-
摘要: 目的 探讨颈部肿瘤手术中对于颈动脉病变的手术处理方式。方法 回顾性分析兰州市第一人民医院肿瘤外科2010年3月-2020年5月治疗的5例颈部肿瘤手术中颈动脉处理的临床资料。分别采用颈动脉切除并结扎,肿瘤受累动脉切除并血管重建,肿瘤剥离及颈动脉破裂口修补的手术方式。结果 5例患者均手术成功。其中颈动脉结扎1例患者术后出现间歇头晕、对侧肢体肌力下降。其余患者无神经系统并发症。颈部低度恶性肌纤维母细胞肉瘤1例患者术后8个月出现肺转移。甲状腺乳头状癌颈淋巴结转移1例患者术后24个月出现肺转移。结论 目前临床处理病变颈动脉的手术方式有颈动脉切除并结扎,单纯肿瘤剥离,肿瘤受侵动脉切除并血管重建以及介入治疗。每种手术方式都有各自的优缺点,具体选择何种治疗方法取决于患者的具体病情、医师临床经验及设备条件。Abstract: Objective To investigate surgical treatment of carotid artery diseases in neck tumor surgery.Methods A retrospective analysis of the clinical data on carotid artery treatment was conducted in the five cases of neck tumor surgeries treated at Department of Surgical Oncology, the First Peoples Hospital of Lanzhou from March 2010 to May 2020. Surgical methods, including carotid artery resection and ligation, tumor-involved artery resection and vascular reconstruction, and tumor peeling and carotid rupture repairing were used, respectively.Results Five cases were successfully operated on. One case of carotid artery ligation was followed by intermittent dizziness and decreased contra-lateral limb strength after the surgery. The remaining patients exhibited no neurological complications. A patient with cervical low-grade myofibroblastoma developed into lung metastases 8 months after the surgery. Another patient with cervical lymph node metastases in papillary thyroid cancer developed into lung metastases 24 months after the surgery.Conclusion Currently, surgical methods for clinical treatment of diseased carotid arteries include carotid artery resection and ligation, simple tumor peeling, tumor invasion artery resection and vascular reconstruction, and interventional therapy. Each surgical method has its own advantages and disadvantages. Therefore, the choice of treatment depends on the patient's specific conditions, physician's clinical experience, and the equipment available.
-
Key words:
- neck tumor /
- carotid artery /
- surgical procedure
-

-
[1] 王劲松, 李勇辉, 姚陈, 等. 颈动脉体瘤切除术后神经并发症的高危因素分析[J]. 中华普通外科杂志, 2020, 35(3): 191-194. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn113855-20191223-00762
[2] Yu Q, Wang P, Shi H, Luo J. Carotid artery and jugular vein invasion of oral-maxillofacial and neck malignant tumors: diagnostic value of computed tomography[J]. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod, 2003, 96(3): 368-372. doi: 10.1016/S1079-2104(03)00366-4
[3] Lodder WL, Lange CA, Teertstra HJ, et al. Value of MR and CT Imaging for Assessment of Internal Carotid Artery Encasement in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma[J]. Int J Surg Oncol, 2013, 2013: 968758.
[4] Chitose SI, Ono T, Shin B, et al. Use of dynamic MRI during swallowing to assess carotid artery invasion by neck metastasis[J]. Head Neck, 2018, 40(2): 330-337. doi: 10.1002/hed.24960
[5] Sivakumaran R, Mohamed AZ, Akhunbay-Fudge CY, et al. Internal Carotid Artery Test Balloon Occlusion Using Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography Scan in the Management of Complex Cerebral Aneurysms and Skull Base Tumors: A 20-Year Review[J]. World Neurosurg, 2020, 139: e32-e37. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2020.03.006
[6] Zhengang X, Colbert S, Brennan PA, et al. Surgical management of metastases that involve the carotid artery in cases of primary squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck[J]. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2013, 42(4): 440-445. doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2012.11.015
[7] Manzoor NF, Russell JO, Bricker A, et al. Impact of surgical resection on survival in patients with advanced head and neck cancer involving the carotid artery[J]. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2013, 139(11): 1219-1225. doi: 10.1001/jamaoto.2013.4917
[8] Krol E, Brandt CT, Blakeslee-Carter J, et al. Vascular interventions in head and neck cancer patients as a marker of poor survival[J]. J Vasc Surg, 2019, 69(1): 181-189. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2018.04.058
[9] Back LJJ, Aro K, Tapiovaara L, et al. Sacrifice and extracranial reconstruction of the common or internal carotid artery in advanced head and neck carcinoma: Review and meta-analysis[J]. Head Neck, 2018, 40(6): 1305-1320. doi: 10.1002/hed.25093
[10] Illuminati G, Schneider F, Minni A, et al. Resection of recurrent neck cancer with carotid artery replacement[J]. J Vasc Surg, 2016, 63(5): 1272-1278. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2015.10.098
[11] 喻国宁, 朱敏辉, 郑宏良, 等. 颈内动脉切除一期血管重建术治疗晚期颈部转移癌的疗效分析[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2020, 34(10): 901-905. https://lceh.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2020.10.009
[12] 孙宇, 王晓雷, 张烨, 等. 大隐静脉重建颈动脉在头颈部恶性肿瘤手术治疗中的应用[J]. 中华解剖与临床杂志, 2020, 25(2): 129-134. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn101202-20191107-00336
[13] 孙滨, 邓先兆, 康杰, 等. 多学科联合诊治累及颈总动脉的晚期甲状腺恶性肿瘤[J]. 中华内分泌外科杂志, 2017, 11(4): 274-277. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1674-6090.2017.04.004
[14] 孙宇, 王晓雷. 头颈部肿瘤侵犯颈动脉治疗的研究进展[J]. 山东医药, 2020, 60(1): 105-108. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-266X.2020.01.029
[15] Suarez C, Fernández-Alvarez V, Hamoir M, et al. Carotid blowout syndrome: modern trends in management[J]. Cancer Manag Res, 2018, 10: 5617-5628. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S180164
[16] Chatani S, Sato Y, Murata S, et al. Transarterial Embolization for Bleeding in Patients with Head and Neck Cancer: Who Benefits?[J]. Laryngoscope, 2021, 131(11): E2777-E2783.
[17] 孙伟, 李肖. 头颈部肿瘤难治性出血的急诊介入栓塞治疗[J]. 中华肿瘤杂志, 2021, 43(2): 224-227.
[18] Wilseck Z, Savastano L, Chaudhary N, et al. Delayed extrusion of embolic coils into the airway after embolization of an external carotid artery pseudoaneurysm[J]. J Neurointerv Surg, 2018, 10(7): e18.
-

| 引用本文: | 王梓年, 李静喆, 何玉奇, 等. 颈部肿瘤手术涉及颈动脉的治疗体会[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2023, 37(7): 570-574. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2023.07.011 |
| Citation: | WANG Zinian, LI Jingzhe, HE Yuqi, et al. Treatment experience of neck tumor surgeries involving carotid artery[J]. J Clin Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2023, 37(7): 570-574. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2023.07.011 |
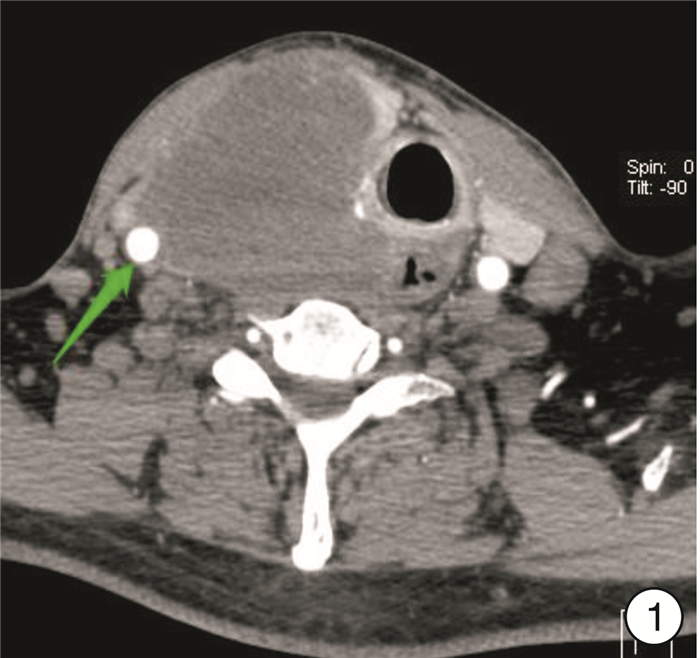
- Figure 1.
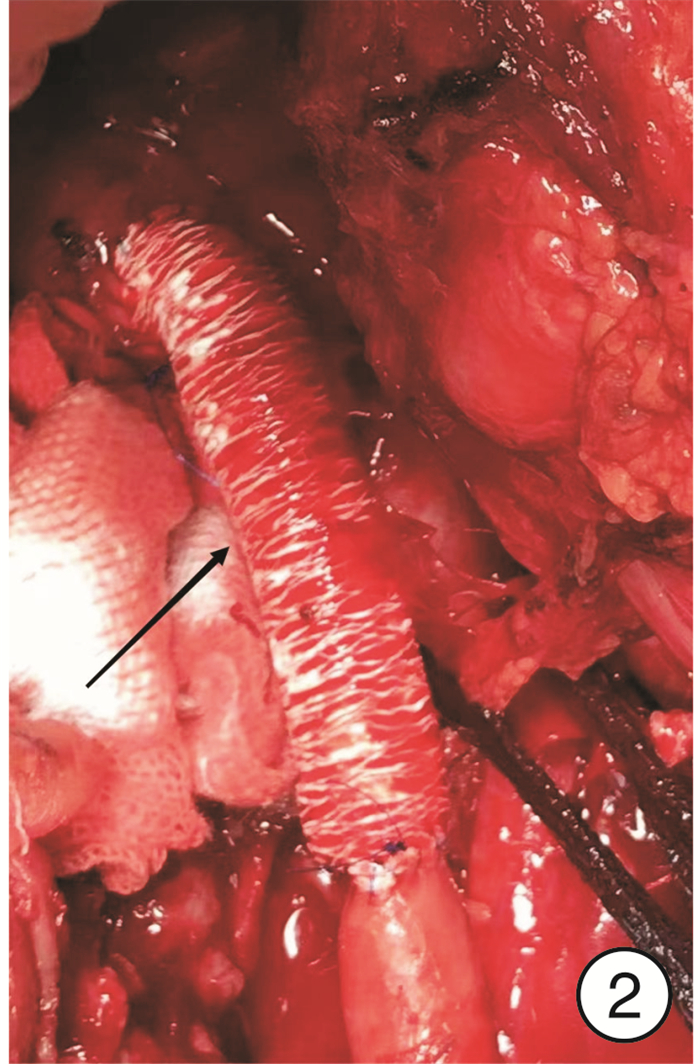
- Figure 2.
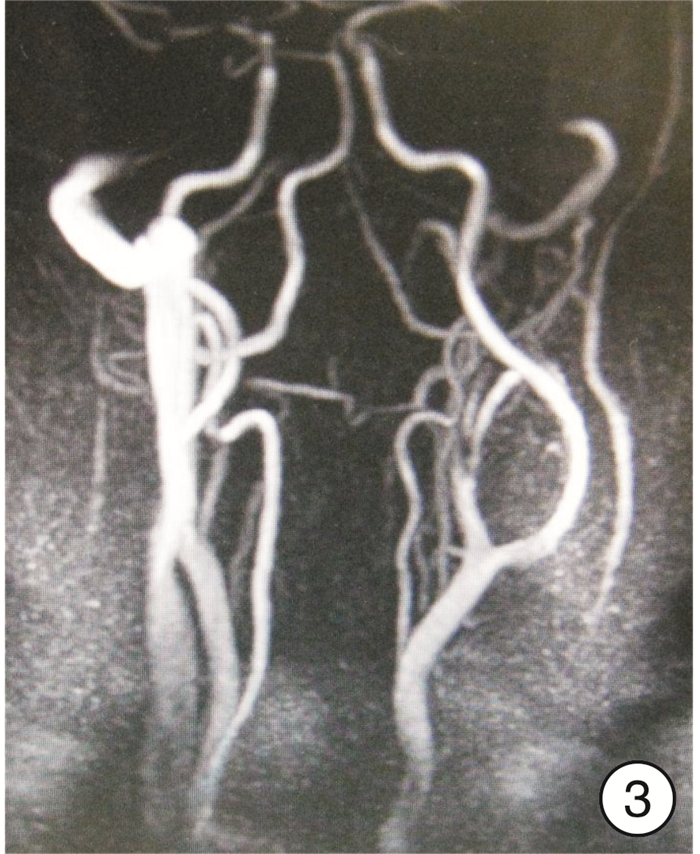
- Figure 3.
- Figure 4.



 下载:
下载: