Characteristics of allergen component in dust mite-induced allergic rhinitis patients
-
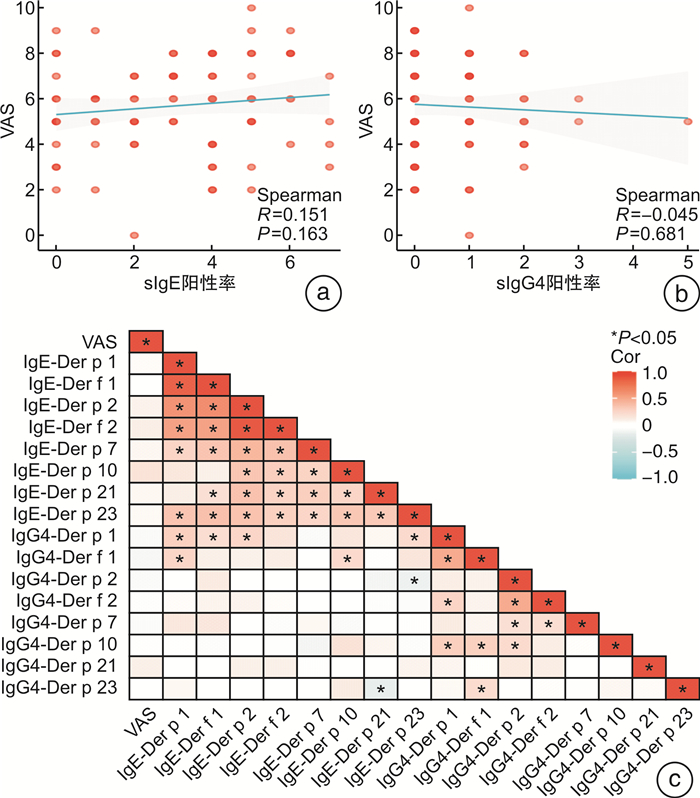
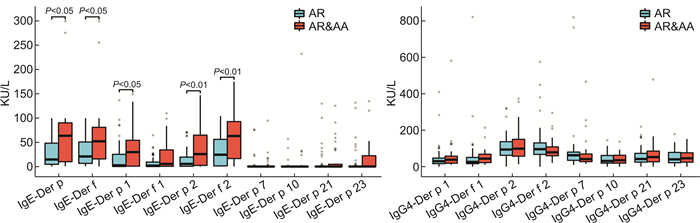
摘要: 目的 探讨尘螨(dust mite,DM)诱发的变应性鼻炎(allergic rhinitis,AR)患者的组分特征,为临床AR的诊断与治疗提供参考。方法 纳入2021—2022年就诊于华中科技大学同济医院过敏反应科就诊的由DM诱发的伴或不伴过敏性哮喘(allergic asthma,AA)的AR患者,记录患者年龄、性别以及症状的视觉模拟量表(visual analogue scale,VAS),采用蛋白芯片法检测粉尘螨(Dermatophagoides farinae,Der f)组分Der f1,Der f2及户尘螨(Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus,Der p)组分Der p1,Der p2,Der p7,Der p10,Der p21,Der p23的sIgE与sIgG4,观察患者的组分致敏特征,评估各组分与VAS的相关性以及不同疾病谱之间的组分差别。结果 纳入87例DM诱发的AR患者,其中AR伴AA(AR&AA)患者占42.5%,其VAS评分明显高于单独AR患者(6.38±1.95 vs 5.25±1.85,P=0.009 8),DM组分致敏率排前的依次为:Der p2(82.8%),Der f2(81.6%),Der p1(74.7%),Der f1(70.1%),Der p23(35.6%);组分sIgG4阳性率排前的依次为:Der p2(21.8%),Der f2(13.8%),Der p21(8.0%),Der p7(6.9%)。组分sIgE、sIgG4浓度以及阳性数量与VAS评分无相关性,但抗体浓度之间分别存在广泛的正相关。与单独AR比较,AR&AA患者Der p[60.5(7.2~91.1) vs 14.0(4.8~45.1),P=0.02],Der f[49.8(15.7~81.6) vs 21.3(7.0~50.2),P=0.04]以及组分Der p1[27.2(0.7~51.5) vs 2.6(0.2~24.9),P=0.02]、Der p2[20.0(1.4~60.6) vs 5.5(0.6~19.1),P=0.004]、Der f2[58.9(16.0~89.2) vs 23.4(0.9~56.8),P=0.009]的sIgE更高,AR&AA患者组分Der p1(70.3% vs 48.0%,P=0.038)与Der p23(27.0% vs 14.0%,P=0.039)的sIgE≥3级的比例更高。结论 DM的第1,2及23组分是DM致敏的AR患者的主要组分,多重组分致敏以及各组分sIgE、sIgG4水平与AR的严重程度无相关性,与AR比较,AR&AA患者的第1,2及23组分的sIgE水平更高。Abstract: Objective To investigate the characteristics of allergen component in dust mite(DM) -induced allergic rhinitis(AR) patients, and provide reference for the diagnosis and treatment of AR.Methods DM-induced AR patients with or without allergic asthma(AA) who visited the Allergy Department of Tongji Hospital, Huazhong University of Science and Technology between 2021 and 2022 were enrolled. Patients'age, gender, and visual analog scale(VAS) for symptoms were recorded. sIgE and sIgG4 levels of allergen components such as Der f1, Der f2, Der p1, Der p2, Der p7, Der p10, Der p21, and Der p23 were detected using a protein chip method. The sensitization characteristics of the allergen components in the patients were observed, and the correlation between sIgE, sIgG of each component and VAS as well as the component differences between AR and AR with AA(AR&AA) were evaluated.Results A total of 87 DM-induced AR patients were enrolled, with 42.5% of them were AR&AA, their VAS scores were significantly higher than those of AR patients(6.38±1.95 vs 5.25±1.85, P=0.009 8). The order of sensitization rates for DM components was as follows: Der p2(82.8%), Der f2(81.6%), Der p1(74.7%), Der f1(70.1%), and Der p23(35.6%). The order of positive rates for sIgG4 was: Der p2(21.8%), Der f2(13.8%), Der p21(8.0%), and Der p7(6.9%). There were no correlation between the sIgE, sIgG4 levels or positive numbers of components and VAS scores, but there were positive correlations between sIgE, sIgG4 concentrations of components. Compared with AR patients, AR&AA patients had higher levels of sIgE for Der p(60.5[7.2-91.1]vs 14.0[4.8-45.1], P=0.02), Der f(49.8[15.7-81.6]vs 21.3[7.0-50.2], P=0.04), Der p1(27.2[0.7-51.5]vs 2.6[0.2-24.9], P=0.02), Der p2(20.0[1.4-60.6]vs 5.5[0.6-19.1], P=0.004), and Der f2(58.9[16.0-89.2]vs 23.4[0.9-56.8], P=0.009), and a higher proportion of AR with AA patients had sIgE levels of Der p1(70.3% vs 48.0%, P=0.038) and Der p23(27.0% vs 14.0%, P=0.039) that were ≥3 grades.Conclusion Der p1/f1, Der p2/f3, and Der p23 are the major components of DM sensitized AR patients. Multiple component sensitization and sIgE, sIgG4 levels of each component are not correlated with the severity of AR. The sIgE levels of the Der p1/f1, Der p2/f3, and Der p23 components in AR&AA patients are higher than AR.
-
Key words:
- allergic rhinitis /
- asthma /
- allergen /
- dust mite /
- component
-

-
表 1 患者的基本资料及各组分sIgE、sIgG4的阳性率
项目 例数(n=87) 百分率/% 性别 男/女 53/34 60.9/39.1 年龄 < 18岁/≥18岁 49/38 56.3/43.7 诊断 AR/AR&AA 50/37 57.4/42.5 尘螨组分IgE阳性 Der p1 65 74.7 Der f1 61 70.1 Der p2 72 82.8 Der f2 71 81.6 Der p7 24 27.6 Der p10 11 12.6 Der p21 28 32.2 Der p23 31 35.6 尘螨组分IgG4阳性 Der p1 3 3.4 Der f1 4 4.6 Der p2 19 21.8 Der f2 12 13.8 Der p7 6 6.9 Der p10 0 0 Der p21 7 8.0 Der p23 1 1.1 表 2 AR及AR&AA患者组分sIgE与sIgG4阳性率比较
例(%) AR组 AR&AS组 P 尘螨组分IgE阳性 Der p1 36(72.0) 29(78.4) 0.499 Der f1 33(66.0) 28(75.7) 0.330 Der p2 39(78.0) 33(89.2) 0.172 Der f2 39(78.0) 32(86.5) 0.312 Der p7 12(24.0) 12(32.4) 0.384 Der p10 6(12.0) 5(13.5) 0.541 Der p21 16(32.0) 12(32.4) 0.966 Der p23 14(28.0) 17(45.9) 0.084 尘螨组分IgE≥3级 Der p1 24(48.0) 26(70.3) 0.038 Der f1 19(38.0) 21(56.8) 0.083 Der p2 27(54.0) 27(73.0) 0.071 Der f2 36(72.0) 28(75.7) 0.701 Der p7 4(8.0) 6(16.2) 0.313 Der p10 3(6.0) 4(10.8) 0.452 Der p21 7(14.0) 10(27.0) 0.130 Der p23 8(16.0) 13(35.1) 0.039 尘螨组分IgG4阳性 Der p1 2(4.0) 1(2.7) 0.613 Der f1 2(4.0) 2(5.4) 0.571 Der p2 10(20.0) 9(24.3) 0.629 Der f2 8(16.0) 4(10.8) 0.488 Der p7 3(6.0) 3(8.1) 0.510 Der p10 0 0 Der p21 5(10) 2(5.4) 0.359 Der p23 1(2.0) 0 0.575 -
[1] Okamoto Y, Fujieda S, Okano M, et al. House dust mite sublingual tablet is effective and safe in patients with allergic rhinitis[J]. Allergy, 2017, 72(3): 435-443 doi: 10.1111/all.12996
[2] Brzozowska A, Woicka-Kolejwa K, Jerzynska J, et al. Allergic Rhinitis and House Dust Mite Sensitization Determine Persistence of Asthma in Children[J]. Indian J Pediatr, 2022, 89(7): 673-681. doi: 10.1007/s12098-021-04052-5
[3] Wang W, Wang J, Song G, et al. Environmental and sensitization variations among asthma and/or rhinitis patients between 2008 and 2018 in China[J]. Clin Transl Allergy, 2022, 12(2): e12116. http://www.socolar.com/Article/Index?aid=200328620744&jid=200000062512
[4] Wang J, Wu Y, Li J, et al. Eight Aeroallergen Skin Extracts May Be the Optimal Panel for Allergic Rhinitis Patients in Central China[J]. Int Arch Allergy Immunol, 2017, 173(4): 193-198. doi: 10.1159/000479429
[5] Chen H, Li J, Cheng L, et al. China Consensus Document on Allergy Diagnostics[J]. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res, 2021, 13(2): 177-205. doi: 10.4168/aair.2021.13.2.177
[6] Custovic A, Lazic N, Simpson A. Pediatric asthma and development of atopy[J]. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol, 2013, 13(2): 173-180. doi: 10.1097/ACI.0b013e32835e82b6
[7] Pittner G, Vrtala S, Thomas WR, et al. Component-resolved diagnosis of house-dust mite allergy with purified natural and recombinant mite allergens[J]. Clin Exp Allergy, 2004, 34(4): 597-603. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2004.1930.x
[8] Weghofer M, Thomas WR, Kronqvist M, et al. Variability of IgE reactivity profiles among European mite allergic patients[J]. Eur J Clin Invest, 2008, 38(12): 959-965. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.2008.02048.x
[9] Tuano K, Anvari S, Hanson IC, et al. Improved diagnostic clarity in shrimp allergic non-dust-mite sensitized patients[J]. Allergy Asthma Proc, 2018, 39(5): 377-383. doi: 10.2500/aap.2018.39.4148
[10] Walsemann T, Böttger M, Traidl S, et al. Specific IgE against the house dust mite allergens Der p 5, 20 and 21 influences the phenotype and severity of atopic diseases[J]. Allergy, 2023, 78(3): 731-742. doi: 10.1111/all.15553
[11] Czaja-Bulsa G, Bulsa M, Gębala A. Food IgG4 antibodies are elevated not only in children with wheat allergy but also in children with gastrointestinal diseases[J]. BMC Gastroenterol, 2016, 16: 39. doi: 10.1186/s12876-016-0450-3
[12] Brożek JL, Bousquet J, Agache I, et al. Allergic Rhinitis and its Impact on Asthma(ARIA)guidelines-2016 revision[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2017, 140(4): 950-958. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2017.03.050
[13] 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志编辑委员会鼻科组, 中华医学会耳鼻咽喉头颈外科学分会鼻科学组. 中国变应性鼻炎诊断和治疗指南(2022年, 修订版)[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2022, 57(2): 106-129. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115330-20211228-00828
[14] Rapiejko P, Jurkiewicz D, Pietruszewska W, et al. Treatment strategy of allergic rhinitis in the face of modern world threats[J]. Otolaryngol Pol, 2018, 72(2): 1-12. doi: 10.5604/01.3001.0011.8057
[15] Gelfand E W. Inflammatory mediators in allergic rhinitis[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2004, 114(5 Suppl): S135-S138. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=ShoppingCartURL&_method=add&_eid=1-s2.0-S0091674904022997&originContentFamily=serial&_origin=article&_ts=1438219162&md5=e39e8e67fea0ee9ddffb9a000c4d64f2
[16] Zou X, Hu H, Huang Z, et al. Serum levels of specific immunoglobulin E to Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus allergen components in patients with allergic rhinitis or/and asthma[J]. Allergy Asthma Proc, 2021, 42(1): e40-e46. doi: 10.2500/aap.2021.42.200105
[17] Zuo Y, Evangelista F, Culton D, et al. IgG4 autoantibodies are inhibitory in the autoimmune disease bullous pemphigoid[J]. J Autoimmun, 2016, 73: 111-119. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2016.06.019
[18] Hu H, Dai J, Zheng X, et al. The relationship of D. pteronyssinus allergic component sIgE and sIgG(4) in house dust mite allergic rhinitis or/and allergic asthma patients[J]. Allergy Asthma Proc, 2023, 44(2): 100-105. doi: 10.2500/aap.2023.44.220078
[19] Hasegawa A, Utsumi D, Lund K, et al. Correlation between sensitization to house dust mite major allergens, age, and symptoms in Japanese house dust mite allergic subjects[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2022, 107: 108640. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2022.108640
[20] Bousquet J, Anto JM, Akdis M, et al. Paving the way of systems biology and precision medicine in allergic diseases: the MeDALL success story: Mechanisms of the Development of ALLergy; EU FP7-CP-IP; Project No: 261357;2010-2015[J]. Allergy, 2016, 71(11): 1513-1525. doi: 10.1111/all.12880
[21] Gao Z, Fu WY, Sun Y, et al. Artemisia pollen allergy in China: Component-resolved diagnosis reveals allergic asthma patients have significant multiple allergen sensitization[J]. Allergy, 2019, 74(2): 284-293. doi: 10.1111/all.13597
[22] Qiu C, Zhong L, Huang C, et al. Cell-bound IgE and plasma IgE as a combined clinical diagnostic indicator for allergic patients[J]. Sci Rep, 2020, 10(1): 4700. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-61455-8
[23] Kalsheker NA, Deam S, Chambers L, et al. The house dust mite allergen Der p1 catalytically inactivates alpha 1-antitrypsin by specific reactive centre loop cleavage: a mechanism that promotes airway inflammation and asthma[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 1996, 221(1): 59-61. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1996.0544
[24] Letrán A, García I, Espinazo-Romeu M, et al. Cut-off value of D. pteronyssinus specific IgE in double negative patients Der p 1 and Der p 2 and its clinical repercussion[J]. Sci Rep, 2021, 11(1): 23585. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-03005-4
[25] Romero-Sánchez L, Otero A, González-Rivas M, et al. Der p 23 sensitisation in patients with house dust mite respiratory allergy[J]. Eur Ann Allergy Clin Immunol, 2022 doi:10.23822/EurAnnACI.1764-1489.264.
[26] Huang Y, Wang C, Lin X, et al. Association between component-resolved diagnosis of house dust mite and efficacy of allergen immunotherapy in allergic rhinitis patients[J]. Clin Transl Allergy, 2019, 9: 64. doi: 10.1186/s13601-019-0305-4
[27] Feng M, Su Q, Lai X, et al. Functional and Immunoreactive Levels of IgG4 Correlate with Clinical Responses during the Maintenance Phase of House Dust Mite Immunotherapy[J]. J Immunol, 2018, 200(12): 3897-3904. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1701690
[28] Jappe U, Schwager C, Schromm AB, et al. Lipophilic Allergens, Different Modes of Allergen-Lipid Interaction and Their Impact on Asthma and Allergy[J]. Front Immunol, 2019, 10: 122. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00122
-





 下载:
下载: