Application and efficacy analysis of tympanic cartilage shaping device in endoscopic type Ⅰ tympanoplasty
-
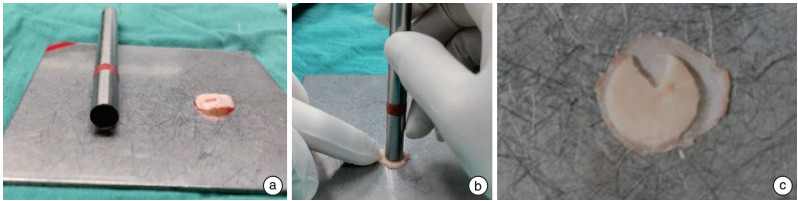
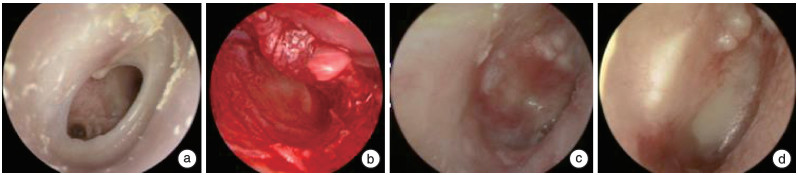
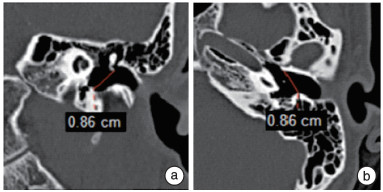
摘要: 目的 研究运用鼓膜软骨塑形器塑形软骨在耳内镜下Ⅰ型鼓室成形术中的可行性和疗效。 方法 通过高分辨率CT(HRCT)影像学测量鼓膜尺寸设计制造一种鼓膜软骨塑形器,用于裁剪和塑形软骨以修补鼓膜。选取2019年8月-2021年10月中南大学湘雅医院耳鼻咽喉头颈外科66例(72耳)慢性化脓性中耳炎患者应用此软骨塑形器在耳内镜下完成Ⅰ型鼓室成形术,术后对鼓膜愈合情况、听力恢复效果等进行观察。术后随访3~24个月,平均9个月。采用SPSS 26.0软件对数据进行统计学分析。 结果 根据影像测量鼓膜紧张部宽为(8.60±0.20) mm、高为(8.64±0.19) mm,设计内径8.60 mm的圆筒状软骨塑形器。用鼓膜软骨塑形器塑形的软骨软骨膜复合物行鼓室成形术后,鼓膜愈合率为100%; 术前平均气骨导差为(23.10±7.33) dB,术后1个月平均气骨导差缩小为(16.80±6.10) dB,差异有统计学意义(t=7.831,P<0.05); 术后3个月平均气骨导差为(14.30±6.40) dB较术后1个月进一步缩小,差异亦有统计学意义(t=6.630,P<0.05)。 结论 鼓膜软骨塑形器塑形软骨在耳内镜下鼓室成形术中应用简便、稳定、可靠,可以减少移植物软骨处理时间,提高手术效率,术后鼓膜形态和功能恢复好。Abstract: Objective To study the feasibility and efficacy of using a tympanic cartilage shaping device in endoscopic type Ⅰ tympanoplasty. Methods A tympanic cartilage shaper was designed and manufactured by measuring tympanic membrane dimensions with HRCT imaging for cutting and shaping cartilage to repair the tympanic membrane. From August 2019 to October 2021, 66 patients(72 ears) with chronic suppurative otitis media in Xiangya Hospital underwent endoscopic type Ⅰ tympanoplasty with this tympanic cartilage shaping device, and were observed the tympanic membrane healing and hearing recovery effect after surgery. Postoperative follow-up ranged from 3-24 months, with an average of 9 months. The data were analyzed by the SPSS 26.0 software. Results According to the imaging measurements, tympanic pars tensa width(8.60±0.20) mm, height(8.64±0.19) mm, design and manufacture a cylindrical cartilage shaping device with inner diameter 8.60 mm. After tympanoplasty, the healing rate of tympanic membrane was 100%; The average air-bone gap before surgery was(23.10±7.33) dB, then(14.30±6.40) dB 1 month after surgery, which were significant reduced compared with those before surgery. The average air-bone gap was(14.30±6.40) dB 3 month after surgery compared with 1 month after surgery, the difference was also statistically significant(t=6.630, P < 0.05). Conclusion The tympanic membrane cartilage shaper shaping cartilage in endoscopic tympanoplasty is simple, stable and reliable, which can reduce the time of graft cartilage processing, improve the efficiency of surgery, and restore the tympanic membrane morphology and function in the postoperative period.
-
Key words:
- tympanic cartilage shaping device /
- tympanoplasty /
- endoscopic surgery /
- cartilage
-

-
[1] Boedts D. Tympanic grafting materials[J]. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Belg, 1995, 49(2): 193-199. http://www.springerlink.com/content/y744683480685n54/
[2] Goodhill V. Tragal perichondrium and cartilage in tympanoplasty[J]. Arch Otolaryngol, 1967, 85(5): 480-491. doi: 10.1001/archotol.1967.00760040482004
[3] Yung M. Cartilage tympanoplasty: literature review[J]. J Laryngol Otol, 2008, 122(7): 663-672. doi: 10.1017/S0022215108001813
[4] Klacansky J. Cartilage myringoplasty[J]. Laryngoscope, 2009, 119(11): 2175-2177. doi: 10.1002/lary.20290
[5] 赵一馨, 余力生. 软骨在中耳手术中的应用[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2018, 32(24): 1912-1916. https://lceh.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.1001-1781.2018.24.017
[6] Dornhoffer J. Cartilage tympanoplasty: indications, techniques, and outcomes in a 1, 000-patient series[J]. Laryngoscope, 2003, 113(11): 1844-56. doi: 10.1097/00005537-200311000-00002
[7] Duckert LG, Müller J, Makielski KH, et al. Composite autograft "shield" reconstruction of remnant tympanic membranes[J]. Am J Otol, 1995, 16(1): 21-26.
[8] Gan RZ, Feng B, Sun Q. Three-dimensional finite element modeling of human ear for sound transmission[J]. Ann Biomed Eng, 2004, 32(6): 847-859. doi: 10.1023/B:ABME.0000030260.22737.53
[9] Daphalapurkar NP, Dai C, Gan RZ, et al. Characterization of the linearly viscoelastic behavior of human tympanic membrane by nanoindentation[J]. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater, 2009, 2(1): 82-92. doi: 10.1016/j.jmbbm.2008.05.008
[10] 郝瑾, 陈树斌, 李永新. 软骨鼓室成形术[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2017, 52(4): 316-320.
[11] Tos M. Cartilage tympanoplasty methods: proposal of a classification[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2008, 139(6): 747-758. doi: 10.1016/j.otohns.2008.09.021
[12] Cavaliere M, Mottola G, Rondinelli M, et al. Tragal cartilage in tympanoplasty: anatomic and functional results in 306 cases[J]. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital, 2009, 29(1): 27-32.
[13] Mürbe D, Zahnert T, Bornitz M, et al. Acoustic properties of different cartilage reconstruction techniques of the tympanic membrane[J]. Laryngoscope, 2002, 112(10): 1769-1776. doi: 10.1097/00005537-200210000-00012
[14] Jalali MM, Motasaddi M, Kouhi A, et al. Comparison of cartilage with temporalis fascia tympanoplasty: A meta-analysis of comparative studies[J]. Laryngoscope, 2017, 127(9): 2139-2148. doi: 10.1002/lary.26451
[15] Lajdam GB, Alahmadi RA, Alhakami M, et al. Comparison of temporalis muscle fascia and cartilage grafts for primary type 1 tympanoplasty: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2023, 280(12): 5153-5165. doi: 10.1007/s00405-023-08170-y
-




 下载:
下载: