λ approach for the repairment of large skin defects after resection of preauricular fistula with cellulitis in children
-
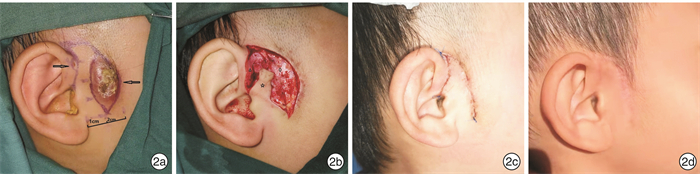
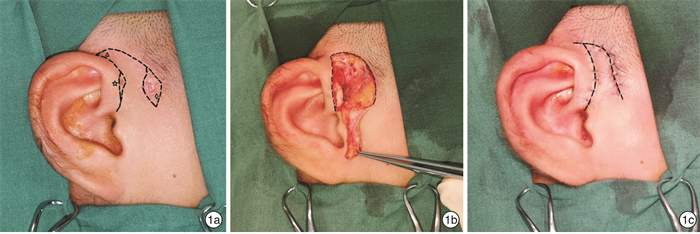
摘要: 目的 探讨使用λ型皮瓣修补儿童感染性耳前瘘管切除术后大面积皮肤缺损的可行性及优势。方法 回顾性分析2016年1月—2021年1月期间采用λ型皮瓣术式治疗的46例感染性耳前瘘管患儿的临床资料。结果 术后随访10~18个月,切口Ⅰ期愈合率97.8%,皮瓣存活率100%。结论 λ型皮瓣安全、有效、美观,可用于修复儿童感染性耳前瘘管切除术后皮肤的大面积缺损。Abstract: Objective To explore the feasibility and advantages of λ approach for the repairment of large skin defects after resection of preauricular fistula with cellulitis in children.Methods The clinical data of patients with preauricular fistula with cellulitis treated by λ approach from January 2016 to January 2021 were analyzed retrospectively.Results After follow-up for 10-18 months, the primary healing rate of incision was 97.8%, and the survival rate of λ flap was 100%.Conclusion λ approach is a safe, effective and cosmetic method. It can be used to repair the large skin defects after resection of preauricular fistula with cellulitis in children.
-
Key words:
- child /
- preauricular fistula /
- reconstructive surgical procedures
-

-
[1] Baatenburg de Jong RJ. A new surgical technique for treatment of preauricular sinus[J]. Surgery, 2005, 137(5): 567-570. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2005.01.009
[2] O'Mara W, Guarisco L. Management of the preauricular sinus[J]. J La State Med Soc, 1999, 151(9): 447-450.
[3] Yeo SW, Jun BC, Park SN, et al. The preauricular sinus: factors contributing to recurrence after surgery[J]. Am J Otolaryngol, 2006, 27(6): 396-400. doi: 10.1016/j.amjoto.2006.03.008
[4] Wang L, Wei L, Lu W, et al. Excision of preauricular sinus with abscess drainage in children[J]. Am J Otolaryngol, 2019, 40(2): 257-259. doi: 10.1016/j.amjoto.2018.10.016
[5] Gan EC, Anicete R, Tan HK, et al. Preauricular sinuses in the pediatric population: techniques and recurrence rates[J]. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, 2013, 77(3): 372-378. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2012.11.029
[6] Han JS, Park JM, Han JJ, et al. Surgical results of infected preauricular sinus: No need for delay[J]. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, 2020, 135: 110129. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2020.110129
[7] Khardali MH, Han JS, Kim SI, et al. Clinical efficacy of standard simple elliptical incision following drain-less and subcutaneous suture technique in preauricular sinus surgery[J]. Am J Otolaryngol, 2020, 41(4): 102465. doi: 10.1016/j.amjoto.2020.102465
[8] Schonauer F, Vuppalapati G, Marlino S, et al. Versatility of the posterior auricular flap in partial ear reconstruction[J]. Plast Reconstr Surg, 2010, 126(4): 1213-1221. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0b013e3181ec1f03
[9] Tom L, Samadi D S. Surgical treatment of preauricular sinus/cysts[J]. Oper Tech Otolaryngology Head Neck Surg, 2002, 13(1): 44-47. doi: 10.1053/otot.2002.32158
[10] Wang L, Wei L, Lu W, et al. Excision of preauricular sinus with abscess drainage in children[J]. Am J Otolaryngol, 2019, 40(2): 257-259. doi: 10.1016/j.amjoto.2018.10.016
[11] Tan B, Lee TS, Loh I. Reconstruction of preauricular soft tissue defects using a superiorly based rotation advancement scalp flap-A novel approach to the surgical treatment of preauricular sinuses[J]. Am J Otolaryngol, 2018, 39(2): 204-207. doi: 10.1016/j.amjoto.2017.11.003
[12] 张海港, 樊明月, 尹德佩, 等. "H"型切口和"∧"型切口在儿童感染性耳前瘘管切除术中的应用[J]. 中国耳鼻咽喉颅底外科杂志, 2021, 27(5): 585-588. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZEBY202105020.htm
[13] Kim WJ, Lee YM, Kim DH, et al. Causes and prevention of revision surgery for preauricular sinus: A histopathological analysis[J]. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, 2019, 116: 199-203. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2018.11.006
-




 下载:
下载: