-
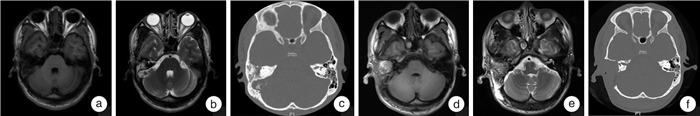
摘要: 目的 分析颞骨罕见恶性肿瘤的临床表现及治疗效果。方法 回顾性分析我院2014年3月-2020年12月收治的4例颞骨罕见恶性肿瘤资料:包括软骨肉瘤2例、纤维肉瘤1例、内淋巴囊乳头状腺癌1例;男3例,女1例,年龄28~56岁;常见症状包括听力下降、面瘫、耳鸣、头痛等;所有患者均经颞骨CT及头颅MRI评估;采用颞骨次全切除术或颞下窝入路切除肿瘤,术后辅助放疗。结果 1例软骨肉瘤患者术后无瘤生存75个月,另1例为术后复发再次手术,无瘤生存112个月;1例纤维肉瘤术后辅以放疗,无瘤生存28个月;1例内淋巴囊乳头状腺癌术后辅以放疗,无瘤生存63个月。结论 颞骨罕见恶性肿瘤发病率极低,病变位置隐蔽,症状不典型,临床上要提高警惕、争取早诊早治。治疗方式以手术切除为主,切缘阳性及无法完全切除者可辅助放疗。Abstract: Objective To analyze the diagnosis, treatment and prognosis of patients with rare malignant tumors of the temporal bone.Methods Four cases of rare temporal bone malignant tumors in our hospital between March 2014 and December 2020 were reviewed, including two cases of chondrosarcoma, one case of fibrosarcoma and one case of endolymphatic cystic papillary adenocarcinoma. There were three males and one female, ages between 28 and 56 years at the time of surgery. Common symptoms included hearing loss, facioplegia, tinnitus, and headache. All patients underwent imaging examinations to evaluate the extent of the lesions. Tumors were removed by subtotal temporal bone resection or infratemporal fossa approach, and postoperative adjuvant radiotherapy was applied if necessary.Results One of the two chondrosarcoma patients was cured by complete resection of the tumor for 75 months, the other one recurred after the first excision of the tumor and underwent infratemporal fossa approach resection of skull base mass again with no recurrence found yet for 112 months. One patient with fibrosarcoma survived for 28 months after surgery with a positive margin and post-operative radiotherapy. One patient with endolymphatic cystic papillary adenocarcinoma recurred 12 months after subtotal lithotomy, and underwent subtotal temporal bone resection again, combined with radiotherapy. No recurrence was found for 63 months.Conclusion The incidence of rare temporal bone malignant tumors is extremely low, the location is hidden, and the symptoms are atypical. Attention should be paid for early detection and early treatment. Surgical resection is the main treatment, and radiotherapy can be supplemented in the advanced stage or with a positive margin.
-
Key words:
- temporal bone /
- malignancies /
- surgery /
- radiotherapy /
- prognosis
-

-
表 1 颞骨罕见恶性肿瘤患者治疗及结果
例序 年龄/岁 性别 临床表现 病理 病变范围 术式 放疗 生存时间/月 预后 1 54 男 视力下降、头痛、头晕、听力下降 纤维肉瘤 乳突、乙状窦 颞骨次全切除术 放疗 28 无瘤生存 2 28 男 面瘫、耳垂下方肿物 高分化软骨肉瘤 中耳、乙状窦、腮腺 颞下窝A型入路颅底肿物切除术 无 75 无瘤生存 3 56 女 耳闷、听力下降、耳鸣、耳溢液、耳出血、头痛 内淋巴囊侵袭性乳头状腺癌 中耳、外耳道、岩尖 颞骨次全切除术 放疗 63 患者第一次于我院行岩骨次全切除术,术后1年发现左侧外耳道肉芽,再次行颞骨次全切除术(术中见肿瘤破坏外耳道前壁累及颞下颌关节囊,累及面神经水平段),术后病理证实面神经未累及,现无瘤生存 4 39 男 面瘫、耳痛、耳鸣、听力下降 软骨肉瘤 中耳、颈静脉孔区 颞下窝A型入路颅底肿物切除术 无 112 患者第一次于外院行颞骨次全切除术,术后5年复发,于我院行颞下窝A型入路颅底肿物切除术,现无瘤生存 -
[1] Madsen AR, Gundgaard MG, Hoff CM, et al. Cancer of the external auditory canal and middle ear in Denmark from 1992 to 2001[J]. Head Neck, 2008, 30(10): 1332-1338. doi: 10.1002/hed.20877
[2] Acharya PP, Sarma D, McKinnon B. Trends of temporal bone cancer: SEER database[J]. Am J Otolaryngol, 2020, 41(1): 102297. doi: 10.1016/j.amjoto.2019.102297
[3] Moody SA, Hirsch BE, Myers EN. Squamous cell carcinoma of the external auditory canal: an evaluation of a staging system[J]. Am J Otol, 2000, 21(4): 582-588. http://www.researchgate.net/profile/Stephanie_Moody/publication/12406544_Moody_SA_Hirsch_BE_Myers_EN_Squamous_cell_carcinoma_of_the_external_auditory_canal_an_evaluation_of_a_staging_system/links/564cc37308ae4988a7a3dfe2.pdf
[4] Rosenberg AE, Nielsen GP, Keel SB, et al. Chondrosarcoma of the base of the skull: a clinicopathologic study of 200 cases with emphasis on its distinction from chordoma[J]. Am J Surg Pathol, 1999, 23(11): 1370-1378. doi: 10.1097/00000478-199911000-00007
[5] Oghalai JS, Buxbaum JL, Jackler RK, et al. Skull base chondrosarcoma originating from the petroclival junction[J]. Otol Neurotol, 2005, 26(5): 1052-1060. doi: 10.1097/01.mao.0000185076.65822.f7
[6] Zhang K, Qu P, Zhang E, et al. Primary temporal bone chondrosarcoma: experience with 10 cases[J]. Acta Otolaryngol, 2019, 139(10): 837-842. doi: 10.1080/00016489.2019.1641220
[7] 张伶, 王振常, 赵鹏飞. 颞骨岩乳交界区软骨肉瘤影像表现1例[J]. 中国医学影像技术, 2017, 33(4): 642. doi: 10.13929/j.1003-3289.201610077
[8] 余宗艳, 邵秋菊, 齐宇红, 等. 颞骨软骨肉瘤1例并文献分析[J]. 山西医科大学学报, 2017, 48(12): 1316-1317. doi: 10.13753/j.issn.1007-6611.2017.12.027
[9] 包亚军, 王荣光, 刘永义. 颞骨软骨肉瘤2例[J]. 中国耳鼻咽喉头颈外科, 2000, 7(3): 174. doi: 10.16066/j.1672-7002.2000.03.023
[10] 吴彦桥, 尚耀东, 王梦寅, 等. 颞骨巨大软骨肉瘤一例[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉科杂志, 1997, 32(5): 267-267. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHEB705.003.htm
[11] Chowhan AK, Rukmangadha N, Patnayak R, et al. Myxoid chondrosarcoma of sphenoid bone[J]. J Neurosci Rural Pract, 2012, 3(3): 395-398. doi: 10.4103/0976-3147.102641
[12] Nomura T, Kobayashi T, Shingaki S, et al. A case of chondrosarcoma arising in the temporomandibular joint[J]. Case Rep Otolaryngol, 2015, 2015: 832532.
[13] Lee K, Kim SH, Kim SM, et al. Temporomandibular joint chondrosarcoma: a case report and literature review[J]. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2016, 42(5): 288-294. doi: 10.5125/jkaoms.2016.42.5.288
[14] 曲斌. 左颞骨软骨肉瘤1例[J]. 中外健康文摘, 2010, 7(36): 175-175. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XHON200206023.htm
[15] Thebaud E, Mezel A, Leroy X, et al. Fibrosarcoma in children and adolescents: different entities for the same name[J]. Bull Cancer, 2012, 99(6): 715-722. doi: 10.1684/bdc.2012.1597
[16] Greager JA, Reichard K, Campana JP, et al. Fibrosarcoma of the head and neck[J]. Am J Surg, 1994, 167(4): 437-439. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(94)90131-7
[17] Lucas C, Leclere JC, Mornet E, et al. Intralabyrinthine sporadic endolymphatic sac tumour[J]. Eur Ann Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Dis, 2018, 135(2): 123-125. doi: 10.1016/j.anorl.2017.10.002
[18] Schnack DT, Kiss K, Hansen S, et al. Sporadic Endolymphatic Sac Tumor-A Very Rare Cause of Hearing Loss, Tinnitus, and Dizziness[J]. J Int Adv Otol, 2017, 13(2): 289-291. doi: 10.5152/iao.2017.2237
[19] Kim WY, Kaelin WG. Role of VHL gene mutation in human cancer[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2004, 22(24): 4991-5004. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000037386311810_0638.html
[20] Kaelin WG Jr. The von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor gene and kidney cancer[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2004, 10(18 Pt 2): 6290S-6295S. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000037317351510_e1cf.html
[21] 龚侃, 王江宜. 中国von Hippel-Lindau病诊治专家共识[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2018, 98(28): 2220-2224. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHYC200401001.htm
[22] Lonser RR, Kim HJ, Butman JA, et al. Tumors of the endolymphatic sac in von Hippel-Lindau disease[J]. N Engl J Med, 2004, 350(24): 2481-2486.
[23] Bausch B, Wellner U, Peyre M, et al. Characterization of endolymphatic sac tumors and von Hippel-Lindau disease in the International Endolymphatic Sac Tumor Registry[J]. Head Neck, 2016, 38 Suppl 1: E673-E679. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/hed.24067
[24] Mendenhall WM, Suarez C, Skalova A, et al. Current Treatment of Endolymphatic Sac Tumor of the Temporal Bone[J]. Adv Ther, 2018, 35(7): 887-898. http://www.xueshufan.com/publication/2809617311
[25] 袁婷, 沙炎, 洪汝建, 等. 内淋巴囊肿瘤的CT和MRI影像学表现分析[J]. 中华放射学杂志, 2021, 55(5): 507-511. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XYXZ202303009.htm
[26] Kim HJ, Hagan M, Butman JA, et al. Surgical resection of endolymphatic sac tumors in von Hippel-Lindau disease: findings, results, and indications[J]. Laryngoscope, 2013, 123(2): 477-483. http://www.sbccp.org.br/arquivos/LG-2013-02/LG-2013-02-Surgical-Resection.pdf
-

| 引用本文: | 高立明, 张文阳, 夏寅. 颞骨罕见恶性肿瘤的诊疗分析[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2023, 37(6): 469-472. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2023.06.012 |
| Citation: | GAO Liming, ZHANG Wenyang, XIA Yin. Diagnosis and treatment of rare malignant temporal bone tumors[J]. J Clin Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2023, 37(6): 469-472. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2023.06.012 |
- Figure 1.



 下载:
下载: