Application of ethmoid artery pedicled septal floor mucosa flap in repair of postoperative cerebrospinal fluid leak after transsphenoidal pituitary surgery
-
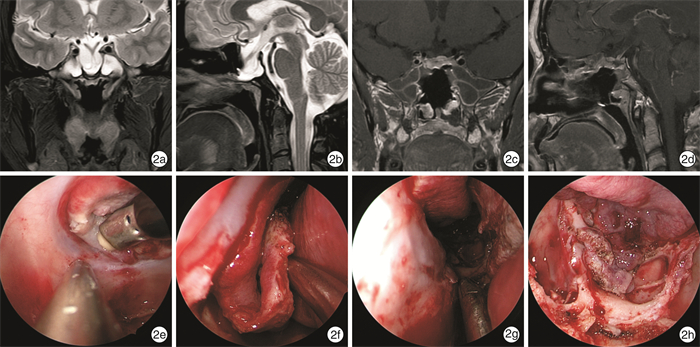
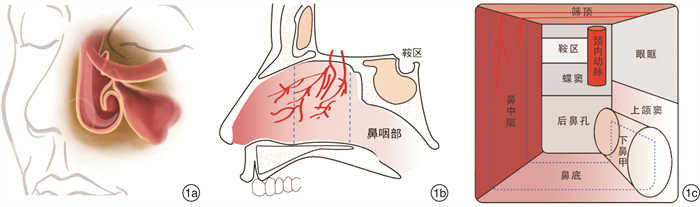
摘要: 目的 探讨采用以筛动脉为蒂的鼻中隔鼻底黏膜瓣修复经蝶垂体瘤术后脑脊液漏的安全性及有效性。方法 回顾上海交通大学医学院附属上海市第六人民医院耳鼻咽喉头颈外科2011年6月—2022年6月收治的6例垂体瘤术后脑脊液漏患者的临床资料,因既往手术采用内镜经蝶扩大入路破坏了双侧鼻中隔后动脉,手术采用以筛动脉为蒂的鼻中隔鼻底黏膜瓣进行修补。结果 6例患者术后随访黏膜瓣均生长良好,未再发生脑脊液漏。结论 垂体瘤术后的高流量脑脊液漏临床修复困难,对于经蝶入路破坏双侧鼻中隔后动脉的患者,其经典的鼻中隔后动脉黏膜瓣不可用,以筛动脉为蒂的鼻中隔鼻底黏膜瓣是可选择的方法之一。Abstract: Objective To investigate the safety and effectiveness of the ethmoid artery pedicled septal floor mucosal flap in repair of postoperative cerebrospinal fluid leakage after transsphenoidal pituitary tumor surgery.Methods The clinical data of 6 patients with cerebrospinal fluid leak in Department of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery, Shanghai Sixth People's Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine from June 2011 to June 2022. In 6 patients with postoperative cerebrospinal fluid leakage after transsphenoidal pituitary surgery, the bilateral posterior septal arteries were sacrificed due to the endoscopic transsphenoidal expanded approach, so the ethmoid artery pedicled septal floor mucosal flaps were adopted.Results All patients had good growth of the mucosal flaps during postoperative follow-up without recurrent cerebrospinal fluid leakage.Conclusion Cerebrospinal fluid leakage is still one of the postoperative complications of pituitary surgery. For patients with bilateral posterior septal arteries sacrificed through the transsphenoidal approach, when the classic posterior septal artery pedicled mucosal flap is not available, the ethmoid artery pedicled septal floor mucosal flap is one of the alternative methods.
-

-
表 1 6例垂体瘤术后脑脊液漏患者的临床资料
例序 性别 年龄/岁 病情 垂体瘤手术史 放疗史 脑脊液漏修补史 修补材料 颅内感染 修补材料 随访时间/年 1 男 50 垂体瘤术后 23 d前 无 无 - 有 筛动脉瓣 8 2 女 64 垂体瘤术后 1个月前 无 无 - 有 筛动脉瓣 8 3 男 48 垂体瘤术后 4年前 无 无 - 有 筛动脉瓣 6 4 女 38 垂体瘤术后 5年前 无 8个月前 脂肪 有 筛动脉瓣 4 5 男 59 垂体瘤术后 6年前 无 无 - 有 筛动脉瓣 2 6 女 27 垂体瘤术后 1年前 无 无 - 有 筛动脉瓣 2 -
[1] Rolston JD, Han SJ, Aghi MK. Nationwide shift from microscopic to endoscopic transsphenoidal pituitary surgery[J]. Pituitary, 2016, 19(3): 248-250. doi: 10.1007/s11102-015-0685-y
[2] 霍显浩, 王立婷, 梁云, 等. 显微镜及神经内镜下经鼻蝶垂体瘤切除术术后嗅觉功能障碍对比分析[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2017, 31(19): 1512-1518. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.1001-1781.2017.19.012 https://lceh.cbpt.cnki.net/WKC/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=0aca6df1-8354-4c2d-8552-0d4dfa10e3dd
[3] Berker M, Hazer DB, Yücel T, et al. Complications of endoscopic surgery of the pituitary adenomas: analysis of 570 patients and review of the literature[J]. Pituitary, 2012, 15(3): 288-300. doi: 10.1007/s11102-011-0368-2
[4] Cappabianca P, Cavallo LM, Colao A, et al. Surgical complications associated with the endoscopic endonasal transsphenoidal approach for pituitary adenomas[J]. J Neurosurg, 2002, 97(3): 293-298.
[5] Hannan CJ, Almhanedi H, Al-Mahfoudh R, et al. Predicting postoperative cerebrospinal fluid(CSF) leak following endoscopic transnasal pituitary and anterior skull base surgery: a multivariate analysis[J]. Acta Neurochir (Wien), 2020, 162(6): 1309-1315. doi: 10.1007/s00701-020-04334-5
[6] Harvey RJ, Parmar P, Sacks R, et al. Endoscopic skull base reconstruction of large dural defects: a systematic review of published evidence[J]. Laryngoscope, 2012, 122(2): 452-459. doi: 10.1002/lary.22475
[7] Wei CC, Palmer JN. Planum, tubercular, sellar and clival defects[J]. Adv Otorhinolaryngol, 2013, 74: 119-129.
[8] Zhou Z, Zuo F, Chen X et al. Risk factors for postoperative cerebrospinal fluid leakage after transsphenoidal surgery for pituitary adenoma: a meta-analysis and systematic review[J]. BMC Neurol, 2021, 21(1): 417. doi: 10.1186/s12883-021-02440-0
[9] Slot EMH, Sabaoglu R, Voormolen EHJ et al. Cerebrospinal Fluid Leak after Transsphenoidal Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis[J]. J Neurol Surg B Skull Base, 2021, 83(Suppl 2): e501-e513.
[10] 刘世贤, 唐如, 李志鹏, 等. 迟发性医源性脑脊液耳鼻漏相关危险因素分析[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2021, 35(12): 1111-1114. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2021.12.011 https://lceh.cbpt.cnki.net/WKC/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=4e924745-8e83-4d1a-aec0-c9e49630a21a
[11] Anderson C, Akbar N, Colley P. Reconstruction of Skull Base Defects in Pituitary Surgery[J]. Otolaryngol Clin North Am, 2022, 55(2): 449-458. doi: 10.1016/j.otc.2022.01.004
[12] Chaskes MB, Barton B, Karsy M, et al. An algorithm for sellar reconstruction following endoscopic transsphenoidal surgery for pituitary adenoma: A review of 582 cases[J]. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol, 2022, 12(9): 1120-1130. doi: 10.1002/alr.22966
[13] Conger A, Zhao F, Wang X, et al. Evolution of the graded repair of CSF leaks and skull base defects in endonasal endoscopic tumor surgery: trends in repair failure and meningitis rates in 509 patients[J]. J Neurosurg, 2018, 130(3): 861-875.
[14] Ruggeri AG, Cappelletti M, Giovannetti F, et al. Proposal of Standardization of Closure Techniques After Endoscopic Pituitary and Skull Base Surgery Based on Postoperative Cerebrospinal Fluid Leak Risk Classification[J]. J Craniofac Surg, 2019, 30(4): 1027-1032. doi: 10.1097/SCS.0000000000005540
[15] Strickland BA, Lucas J, Harris B, et al. Identification and repair of intraoperative cerebrospinal fluid leaks in endonasal transsphenoidal pituitary surgery: surgical experience in a series of 1002 patients[J]. J Neurosurg, 2018, 129(2): 425-429. doi: 10.3171/2017.4.JNS162451
[16] Rivera-Serrano CM, Snyderman CH, Gardner P, et al. Nasoseptal "Rescue" flap: A novel modification of the nasoseptal flap technique for pituitary surgery[J]. Laryngoscope, 2011, 121(5): 990-993. doi: 10.1002/lary.21419
[17] Rawal RB, Kimple AJ, Dugar DR, et al. Minimizing morbidity in endoscopic pituitary surgery: outcomes of the novel nasoseptal rescue flap technique[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2012, 147(3): 434-437. doi: 10.1177/0194599812443042
[18] 马翔宇, 时传君, 倪石磊, 等. 补救黏膜瓣技术在神经内镜经鼻蝶垂体腺瘤切除术中的应用[J]. 中华神经外科杂志, 2018, 34(6): 568-571. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1001-2346.2018.06.007
[19] 吕洪柱, 冷基勇, 王克臻, 等. 改良带蒂鼻中隔黏膜瓣在经蝶垂体瘤手术脑脊液漏中的应用[J]. 中国医师进修杂志, 2019, 42(12): 1118-1120. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-4904.2019.12.014
[20] Castelnuovo P, Ferreli F, Khodaei I, et al. Anterior ethmoidal artery septal flap for the management of septal perforation[J]. Arch Facial Plast Surg, 2011, 13(6): 411-414. doi: 10.1001/archfaci.2011.44
[21] Bozkurt G, Leone F, Arosio AD, et al. Septal Flip Flap for Anterior Skull Base Reconstruction After Endoscopic Transnasal Craniectomy: Long-Term Outcomes[J]. World Neurosurg, 2019, 128: e409-e416. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2019.04.166
[22] Erdogmus S, Govsa F. The anatomic landmarks of ethmoidal arteries for the surgical approaches[J]. J Craniofac Surg, 2006, 17(2): 280-285. doi: 10.1097/00001665-200603000-00014
[23] 冯燕军, 闫素英, 王建宏, 等. 内镜鼻窦手术中眶上筛房的定位作用和筛前动脉分型的意义[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2021, 35(6): 495-500. https://lceh.cbpt.cnki.net/WKC/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=b13385e9-6f4a-43a6-9289-72f2cb35c42d
[24] Mao S, Li M, Li D, et al. Septal floor rotational flap pedicled on ethmoidal arteries for endoscopic skull base reconstruction[J]. Laryngoscope, 2019, 129(12): 2696-2701. doi: 10.1002/lary.27942
-




 下载:
下载: