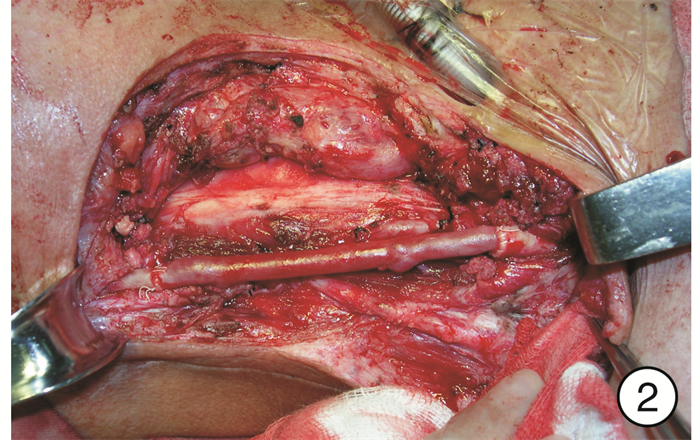
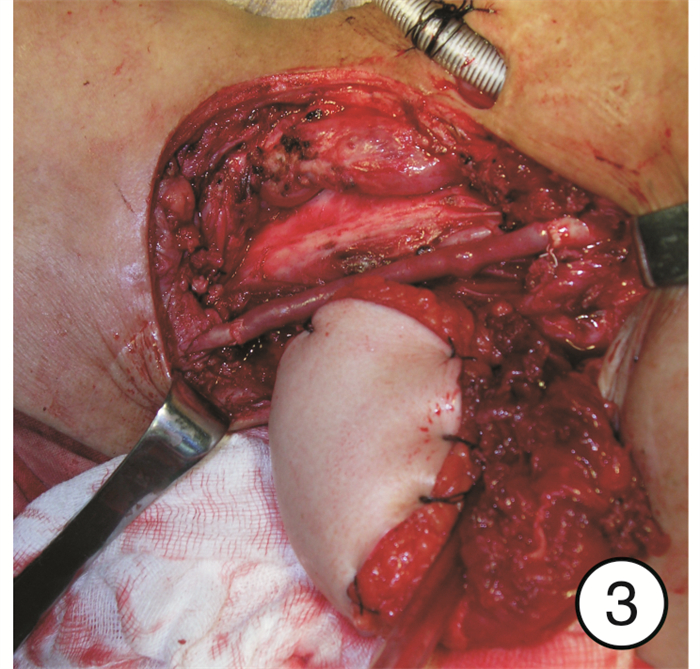
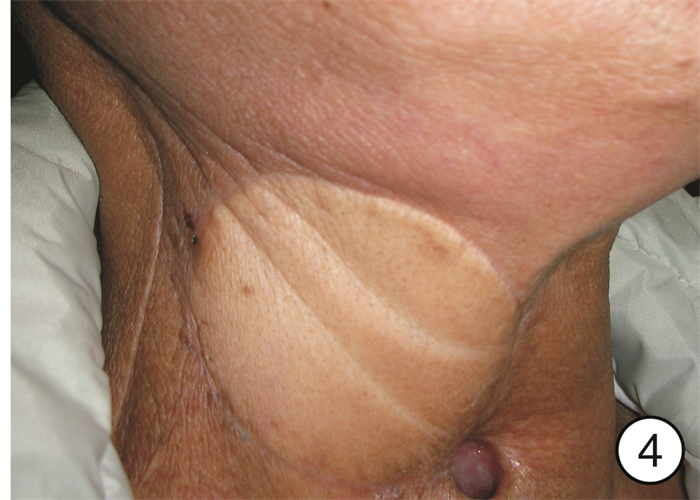
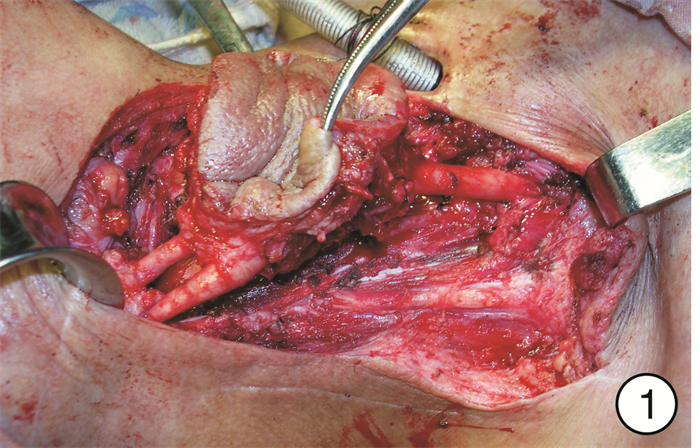
Analysis of the effect of one-stage revascularization with internal carotid artery resection on cervical metastatic carcinoma in advanced head and neck carcinomas
-
摘要: 目的 分析颈内动脉切除一期血管重建术在晚期颈部转移癌中的治疗效果。方法 回顾性分析接受颈内动脉切除一期血管重建术的21例晚期头颈部恶性肿瘤患者的临床资料, 其中下咽癌11例, 喉癌5例, 外耳道癌2例, 中耳癌1例, 腮腺癌2例。所有患者术前均接受了CT、MRI、DSA等检查, 发现颈内动脉管壁已受肿瘤侵犯, 并有不同程度的管腔狭窄。一期重建材料中, 18例患者使用了自体大隐静脉、3例患者使用了人工血管进行血管重建。重建成功后均使用带蒂或游离组织瓣对吻合部位进行保护。所有患者术后视情况进行了放疗、化疗等综合治疗。结果 21例患者中, 接受颈段颈内动脉重建术16例, 颅底段颈内动脉重建术5例。20例患者一期重建成功, 术后未发生因血管重建所致的中枢神经系统并发症, 术后影像学显示重建血管再通良好, 成功率达95.2%(20/21);1例患者经多次重建血管失败后, 最终接受颈内动脉结扎术。所有患者术后1年生存率为90.5%, 3年生存率为40.4%。结论 在颈部转移癌侵犯颈内动脉的晚期头颈部恶性肿瘤患者中, 根治性切除肿瘤的同时一期血管重建可以获得良好的治疗效果。仔细的术前评估、熟练的血管吻合技术、充分的风险评估与防范是手术成功的关键。Abstract: Objective To analyze the therapeutic effect of internal carotid artery resection and one-stage revascularization in advanced cervical metastatic carcinoma.Method Twenty-one patients with advanced head and neck malignant tumors who underwent internal carotid artery resection and one-stage revascularization were analyzed retrospectively. Among those, 11 patients suffered from hypo-pharyngeal carcinomas, 5 laryngeal carcinomas, 2 external auditory carcinomas, 1 middle ear carcinoma, and 2 parotid gland carcinomas. All patients received CT, MRI, DSA and other examinations before operation. It was found that all the internal carotid artery walls had been invaded by tumors, and there were different degrees of lumen stenosis. Autogenous saphenous vein grafts were used in 18 cases; artificial vessels were used in 3 cases. After revascularization, pedicled or free flaps were used to protect the anastomotic areas. All patients were treated with radiotherapy and chemotherapy according to different situations.Result Among the 21 cases, 16 cases underwent reconstruction of cervical segment internal carotid and 5 cases were the skull base segment internal carotid. Twenty patients were successfully reconstructed in the first stage, and no vascular reconstruction-related nervous system complications occurred after operations. Postoperative imaging showed that the reconstructed blood vessels were well recanalized, with a success rate of 95.2%(20/21). Only 1 case received ligation of internal carotid artery after the failure of vascular reconstruction. Among all the cases, the 1-year survival rate and 3-year survival rate were 90.5% and 40.4%, respectively.Conclusion In patients with advanced head and neck malignant tumors with cervical metastatic cancer invading the internal carotid artery, one-stage revascularization after radical resection of the tumor and the internal carotid can achieve good therapeutic effect. Careful preoperative evaluation, proficient vascular anastomosis technology, adequate risk assessment and prevention are the key to the success of the operations.
-
Key words:
- head and neck neoplasms /
- internal carotid artery /
- revascularization
-

-
[1] Elbers JBW, Veldhuis LI, Bhairosing PA, et al. Salvage surgery for advanced stage head and neck squamous cell carcinoma following radiotherapy or chemoradiation[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2019, 276(3): 647-655. doi: 10.1007/s00405-019-05292-0
[2] Elbers JBW, Al-Mamgani A, van den Brekel MWM, et al. Salvage surgery for recurrence after radiotherapy for squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2019, 160(6): 1023-1033. doi: 10.1177/0194599818818443
[3] Taguchi T, Nishimura G, Takahashi M, et al. Treatment results and prognostic factors for advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck treated with salvage surgery after concurrent chemoradiotherapy[J]. Int J Clin Oncol, 2016, 21(5): 869-874. doi: 10.1007/s10147-016-0964-2
[4] Mourad M, Saman M, Stroman D, et al. Carotid artery sacrifice and reconstruction in the setting of advanced head and neck cancer[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2015, 153(2): 225-230. doi: 10.1177/0194599815586719
[5] Ricco JB, Illuminati G, Belmonte R. Resection of recurrent neck cancers with replacement of the carotid artery[J]. J Med Vasc, 2017, 42(5): 282-289.
[6] Illuminati G, Schneider F, Minni A, et al. Resection of recurrent neck cancer with carotid artery replacement[J]. J Vasc Surg, 2016, 63(5): 1272-1278. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2015.10.098
[7] Verhaeghe JL, Montagne S, Belotzerkovski I, et al. 〔Is carotid resection a valuable option in advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinomas〕[J]. Bull Cancer, 2003, 90(7): 607-613.
[8] Loré JM Jr, Boulos EJ. Resection and reconstruction of the carotid artery in metastatic squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Am J Surg, 1981, 142(4): 437-442. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(81)90370-6
[9] Relic A, Scheich M, Stapf J, et al. Salvage surgery after induction chemotherapy with paclitaxel/cisplatin and primary radiotherapy for advanced laryngeal and hypopharyngeal carcinomas[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2009, 266(11): 1799-1805. doi: 10.1007/s00405-009-0946-3
[10] Biller HF, Urken M, Lawson W, et al. Carotid artery resection and bypass for neck carcinoma[J]. Laryngoscope, 1988, 98(2): 181-183.
[11] Osgood MJ, Hocking KM, Voskresensky IV, et al. Surgical vein graft preparation promotes cellular dysfunction, oxidative stress, and intimal hyperplasia in human saphenous vein[J]. J Vasc Surg, 2014, 60(1): 202-211. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2013.06.004
[12] Yokoyama J, Yazawa M, Yoshimoto H. A novel procedure for reconstruction utilizing superficial femoral vein grafts following en bloc resection of carotid artery and head and neck malignant tumours[J]. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg, 2014, 19(2): 175-177. doi: 10.1093/icvts/ivu112
[13] 朱敏辉, 郑宏良, 陈世彩, 等. 侧颅底恶性肿瘤累及颈内动脉的外科处理与血管重建[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2012, 47(12): 1008-1012. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-0860.2012.12.009
[14] Nishinari K, Krutman M, Valentim L A, et al. Surgical outcomes of carotid resection and saphenous vein graft revascularization in patients with advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Ann Vasc Surg, 2014, 28(8): 1878-1884. doi: 10.1016/j.avsg.2014.07.011
-




 下载:
下载: