Predictive value of PTH level on day 1 after surgery for papillary thyroid carcinoma in patients with permanent hypoparathyroidism
-
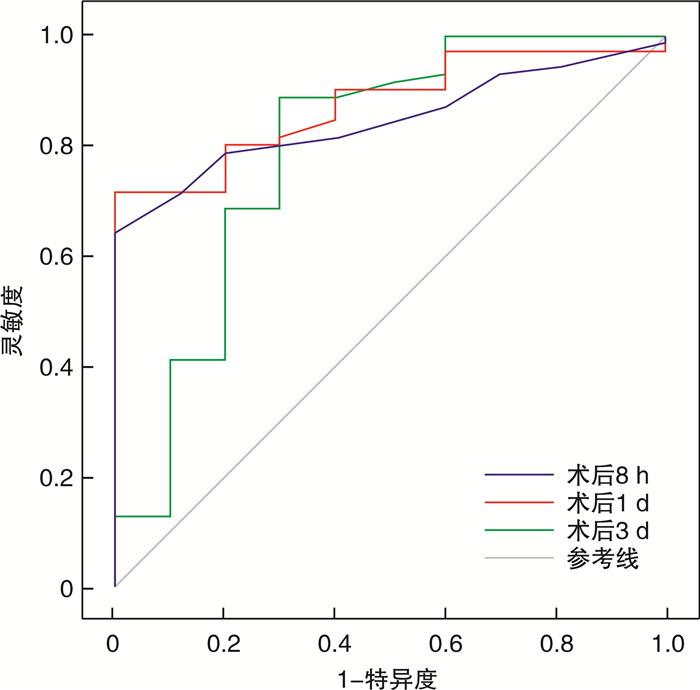
摘要: 目的 探讨甲状腺乳头状癌(papillary thyroid carcinoma,PTC)根治术后第1天甲状旁腺激素(parathyroid hormone,PTH)水平与永久性甲状旁腺功能减退(permanent hypoparathyroidism,PHPP)之间的关系及预测价值。方法 收集并分析甘肃省人民医院普外科2021年1月—2022年1月收治的行甲状腺全切及中央区淋巴结清扫的PTC患者80例。根据术后是否发生PHPP将患者分为甲状旁腺功能减退组和甲状旁腺功能正常组,采用单因素及二元logistics回归对两组患者术后第1天甲状旁腺激素PTH和血清钙离子水平与PHPP的相关性进行分析;对患者术后不同时间点PTH的动态变化情况进行分析;采用受试者工作曲线下面积评估PTH对术后发生PHPP的预测效力。结果 在纳入的80例PTC患者中有10例发生PHPP,发生率为12.5%;二元logistics回归分析显示,术后第1天PTH(OR=14.534,95%CI:2.377~88.858,P=0.004),是术后发生PHPP的独立性预测危险因素。以术后第1天PTH=8.75 ng/L为临界值,曲线下面积为0.874(95%CI:0.790~0.958,P<0.001),灵敏度为71.4%,特异度为100%,约登指数为0.714。结论 PTC全切术后第1天PTH水平与PHPP密切相关,也是发生PHPP的独立性预测危险因素。
-
关键词:
- 甲状旁腺激素 /
- 甲状腺癌根治术 /
- 永久性甲状旁腺功能减退
Abstract: Objective To investigate the relationship between parathyroid hormone(PTH) level and permanent hypoparathyroidism(PHPP) on the first day after radical papillary thyroidectomy, and its predictive value.Methods A total of 80 patients with papillary thyroid cancer who underwent total thyroid resection and central lymph node dissection were collected and analyzed from January 2021 to January 2022. According to whether PHPP occurred after surgery, the patients were divided into hypoparathyroidism group and normal parathyroid function group, and univariate and binary logistics regression were used to analyze the correlation between PTH and serum calcium levels and PHPP on the first day after surgery in two groups. The dynamic changes of PTH at different time points after operation were analyzed. The area under the receiver operating characteristic was used to evaluate the predictive power of PTH on the development of PHPP after surgery.Results Among the 80 patients with papillary thyroid cancer, 10 cases developed PHPP, with an incidence rate of 12.5%. Binary logistics regression analysis showed that PTH on the first postoperative day(OR=14.534, 95%CI: 2.377-88.858, P=0.004) was an independent predictive risk factor for postoperative PHPP. Taking PTH=8.75 ng/L on the first postoperative day as the cut-off value, the AUC of the area under the curve was 0.874(95%CI: 0.790-0.958, P < 0.001), the sensitivity was 71.4%, the specificity was 100%, and the Yoden index was 0.714.Conclusion PTH level on the first day after total thyroid papillary carcinoma surgery is closely related to PHPP, and is an independent predictor of PHPP. -

-
表 1 术后6个月发生PHPP的单因素分析
例(%) 项目 PHPP组(n=10) 正常组(n=70) χ2 P 性别/例 男∶女 4∶6 22∶48 0.033 0.857 年龄/岁 1.616 0.204 < 55 7(70.00) 42(60.00) ≥55 3(30.00) 28(40.00) 合并疾病 高血压 7(70.00) 30(42.86) 1.616 0.204 心脏病 2(20.00) 25(35.71) 0.391 0.532 糖尿病 4(40.00) 18(25.71) 0.322 0.570 肿瘤大小/cm 0.588 0.443 < 2 6(60.00) 29(41.43) ≥2 4(40.00) 41(58.57) 术后1 d PTH 19.175 0.001 正常 0(0) 53(75.71) 减低 10(100.00) 17(24.29) 术后1 d血钙 4.535 0.033 正常 2(20.00) 43(61.43) 减低 8(80.00) 27(38.57) 表 2 术后6个月发生PHPP多因素分析
项目 β 标准误 Wald P OR 95%CI 性别 -0.692 1.072 0.416 0.519 0.501 0.061~4.092 年龄 -0.917 0.895 1.050 0.306 0.400 0.069~2.311 肿瘤是否>2 cm -0.571 0.848 0.454 0.500 0.565 0.107~2.977 合并疾病 高血压 1.204 0.918 1.722 0.189 3.333 0.552~20.131 心脏病 -1.318 1.072 1.509 0.219 0.268 0.033~2.191 糖尿病 1.309 0.984 1.770 0.183 3.702 0.538~25.466 术后1 d PTH水平 2.677 0.924 8.395 0.004 14.534 2.377~88.858 术后1 d血钙水平 0.885 1.073 0.679 0.410 2.422 0.295~19.860 -
[1] 李朝喜, 温德惠, 陆海永, 等. ACR-TIRADS和C-TIRADS对桥本甲状腺炎背景下的桥本结节和甲状腺乳头状癌的诊断价值[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2022, 36(6): 447-452. https://lceh.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2022.06.008
[2] 葛现才, 殷德英, 张勤, 等. 一次性切口牵开固定器在甲状腺微小乳头状癌中的临床研究[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2021, 35(11): 1028-1030. https://lceh.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2021.11.014
[3] Canu GL, Medas F, Cappellacci F, et al. Intact parathyroid hormone value on the first postoperative day following total thyroidectomy as a predictor of permanent hypoparathyroidism: a retrospective analysis on 426 consecutive patients[J]. Endokrynol Pol, 2022, 73(1): 48-55.
[4] Díez JJ, Anda E, Sastre J, et al. Permanent postoperative hypoparathyroidism: an analysis of prevalence and predictive factors for adequacy of control in a cohort of 260 patients[J]. Gland Surg, 2020, 9(5): 1380-1388. doi: 10.21037/gs-20-288
[5] 张鹏, 林辉, 陈峰. 不同剂量利多卡因对碘缺乏型甲状腺肿全麻切除术后患者恢复质量的影响[J]. 中华地方病学杂志, 2021, 40(4): 321-325.
[6] 朱少问, 周立. 血清校正钙及iPTH对甲状腺全切术后发生甲状旁腺功能减退的预测价值[J]. 中华地方病学杂志, 2021, 40(6): 483-487.
[7] Canu GL, Medas F, Longheu A, et al. Correlation between iPTH Levels on the First Postoperative Day After Total Thyroidectomy and Permanent Hypoparathyroidism: Our Experience[J]. Open Med(Wars), 2019, 14: 437-442. doi: 10.1515/med-2019-0047
[8] 马炜柯, 李爽, 张弘. 甲状腺全切术后甲状旁腺功能减退症研究进展[J]. 临床误诊误治, 2019, 32(9): 113-116. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCWZ201909022.htm
[9] 陈思行, 王亚冰, 王鸥, 等. 大剂量普通维生素D和活性维生素D治疗甲状旁腺功能减退症有效性和安全性的比较[J]. 中华内分泌代谢杂志, 2019(10): 859-863. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YLYS202103024.htm
[10] 付书彩. 精细化被膜解剖在全甲状腺切除术中保护甲状旁腺功能的效果[J]. 中国医学创新, 2022, 19(30): 95-98. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYCX202230023.htm
[11] 张琪, 屈坤鹏, 成晓舟, 等. 腔镜下甲状腺切除术联合甲状旁腺移植术对甲状旁腺功能的影响[J]. 实用医学杂志, 2021, 37(19): 2492-2496. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYZ202119012.htm
[12] 邢小燕, 赵贵芹. 甲状腺全切术后低钙血症的高危因素分析与相应干预措施[J]. 护理实践与研究, 2020, 17(4): 16-17. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HLSJ202004007.htm
[13] 张敏, 周蕾. 三种甲状腺全切除术式的临床疗效及对甲状旁腺功能的影响对比[J]. 中华普外科手术学杂志(电子版), 2018, 12(3): 261-264. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHPW201803027.htm
[14] 陈静, 韦传娃, 范平明. 肾性甲状腺功能亢进患者甲状旁腺切除术后iPTH检测及其对血管钙化的影响[J]. 湖南师范大学学报(医学版), 2019, 16(4)65-68. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNYG201904022.htm
[15] 蔡淑艳, 郑建伟. 血清全段甲状旁腺激素浓度对甲状腺全切除术后发生永久性甲状旁腺功能减退症的预测效果[J]. 首都医科大学学报, 2021, 42(1): 148-152. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDYD202101026.htm
[16] Nixon IJ, Wang LY, Migliacci JC, et al. An International Multi-Institutional Validation of Age 55 Years as a Cutoff for Risk Stratification in the AJCC/UICC Staging System for Well-Differentiated Thyroid Cancer[J]. Thyroid, 2016, 26(3): 373-380.
[17] Kim K, Kim JK, Lee CR, et al. Comparison of long-term prognosis for differentiated thyroid cancer according to the 7th and 8th editions of the AJCC/UICC TNM staging system[J]. Ther Adv Endocrinol Metab, 2020, 11: 2042018820921019.
[18] Díaz-Soto G, Mora-Porta M, Nicolau J, et al. Efficacy and safety of long term treatment of unresponsive hypoparathyroidism using multipulse subcutaneous infusion of teriparatide[J]. Horm Metab Res, 2012, 44(9): 708-710.
[19] 郑建伟, 蔡淑艳, 宋慧敏, 等. 甲状腺全切除术后第1天血清全段甲状旁腺激素水平评估术后发生永久性甲状旁腺功能减退症的价值[J]. 中华外科杂志, 2020, 58(8): 626-630.
[20] Almquist M, Ivarsson K, Nordenström E, et al. Mortality in patients with permanent hypoparathyroidism after total thyroidectomy[J]. Br J Surg, 2018, 105(10): 1313-1318.
[21] Ertaş B, Veyseller B, Karataş A, et al. Hypoparathyroidism in Total Thyroidectomy due to Benign Thyroid Diseases[J]. Clin Ther, 2018, 40(5): 762-767.
[22] Imga NN, Atas H, Torgutalp M, et al. Stratifying the risk factors for hypoparathyroidism after total thyroidectomy. A single Center study[J]. Ann Ital Chir, 2019, 90: 21-30.
[23] Lin YS, Hsueh C, Wu HY, et al. Incidental parathyroidectomy during thyroidectomy increases the risk of postoperative hypocalcemia[J]. Laryngoscope, 2017, 127(9): 2194-2200.
[24] 董治中, 刘文, 程若川. 甲状腺全切术中甲状旁腺自体移植的现状和思考[J]. 中国普通外科杂志, 2021, 30(5): 600-605. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZPWZ202105013.htm
[25] 金德斌, 吴佳龙, 杨艳, 等. 甲状腺全切术后甲状旁腺激素变化及对血钙影响的临床研究[J]. 中国耳鼻咽喉头颈外科, 2021, 28(5): 310-312. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-EBYT202105012.htm
[26] Almquist M, Hallgrimsson P, Nordenström E, et al. Prediction of permanent hypoparathyroidism after total thyroidectomy[J]. World J Surg, 2014, 38(10): 2613-2620.
[27] 曹婉婷, 申红梅. 亚临床甲状腺功能减退症的流行现状病因与危害[J]. 中华地方病学杂志, 38(5): 422-425.
[28] Yano Y, Masaki C, Sugino K, et al. Serum intact parathyroid hormone level after total thyroidectomy or total thyroidectomy plus lymph node dissection for thyroid nodules: report from 296 surgical cases[J]. Int J Endocrinol Metab, 2012, 10(4): 594-598.
[29] 王天笑, 于文斌, 马骁, 等. 甲状腺全切除术和近全切除术术后甲状旁腺功能损伤的危险因素分析[J]. 中华外科杂志, 2016, 54(3): 206-211.
[30] McLeod IK, Arciero C, Noordzij JP, et al. The use of rapid parathyroid hormone assay in predicting postoperative hypocalcemia after total or completion thyroidectomy[J]. Thyroid, 2006, 16(3): 259-265.
[31] Sywak MS, Palazzo FF, Yeh M, et al. Parathyroid hormone assay predicts hypocalcaemia after total thyroidectomy[J]. ANZ J Surg, 2007, 77(8): 667-670.
[32] 董丽英, 李燕, 李思齐, 等. 引流液甲状旁腺激素测定对甲状腺术后甲状旁腺功能评估的临床意义[J]. 中国普外基础与临床杂志, 2019, 26(10): 1196-1200. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZPWL201910010.htm
[33] 黄华, 孙蕊, 曹越, 等. 甲状腺全切术后血钙变化规律的研究[J]. 协和医学杂志, 2020, 11(4): 420-424. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XHYX202004012.htm
[34] 刘先栋, 张翠明, 杨林花. 免疫性血小板减少症与甲状腺功能异常关系研究[J]. 临床血液学杂志, 2022, 35(7): 474-478. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCXZ202207005.htm
-




 下载:
下载: