Prognostic impact of different tumor invasion patterns in the surgical treatment of T3 glottic laryngeal cancer
-
摘要: 目的 研究不同肿瘤扩展模式在T3期声门型喉癌手术治疗中的预后影响。方法 对91例T3期声门型喉癌患者的临床资料进行了回顾性分析。结果 91例患者中,前侵犯58例(63.7%),后侵犯33例(36.3%),后侵犯与环状软骨背板(P < 0.001)、杓状软骨(P=0.001)、声门下(P=0.001)侵犯显著相关。部分喉切除组与全喉切除组生存结局差异无统计学意义;部分喉切除组中前侵犯肿瘤5年无病生存率优于后侵犯肿瘤(HR:4.681,95%CI 1.337~16.393,P=0.016),声门下侵犯与较差的5年局部区域无复发生存率相关(HR:3.931,95%CI 1.054~14.658,P=0.041)。同时,还发现环状软骨背板侵犯是部分喉切除术后发生喉狭窄的独立危险因素(HR:11.67,95%CI 1.89~71.98,P=0.008)。结论 经选择的部分喉切除术较全喉切除术同样能获得良好的肿瘤学结果。后侵犯和声门下侵犯是T3期声门型喉癌部分喉手术复发的独立预后因素,环状软骨背板侵犯与部分喉术后喉狭窄相关。应进一步细分喉癌患者的肿瘤侵犯模式,以选择更为个体化的治疗方案。Abstract: Objective To investigate the prognostic impact of different tumor invasion patterns in the surgical treatment of T3 glottic laryngeal cancer.Methods A retrospective analysis was conducted on the clinical data of 91 patients with T3 glottic laryngeal cancer.Results Among the 91 patients, 58 cases (63.7%) had anterior invasion and 33 cases (36.3%) had posterior invasion. The posterior invasion was significantly correlated with invasions of the dorsal plate of cricoid cartilage (P < 0.001), arytenoid cartilage (P= 0.001), and subglottic region(P = 0.001). There was no statistical difference in survival outcomes between the total laryngectomy group and the partial laryngectomy group. But in the partial laryngectomy group, the 5-year disease-free survival(DFS) of patients with anterior invasive tumors was better than that of patients with posterior invasion tumors (HR: 4.681, 95%CI 1.337-16.393, P=0.016), and subglottic invasion was associated with worse loco-regional recurrence-free survival(LRRFS)(HR: 3.931, 95%CI 1.054-14.658, P=0.041). At the same time, we found that involvement of the dorsal plate of cricoid cartilage was an independent risk factor for postoperative laryngeal stenosis in partial laryngectomy patients (HR: 11.67, 95%CI 1.89-71.98, P=0.008).Conclusion Compared with total laryngectomy, selected partial laryngectomy can also achieve favorable oncological outcomes. Posterior invasion and subglottic extension are independent prognostic factors for recurrence of partial laryngectomy in T3 glottic laryngeal cancer, and the involvement of the dorsal plate of cricoid cartilage is associated with postoperative laryngeal stenosis. The tumor invasion pattern of laryngeal cancer should be further subdivided in order to select a more individualized treatment plan.
-
Key words:
- laryngeal neoplasms /
- neoplasm invasion /
- laryngectomy /
- prognosis
-

-
表 1 91例T3期声门型喉鳞状细胞癌的人口特征
变量 例数(%) 变量 例数(%) 年龄/岁 查尔森指数 < 60 40(44.0) 1 11(12.1) ≥60 51(56.0) 2 24(26.4) 性别 3 33(36.3) 男 91(100.0) 4 21(23.1) 女 0 5 0 吸烟史 6 2(2.2) 是 85(93.4) N分期 否 6(6.6) N0 77(84.6) 饮酒史 N1 11(12.1) 是 65(71.4) N2 3(3.3) 否 26(28.6) N3 0 临床分期 M分期 Ⅲ 88(96.7) M0 91(100.0) Ⅳ 3(3.3) 表 2 不同分组肿瘤前后侵犯特征
例(%) 变量 整个研究人群(n=91) 部分喉(n=55) 全喉(n=36) 前侵犯 后侵犯 P 前侵犯 后侵犯 P 前侵犯 后侵犯 P 例数 58(63.7) 33(36.3) 44(80.0) 11(20.0) 14(38.9) 22(61.1) N分期 0.245 0.558 0.712 N0 51(87.9) 26(78.8) 41(93.2) 9(81.8) 10(71.4) 17(77.3) N+ 7(12.1) 7(21.2) 3(6.8) 2(18.2) 4(28.6) 5(22.7) 颈清类型 0.051 0.832 0.908 单侧 34(58.6) 17(51.5) 28(63.6) 8(72.7) 6(42.9) 9(40.9) 双侧 24(41.4) 16(48.5) 16(36.4) 3(27.3) 8(57.1) 13(59.1) 辅助治疗 0.796 0.176 0.733 否 30(51.7) 18(54.5) 22(50.0) 8(72.7) 8(57.1) 10(45.5) 是 28(48.3) 15(45.5) 22(50.0) 3(27.3) 6(42.9) 12(54.5) 声带固定 0.005 0.001 0.596 否 36(62.1) 9(27.3) 32(72.7) 2(18.2) 4(28.6) 7(31.8) 欠佳 9(15.5) 8(24.2) 5(11.4) 5(45.5) 4(28.6) 3(13.6) 是 13(22.4) 16(48.5) 7(15.9) 4(36.4) 6(42.9) 12(54.5) 环状软骨背板 <0.001 <0.001 0.002 否 56(96.6) 16(48.5) 42(95.5) 5(45.5) 14(100.0) 11(50.0) 是 2(3.4) 17(51.5) 2(4.5) 6(54.5) 0(0) 11(50.0) 杓状软骨 0.001 0.614 0.025 否 56(96.6) 23(69.7) 43(97.7) 11(100.0) 13(92.9) 12(54.5) 是 2(3.4) 10(30.3) 1(2.3) 0 1(7.1) 10(45.5) 会厌前间隙 0.405 0.785 0.755 否 45(77.6) 23(69.7) 36(81.8) 10(90.9) 9(64.3) 13(59.1) 是 13(22.4) 10(30.3) 8(18.2) 1(9.1) 5(35.7) 9(40.9) 声门下 0.001 0.021 0.932 否 41(70.7) 11(33.3) 37(84.1) 5(45.5) 4(28.6) 6(27.3) 是 17(29.3) 22(66.7) 7(15.9) 6(54.5) 10(71.4) 16(72.7) 表 3 部分喉切除组单因素生存分析
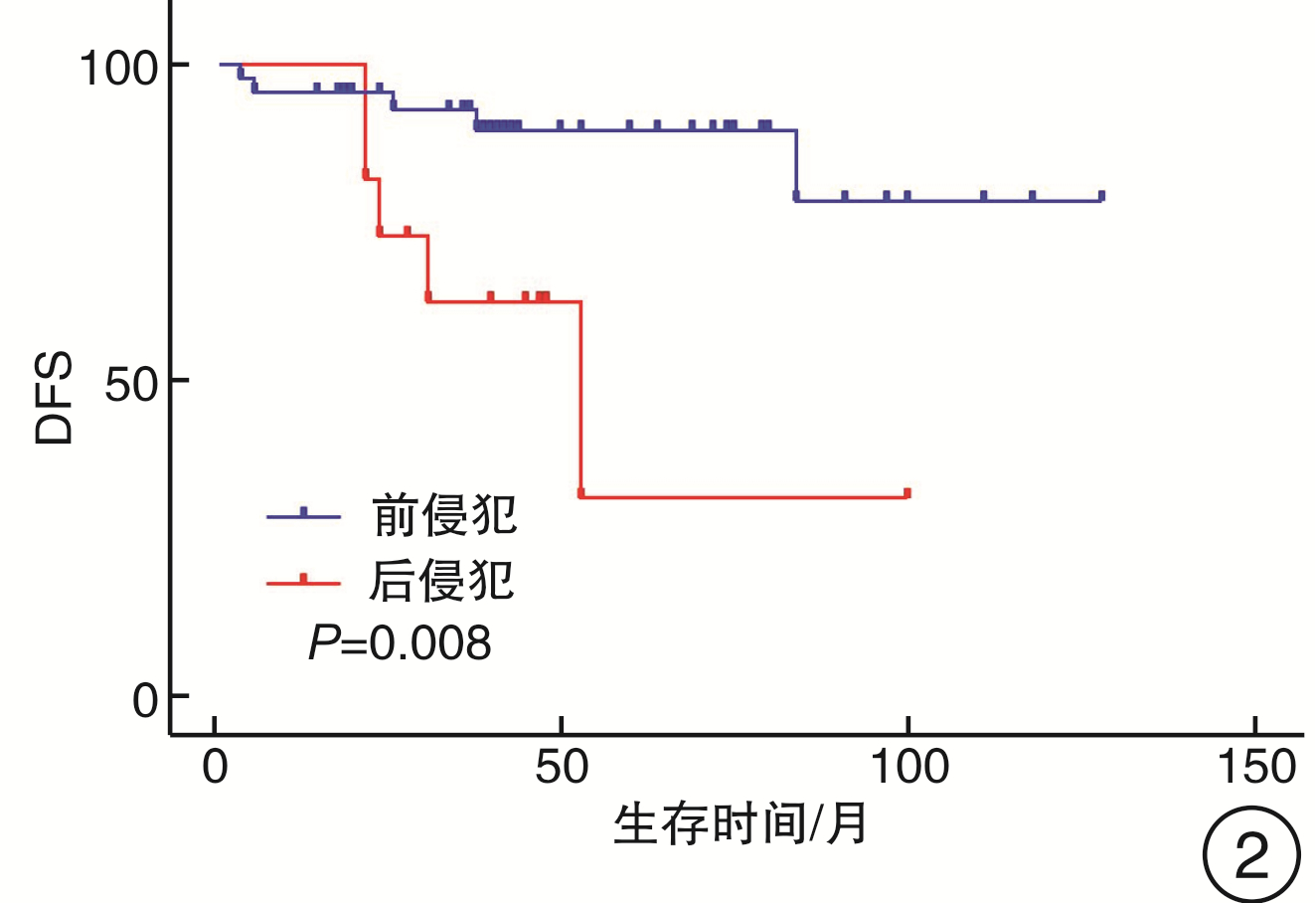
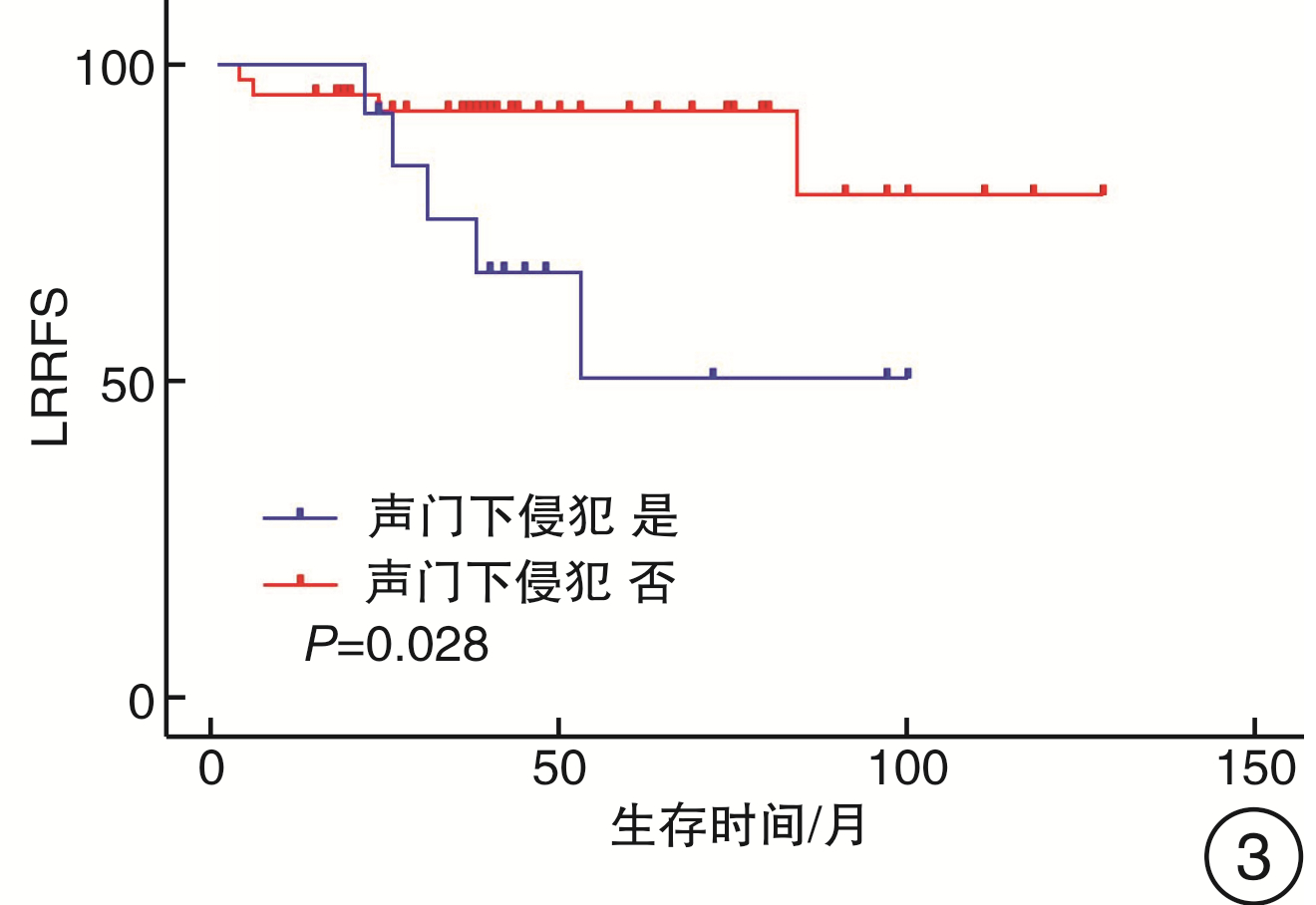
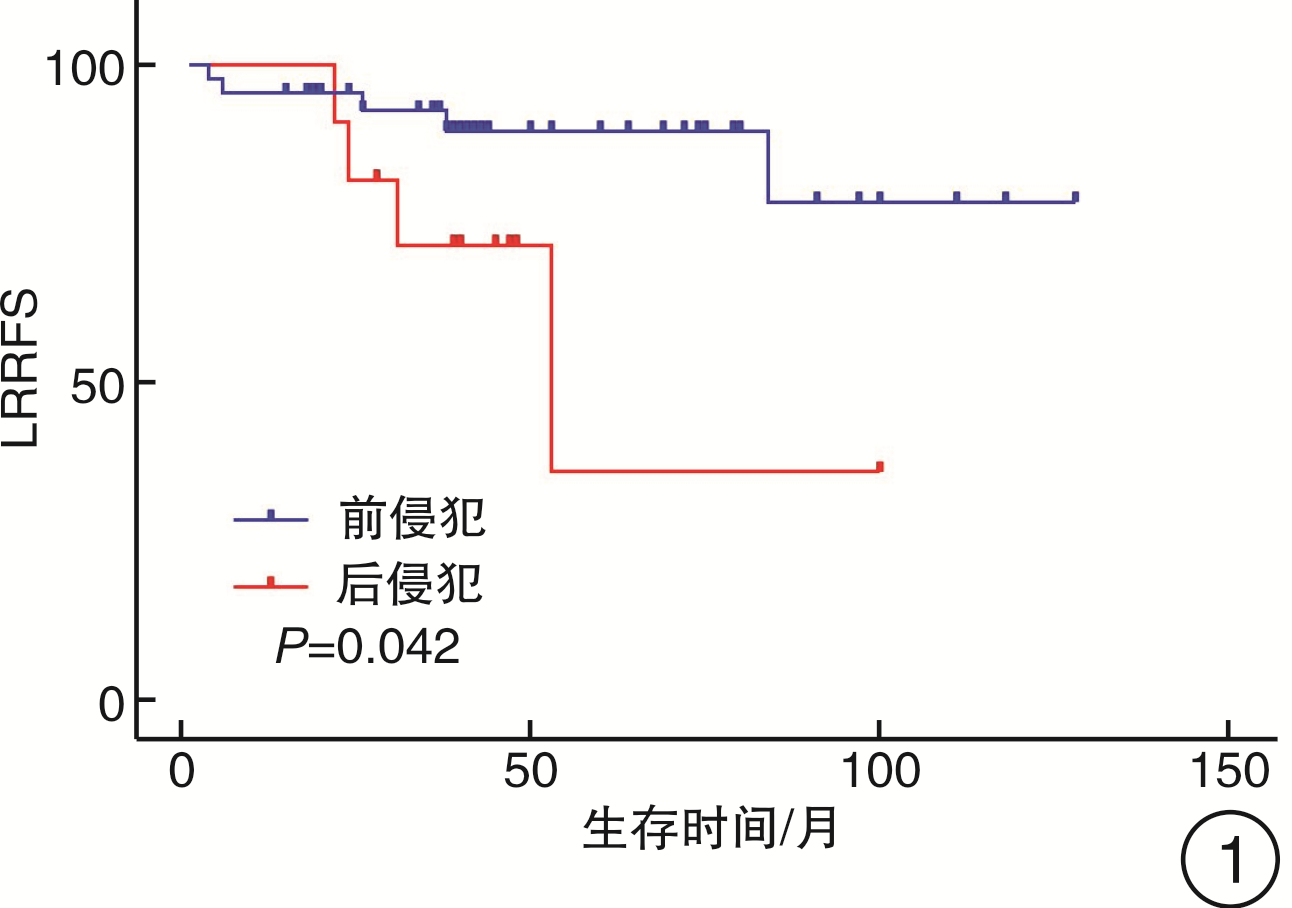
变量 OS/% P DSS/% P LRRFS/% P DFS/% P N分期 0.321 0.577 0.900 0.999 N0 90.8 95.4 81.1 79.0 N+ 100.0 100.0 80.0 80.0 颈清类型 0.981 0.881 0.559 0.762 单侧 90.6 96.7 82.7 79.9 双侧 94.1 94.1 75.7 75.7 辅助治疗 0.573 0.342 0.145 0.082 否 91.6 91.6 76.0 72.1 是 91.6 100.0 89.3 89.3 前后侵犯 0.759 0.455 0.042 0.008 前侵犯 91.9 97.2 89.5 89.5 后侵犯 90.0 90.0 35.8 31.2 环状软骨背板 0.229 0.425 0.132 0.205 否 90.2 95.1 85.1 82.9 是 100.0 100.0 62.5 62.5 杓状软骨 0.514 0.682 0.562 0.548 否 91.4 95.7 80.6 78.7 是 100.0 100.0 100.0 100.0 会厌前间隙 0.38 0.401 0.673 0.569 否 92.2 97.3 79.9 77.6 是 88.9 88.9 88.9 88.9 声门下 0.396 0.334 0.028 0.062 否 89.0 94.4 92.6 89.9 是 100.0 100.0 50.3 50.3 -
[1] Fitzmaurice C, Allen C, Barber RM, et al. Global, Regional, and National Cancer Incidence, Mortality, Years of Life Lost, Years Lived With Disability, and Disability-Adjusted Life-years for 32 Cancer Groups, 1990 to 2015: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study[J]. JAMA Oncol, 2017, 3(4): 524-548. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2016.5688
[2] Divakar P, Davies L. Trends in Incidence and Mortality of Larynx Cancer in the US[J]. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2023, 149(1): 34-41. doi: 10.1001/jamaoto.2022.3636
[3] Megwalu UC, Sikora AG. Survival outcomes in advanced laryngeal cancer[J]. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2014, 140(9): 855-860. doi: 10.1001/jamaoto.2014.1671
[4] Stokes WA, Jones BL, Bhatia S, et al. A comparison of overall survival for patients with T4 larynx cancer treated with surgical versus organ-preservation approaches: A National Cancer Data Base analysis[J]. Cancer, 2017, 123(4): 600-608. doi: 10.1002/cncr.30382
[5] Succo G, Crosetti E, Bertolin A, et al. Treatment for T3 to T4a laryngeal cancer by open partial horizontal laryngectomies: Prognostic impact of different pathologic tumor subcategories[J]. Head Neck, 2018, 40(9): 1897-1908. doi: 10.1002/hed.25176
[6] Gomez Serrano M, Iglesias Moreno MC, Gimeno Hernández J, et al. Cartilage invasion patterns in laryngeal cancer[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2016, 273(7): 1863-1869. doi: 10.1007/s00405-015-3687-5
[7] Del Bon F, Piazza C, Lancini D, et al. Open Partial Horizontal Laryngectomies for T3-T4 Laryngeal Cancer: Prognostic Impact of Anterior vs. Posterior Laryngeal Compartmentalization[J]. Cancers(Basel), 2019, 11(3): 289.
[8] Wolf GT, Fisher SG, Hong WK, et al. Induction chemotherapy plus radiation compared with surgery plus radiation in patients with advanced laryngeal cancer[J]. N Engl J Med, 1991, 324(24): 1685-1690. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199106133242402
[9] Forastiere AA, Ismaila N, Lewin JS, et al. Use of Larynx-Preservation Strategies in the Treatment of Laryngeal Cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology Clinical Practice Guideline Update[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2018, 36(11): 1143-1169. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2017.75.7385
[10] Al-Gilani M, Skillington SA, Kallogjeri D, et al. Surgical vs Nonsurgical Treatment Modalities for T3 Glottic Squamous Cell Carcinoma[J]. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2016, 142(10): 940-946. doi: 10.1001/jamaoto.2016.1609
[11] Zhou J, Zhou L, Tao L, et al. Oncologic outcomes of surgical treatment for T3 glottic laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Head Neck, 2018, 40(8): 1734-1742. doi: 10.1002/hed.25144
[12] Xia X, Zhu YY, Diao WW, et al. Matched-pair analysis of survival in the patients with T3 laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma treated with supracricoid partial laryngectomy or total laryngectomy[J]. Onco Targets Ther, 2018, 11: 7947-7953. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S175358
[13] Campo F, Mazzola F, Bianchi G, et al. Partial laryngectomy for naive pT3N0 laryngeal cancer: Systematic review on oncological outcomes[J]. Head Neck, 2023, 45(1): 243-250. doi: 10.1002/hed.27205
[14] de Vincentiis M, Greco A, Campo F, et al. Open partial horizontal laryngectomy for T2-T3-T4a laryngeal cancer: oncological outcomes and prognostic factors of two Italian hospitals[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2022, 279(6): 2997-3004. doi: 10.1007/s00405-021-07238-x
[15] Mattioli F, Fermi M, Molinari G, et al. pT3 N0 Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Oncologic Outcomes and Prognostic Factors of Surgically Treated Patients[J]. Laryngoscope, 2021, 131(10): 2262-2268. doi: 10.1002/lary.29528
[16] Marchi F, Missale F, Sampieri C, et al. Laryngeal Compartmentalization Does Not Affect the Prognosis of T3-T4 Laryngeal Cancer Treated by Upfront Total Laryngectomy[J]. Cancers(Basel), 2020, 12(8): 2241.
[17] Lucioni M, Lionello M, Guida F, et al. The thyro-cricoarytenoid space(TCAS): clinical and prognostic implications in laryngeal cancer[J]. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital, 2020, 40(2): 106-112. doi: 10.14639/0392-100X-N0373
[18] Lucioni M, Lionello M, Machin P, et al. Sclerosis of the arytenoid cartilage and glottic carcinoma: A clinical-pathological study[J]. Head Neck, 2019, 41(1): 72-78. doi: 10.1002/hed.25372
[19] Succo G, Cirillo S, Bertotto I, et al. Arytenoid Fixation in Laryngeal Cancer: Radiological Pictures and Clinical Correlations with Respect to Conservative Treatments[J]. Cancers(Basel), 2019, 11(3): 360.
[20] Lucioni M, D'Ascanio L, De Nardi E, et al. Management of paratracheal lymph nodes in laryngeal cancer with subglottic involvement[J]. Head Neck, 2018, 40(1): 24-33. doi: 10.1002/hed.24905
[21] Baghel SS, Singhal P, Verma N, et al. Is thyroid excision mandatory with laryngectomy in carcinoma larynx?[J]. BMC Cancer, 2020, 20(1): 700. doi: 10.1186/s12885-020-07205-5
[22] Al-Hakami HA, Al Garni MA, AlSubayea H, et al. The incidence of thyroid gland invasion in advanced laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol, 2021, 87(5): 533-537. doi: 10.1016/j.bjorl.2019.11.003
[23] 李俊虹, 邱轲, 任建君, 等. 进展期喉癌患者甲状腺侵犯概况及其预后价值[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2023, 37(1): 72-75, 80. https://lceh.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2023.01.014
[24] Elicin O, Giger R. Comparison of Current Surgical and Non-Surgical Treatment Strategies for Early and Locally Advanced Stage Glottic Laryngeal Cancer and Their Outcome[J]. Cancers(Basel), 2020, 12(3): 732.
[25] Graboyes EM, Zhan KY, Garrett-Mayer E, et al. Effect of postoperative radiotherapy on survival for surgically managed pT3N0 and pT4aN0 laryngeal cancer: Analysis of the National Cancer Data Base[J]. Cancer, 2017, 123(12): 2248-2257. doi: 10.1002/cncr.30586
[26] Luna-Ortiz K, Reynoso-Noveron N, Zacarias-Ramon LC, et al. Supracricoid Partial Laryngectomy With and Without Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Glottic Cancer[J]. Laryngoscope, 2022, 132(1): 156-162. doi: 10.1002/lary.29713
[27] Sanabria A, Shah JP, Medina JE, et al. Incidence of Occult Lymph Node Metastasis in Primary Larynx Squamous Cell Carcinoma, by Subsite, T Classification and Neck Level: A Systematic Review[J]. Cancers(Basel), 2020, 12(4): 1059.
-




 下载:
下载: