Differential expression of NEDD8 in different pathological types of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps
-
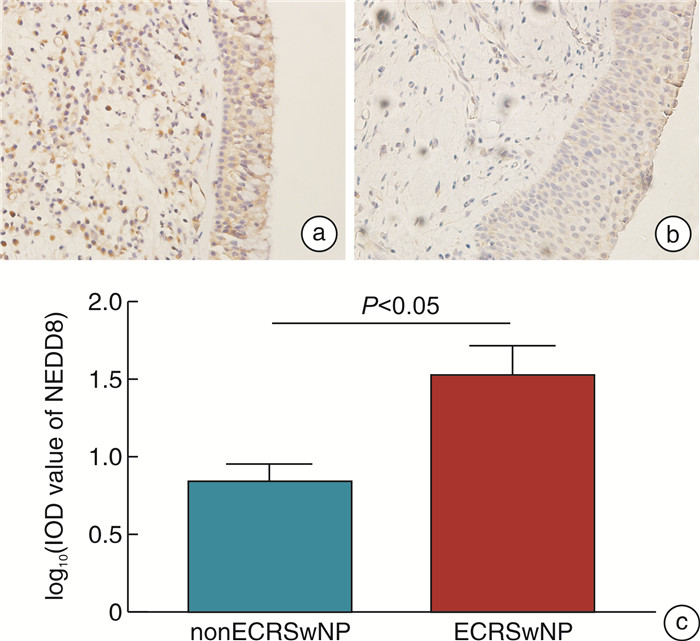
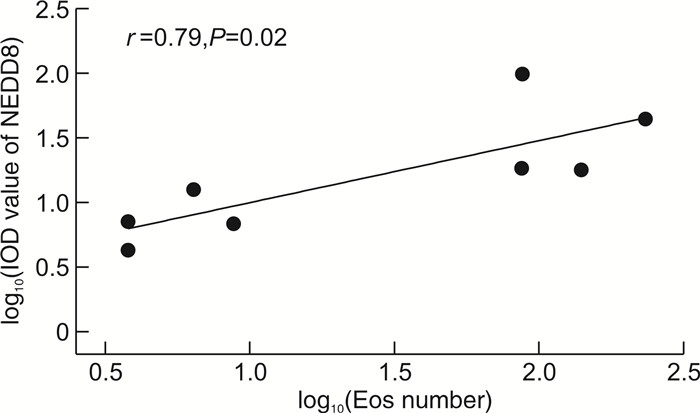
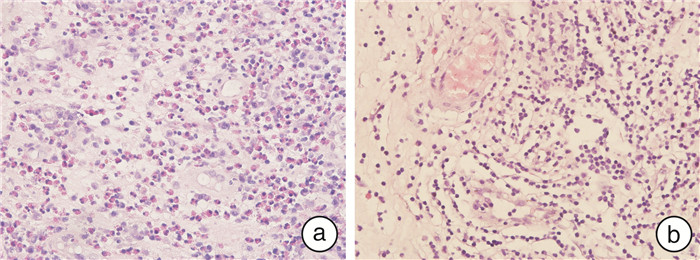
摘要: 目的 分析不同病理类型的慢性鼻窦炎伴鼻息肉(chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps,CRSwNP)患者的鼻息肉组织中神经前体细胞表达发育下调蛋白8(Neural precursor cell-expressed developmentally downregulated 8,NEDD8)表达水平差异。方法 使用在北京同仁医院耳鼻咽喉头颈外科因慢性鼻窦炎行鼻内镜手术的患者标本。利用苏木精-伊红染色检测鼻息肉组织中的嗜酸性粒细胞数量,并根据鼻息肉组织中嗜酸性粒细胞的数量对CRSwNP患者进行分组,采用免疫组织化学法检测分析鼻息肉组织中的NEDD8蛋白表达水平。结果 嗜酸性粒细胞型慢性鼻窦炎伴鼻息肉患者鼻息肉中NEDD8蛋白表达水平显著高于非嗜酸性粒细胞型慢性鼻窦炎伴鼻息肉患者(P<0.05)。NEDD8蛋白表达水平和鼻息肉组织中嗜酸性粒细胞数量呈显著正相关(r=0.79,P=0.02)。结论 不同病理类型的CRSwNP患者NEDD8蛋白表达存在差异。
-
关键词:
- 神经前体细胞表达发育下调蛋白8 /
- 鼻窦炎 /
- 鼻息肉 /
- 嗜酸性粒细胞
Abstract: Objective To analyze the differential expression of neural precursor cell-expressed developmentally downregulated 8(NEDD8) protein in nasal polyp tissues of patients with different pathological types of chronic rhinorhinosinusitis with nasal polyps(CRSwNP).Methods All specimens were obtained from the specimen library of Beijing Tongren Hospital, and were all patients who underwent nasal endoscopic surgery for chronic rhinosinusitis in Beijing Tongren Hospital. Hematoxylin-eosin staining(HE) was used to detect the number of eosinophils in nasal polyps, and CRSwNP patients were grouped according to the number of eosinophils in nasal polyps, immunohistochemistry was used to detect and analyze the expression level of NEDD8 protein in nasal polyps.Results The expression level of NEDD8 protein in nasal polyps of patients with eosinophilic chronic rhinorhinosinusitis with nasal polyps was significantly higher than that of patients with non-eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis and nasal polyps(P<0.05). In addition, there was a significant positive correlation between the expression level of NEDD8 protein and the number of eosinophils in nasal polyp tissue(r=0.79, P=0.02).Conclusion There are differences in the expression of NEDD8 protein in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis and nasal polyps of different pathological types. -

-
[1] Fokkens WJ, Lund VJ, Hopkins C, et al. European position paper on rhinosinusitis and nasal polyps 2020[J]. Rhinology, 2020, 58(Suppl S29): 1-464.
[2] Stevens WW, Schleimer RP, Kern RC. Chronic ehinosinusitis with nasal polyps[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract, 2016, 4(4): 565-572. doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2016.04.012
[3] 王梦瑶, 王斌全, 王磊, 等. 慢性鼻窦炎患者生存质量研究进展[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2021, 35(1): 84-87. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2021.01.022
[4] Lou H, Meng Y, Piao Y, et al. Cellular phenotyping of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps[J]. Rhinology, 2016, 54(2): 150-159. doi: 10.4193/Rhino15.271
[5] 赵传亮, 余少卿. 难治性慢性鼻窦炎的临床研究进展[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2020, 34(1): 19-22. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.1001-1781.2020.01.005
[6] Baek K, Krist DT, Prabu JR, et al. NEDD8 nucleates a multivalent cullin-RING-UBE2D ubiquitin ligation assembly[J]. Nature, 2020, 578(7795): 461-466. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2000-y
[7] Jiang X, Chen ZJ. The role of ubiquitylation in immune defence and pathogen evasion[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2011, 12(1): 35-48.
[8] Hao R, Song Y, Li R, et al. MLN4924 protects against interleukin-17A-induced pulmonary inflammation by disrupting ACT1-mediated signaling[J]. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol, 2019, 316(6): L1070-L1080. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00349.2018
[9] Xie P, Yang JP, Cao Y, et al. Promoting tumorigenesis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma, NEDD8 serves as a potential theranostic target[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2017, 8(6): e2834. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2017.195
[10] Wang X, Chen C, Vuong D, et al. Pharmacologic targeting of Nedd8-activating enzyme reinvigorates T-cell responses in lymphoid neoplasia[J]. Leukemia, 2023, 37(6): 1324-1335. doi: 10.1038/s41375-023-01889-x
[11] Godbersen JC, Humphries LA, Danilova OV, et al. The Nedd8-activating enzyme inhibitor MLN4924 thwarts microenvironment-driven NF-κB activation and induces apoptosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2014, 20(6): 1576-1589. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-0987
[12] Chang FM, Reyna SM, Granados JC, et al. Inhibition of neddylation represses lipopolysaccharide-induced proinflammatory cytokine production in macrophage cells[J]. J Biol Chem, 2012, 287(42): 35756-35767. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.397703
[13] Majolée J, Pronk MCA, Jim KK, et al. CSN5 inhibition triggers inflammatory signaling and Rho/ROCK-dependent loss of endothelial integrity[J]. Sci Rep, 2019, 9(1): 8131. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-44595-4
[14] Yan B, Lou H, Wang Y, et al. Epithelium-derived cystatin SN enhances eosinophil activation and infiltration through IL-5 in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2019, 144(2): 455-469. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2019.03.026
[15] Lou H, Meng Y, Piao Y, et al. Predictive significance of tissue eosinophilia for nasal polyp recurrence in the Chinese population[J]. Am J Rhinol Allergy, 2015, 29(5): 350-356. doi: 10.2500/ajra.2015.29.4231
[16] Yang W, Zhang Z, Li L, et al. ZNF582 overexpression restrains the progression of clear cell renal cell carcinoma by enhancing the binding of TJP2 and ERK2 and inhibiting ERK2 phosphorylation[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2023, 14(3): 212. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-05750-y
[17] Cao C, Shi Y, Zhang X, et al. Cholesterol-induced LRP3 downregulation promotes cartilage degeneration in osteoarthritis by targeting Syndecan-4[J]. Nat Commun, 2022, 13(1): 7139. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-34830-4
[18] Bachert C, Marple B, Schlosser RJ, et al. Adult chronic rhinosinusitis[J]. Nat Rev Dis Primers, 2020, 6(1): 86. doi: 10.1038/s41572-020-00218-1
[19] Kato A, Schleimer RP, Bleier BS. Mechanisms and pathogenesis of chronic rhinosinusitis[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2022, 149(5): 1491-1503. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2022.02.016
[20] Bankova LG, Barrett NA. Epithelial cell function and remodeling in nasal polyposis[J]. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol, 2020, 124(4): 333-341. doi: 10.1016/j.anai.2020.01.018
[21] Karamanos NK, Theocharis AD, Piperigkou Z, et al. A guide to the composition and functions of the extracellular matrix[J]. FEBS J, 2021, 288(24): 6850-6912. doi: 10.1111/febs.15776
[22] Bassiouni W, Ali M, Schulz R. Multifunctional intracellular matrix metalloproteinases: implications in disease[J]. FEBS J, 2021, 288(24): 7162-7182 doi: 10.1111/febs.15701
[23] Kostamo K, Toskala E, Tervahartiala T, et al. Role of matrix metalloproteinases in chronic rhinosinusitis[J]. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol, 2008, 8(1): 21-27. doi: 10.1097/ACI.0b013e3282f3f461
[24] Li X, Huang J, Chen X, et al. IL-19 induced by IL-13/IL-17A in the nasal epithelium of patients with chronic rhinosinusitis upregulates MMP-9 expression via ERK/NF-κB signaling pathway[J]. Clin Transl Allergy, 2021, 11(1): e12003. doi: 10.1002/clt2.12003
[25] Wang M, Wang X, Zhang N, et al. Association of periostin expression with eosinophilic inflammation in nasal polyps[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2015, 136(6): 1700-1703. e1709. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2015.09.005
[26] Kim DW, Kulka M, Jo A, et al. Cross-talk between human mast cells and epithelial cells by IgE-mediated periostin production in eosinophilic nasal polyps[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2017, 139(5): 1692-1695. e1696. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2016.09.026
[27] Liu K, Chen K, Zhang Q, et al. TRAF6 neddylation drives inflammatory arthritis by increasing NF-κB activation[J]. Lab Invest, 2019, 99(4): 528-538. doi: 10.1038/s41374-018-0175-8
[28] Segovia JA, Tsai SY, Chang TH, et al. Nedd8 regulates inflammasome-dependent caspase-1 activation[J]. Mol Cell Biol, 2015, 35(3): 582-597. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00775-14
[29] Vitetta L, Briskey D, Hayes E, et al. A review of the pharmacobiotic regulation of gastrointestinal inflammation by probiotics, commensal bacteria and prebiotics[J]. Inflammopharmacology, 2012, 20(5): 251-266. doi: 10.1007/s10787-012-0126-8
[30] Muraoka H, Yoshimura C, Kawabata R, et al. Activity of TAS4464, a novel NEDD8 activating enzyme E1 inhibitor, against multiple myeloma via inactivation of nuclear factor κB pathways[J]. Cancer Sci, 2019, 110(12): 3802-3810. doi: 10.1111/cas.14209
[31] Lawrence T. The nuclear factor NF-kappaB pathway in inflammation[J]. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol, 2009, 1(6): a001651.
[32] Jeong HD, Kim JH, Kwon GE, et al. Expression of polyamine oxidase in fibroblasts induces MMP-1 and decreases the integrity of extracellular matrix[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23(18): 10487. doi: 10.3390/ijms231810487
[33] Bond M, Chase AJ, Baker AH, et al. Inhibition of transcription factor NF-kappaB reduces matrix metalloproteinase-1, -3 and -9 production by vascular smooth muscle cells[J]. Cardiovasc Res, 2001, 50(3): 556-565. doi: 10.1016/S0008-6363(01)00220-6
[34] Nagumo Y, Kandori S, Tanuma K, et al. PLD1 promotes tumor invasion by regulation of MMP-13 expression via NF-κB signaling in bladder cancer[J]. Cancer Lett, 2021, 511: 15-25. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2021.04.014
[35] de Almeida L, Thode H, Eslambolchi Y, et al. Matrix metalloproteinases: from molecular mechanisms to physiology, pathophysiology, and pharmacology[J]. Pharmacol Rev, 2022, 74(3): 712-768.
[36] Jabłońska-Trypuc ' A, Matejczyk M, Rosochacki S. Matrix metalloproteinases(MMPs), the main extracellular matrix(ECM)enzymes in collagen degradation, as a target for anticancer drugs[J]. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem, 2016, 31(sup1): 177-183. doi: 10.3109/14756366.2016.1161620
[37] Shi LL, Ma J, Deng YK, et al. Cold-inducible RNA-binding protein contributes to tissue remodeling in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps[J]. Allergy, 2021, 76(2): 497-509. doi: 10.1111/all.14287
-




 下载:
下载: