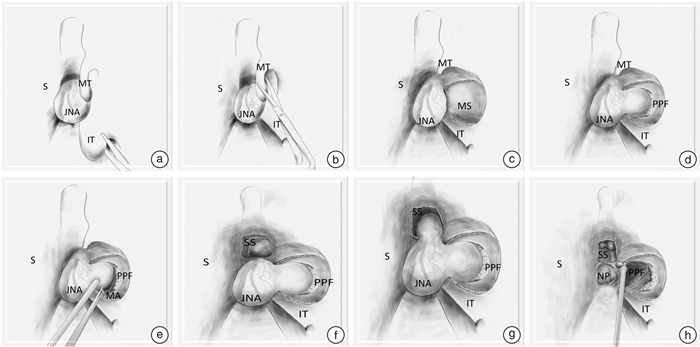
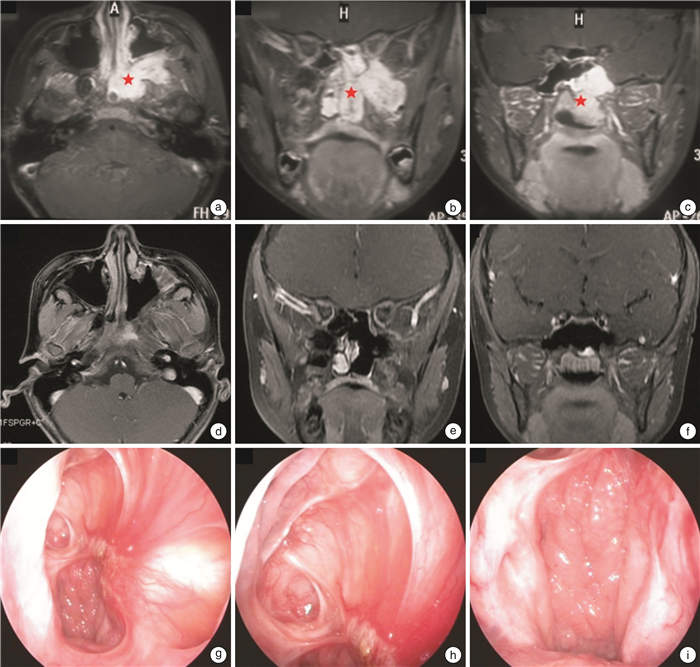
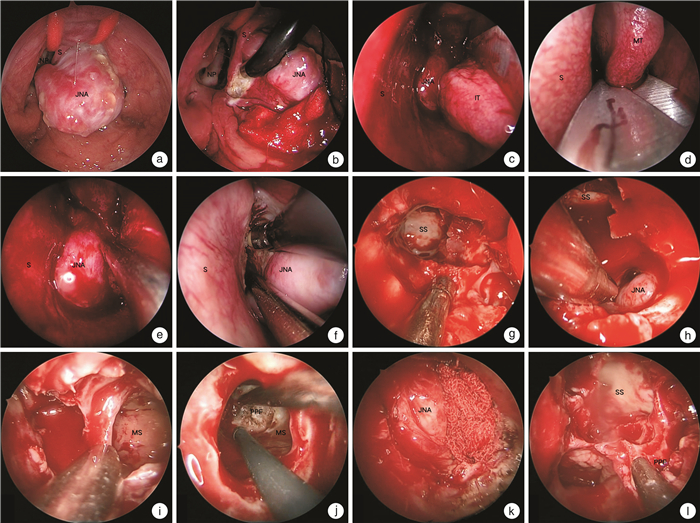
Coblation-assisted endoscopic excision of juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma and outcomes
-
摘要: 目的 总结AndrewⅠ~Ⅲ期鼻咽纤维血管瘤的手术方法和疗效。方法 收集2016年1月-2021年12月手术的鼻咽纤维血管瘤患者12例,Ⅰ期1例,Ⅱ期3例,Ⅲ期8例。采用单独经鼻内镜,或联合经口或柯陆氏入路鼻咽纤维血管瘤切除术。结果 手术未出现严重并发症。术中中位数出血量为200 mL,1例输血。中位数手术时间为110 min。中位数随访时间3年。11例完整切除,术后无复发,1例残留,行二次手术,未再复发残留。结论 通过建立标准化的手术步骤,借助内镜和低温等离子技术,AndrewⅠ~Ⅲ期的鼻咽纤维血管瘤基本可达到快速、安全、完整切除。Abstract: Objective To summarize the procedures and efficacy of surgical treatment for Andrew stage Ⅰ-Ⅲ juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma(JNA).Methods A total of 12 patients with JNA who underwent surgery from 2016 to 2021 were enrolled, including 1 case in stage Ⅰ, 3 cases in stage Ⅱ, and 8 cases in stage Ⅲ. JNA was resected by transnasal endoscopic approach alone, or combined with transoral approach or Caldwell-Luc approach was performed.Results Eleven cases underwent complete resection without recurrence and 1 case had residual tumor. There were no serious complications. The median intraoperative blood loss was 200 mL, and 1 patient received blood transfusion. The median operative time was 110 minutes.Conclusion JNA in Andrew stage Ⅰ-Ⅲ can be quickly and completely resected by standardized surgical procedures using endoscopy and coblation technology.
-
Key words:
- juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma /
- nasal endoscope /
- surgery /
- coblation /
- outcome
-

-
表 1 患者的一般情况、术前影像学检查、手术情况和随访
序号 年龄/岁 分期 CT/MRI最大径/cm CT/MRI示侵犯部位 估计出血量/mL 手术时间/min 住院日/d 随访时间/年 1 20 Ⅲa 6.6 NC/NP/SS/PPF/ITF 750 100 11 6.0 2 12 Ⅱ 3.6 NC/NP/SS/PPF 80 45 14 5.8 3 24 Ⅲa 4.2 NC/NP/PPF/MS/SS/ITF 450 135 12 5.5 4 14 Ⅲa 6.9 NP/NC/ES/SS/PPF/ITF 100 90 13 4.8 5 15 Ⅱ 5.6 NC/NP/SS/ES/PPF 100 60 13 4.5 6 16 Ⅲa 4.4 NC/NP/ SS/PPF/ITF 600 150 18 3.8 7 13 Ⅱ 4.5 NC/NP/PPF 200 180 18 2.5 8 11 Ⅲa 4.7 NC/NP/SS/PPF/OA 500 210 12 2.2 9 18 Ⅲa 6.6 NC/NP/SS/PPF/ITF 250 60 8 1.7 10* 14 Ⅲb 6.5 NP/MS/PPF/IC 800 230 12 1.2 11 19 Ⅰ 3.8 NC/NP 20 35 20 1.0 12 13 Ⅲa 4.2 NC/NP/MS/SS/PPF/ITF 350 120 10 0.5 *为输血和肿瘤残留二次手术患者;NC:鼻腔;NP:鼻咽部;SS:蝶窦;PPF:翼腭窝;ITF:颞下窝;MS:上颌窦;ES:筛窦;OA:眶尖;IC:颅内。 -
[1] Gullane PJ, Davidson J, O'Dwyer T, et al. Juvenile angiofibroma: a review of the literature and a case series report[J]. Laryngoscope, 1992, 102(8): 928-933. doi: 10.1288/00005537-199208000-00014
[2] Lund VJ, Stammberger H, Fokkens WJ, et al. European position paper on the anatomical terminology of the internal nose and paranasal sinuses[J]. Rhinol Suppl, 2014, 24: 1-34.
[3] López F, Triantafyllou A, Snyderman CH, et al. Nasal juvenile angiofibroma: Current perspectives with emphasis on management[J]. Head Neck, 2017, 39(5): 1033-1045. doi: 10.1002/hed.24696
[4] Andrews JC, Fisch U, Valavanis A, et al. The surgical management of extensive nasopharyngeal angiofibromas with the infratemporal fossa approach[J]. Laryngoscope, 1989, 99(4): 429-437. doi: 10.1288/00005537-198904000-00013
[5] Kamel RH. Transnasal endoscopic surgery in juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma[J]. J Laryngol Otol, 1996, 110(10): 962-968. doi: 10.1017/S0022215100135467
[6] 韩德民, 陈学军, 王景礼, 等. 鼻内窥镜引导下鼻咽血管纤维瘤切除术[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 1998, 33(6): 358-360. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YXLT200311049.htm
[7] Boghani Z, Husain Q, Kanumuri VV, et al. Juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma: a systematic review and comparison of endoscopic, endoscopic-assisted, and open resection in 1047 cases[J]. Laryngoscope, 2013, 123(4): 859-869. doi: 10.1002/lary.23843
[8] Ye L, Zhou X, Li J, et al. Coblation-assisted endonasal endoscopic resection of juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma[J]. J Laryngol Otol, 2011, 125(9): 940-944. doi: 10.1017/S0022215111001344
[9] Pei R, Yang M, Wang J, et al. Efficacy and safety of preoperative internal maxillary arterial embolization with gelfoam for nasopharyngeal angiofibroma[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2019, 276(3): 865-869. doi: 10.1007/s00405-018-05276-6
[10] Lutz J, Holtmannspötter M, Flatz W, et al. Preoperative Embolization to Improve the Surgical Management and Outcome of Juvenile Nasopharyngeal Angiofibroma(JNA)in a Single Center: 10-Year Experience[J]. Clin Neuroradiol, 2016, 26(4): 405-413. doi: 10.1007/s00062-015-0374-2
[11] Pamuk AE, Özer S, Süslü AE, et al. Juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma: a single centre's 11-year experience[J]. J Laryngol Otol, 2018, 132(11): 978-983. doi: 10.1017/S0022215118001779
[12] Mohammadi M, Saedi B, Basam A. Effect of embolisation on endoscopic resection of angiofibroma[J]. J Laryngol Otol, 2010, 124(6): 631-635. doi: 10.1017/S0022215109992726
[13] Wael Ibrahim HA, Bao NUI. Juvenile Nasopharyngeal Angiofibroma: Imaging Characteristics and Pre-Operative Embolization[J]. Bahrain Medical Bulletin, 2016, 38: 230-231. doi: 10.12816/0047514
[14] Bignami M, Pietrobon G, Arosio AD, et al. Juvenile Angiofibroma: What Is on Stage?[J]. Laryngoscope, 2022, 132(6): 1160-1165. doi: 10.1002/lary.29801
[15] Reyes C, Bentley H, Gelves JA, et al. Recurrence Rate after Endoscopic vs. Open Approaches for Juvenile Nasopharyngeal Angiofibroma: A Meta-analysis[J]. J Neurol Surg B Skull Base, 2019, 80(6): 577-585. doi: 10.1055/s-0038-1676562
[16] Liu Z, Hua W, Zhang H, et al. The risk factors for residual juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma and the usual residual sites[J]. Am J Otolaryngol, 2019, 40(3): 343-346. doi: 10.1016/j.amjoto.2018.11.010
[17] Jaiswal AS, Kumar R, Thakar A, et al. Plasma ablation-assisted endoscopic excision versus traditional technique of endoscopic excision of juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma[J]. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, 2020, 139: 110410. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2020.110410
[18] Rupa V, Mani SE, Backianathan S, et al. Management and Outcome in Patients with Advanced Juvenile Nasopharyngeal Angiofibroma[J]. J Neurol Surg B Skull Base, 2018, 79(4): 353-360. doi: 10.1055/s-0037-1608658
[19] Abdelwahab M, Overdevest JB, Elmokadem A, et al. Nasopharyngeal Angiofibroma Staging with a Novel Nominal Basis: An 18-Year Study in a Tertiary Center[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2019, 161(2): 352-361. doi: 10.1177/0194599819842155
[20] Szyfter W, Balcerowiak A, Gawęcki W, et al. Juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma-20 years of experience in endoscopic treatment[J]. Otolaryngol Pol, 2021, 75(2): 9-14. doi: 10.5604/01.3001.0014.5220
[21] Lloyd G, Howard D, Phelps P, et al. Juvenile angiofibroma: the lessons of 20 years of modern imaging[J]. J Laryngol Otol, 1999, 113(2): 127-134. doi: 10.1017/S0022215100143373
[22] 许肖杰, 李萍, 金晓朗, 等. 经鼻内镜手术治疗鼻咽纤维血管瘤87例经验总结[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2023, 37(7): 556-561. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2023.07.009
-

计量
- 文章访问数: 101
- 施引文献: 0



 下载:
下载: