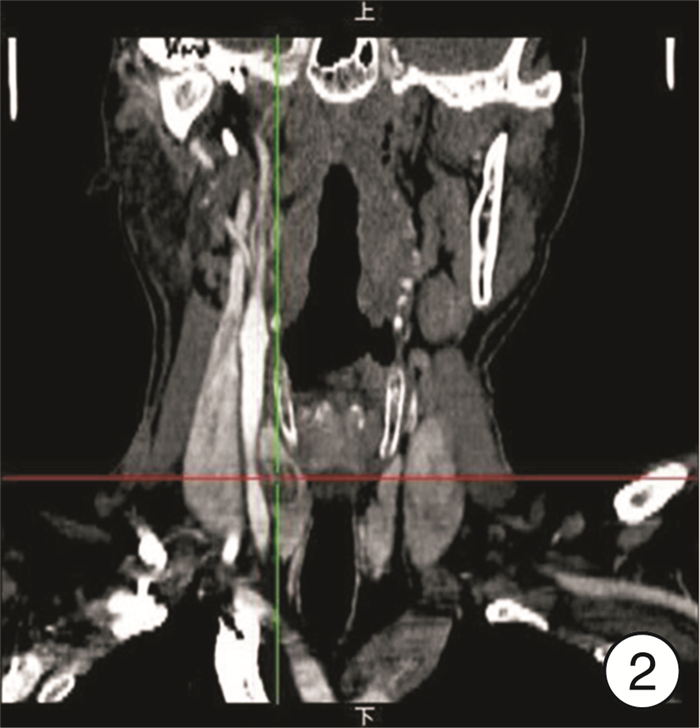
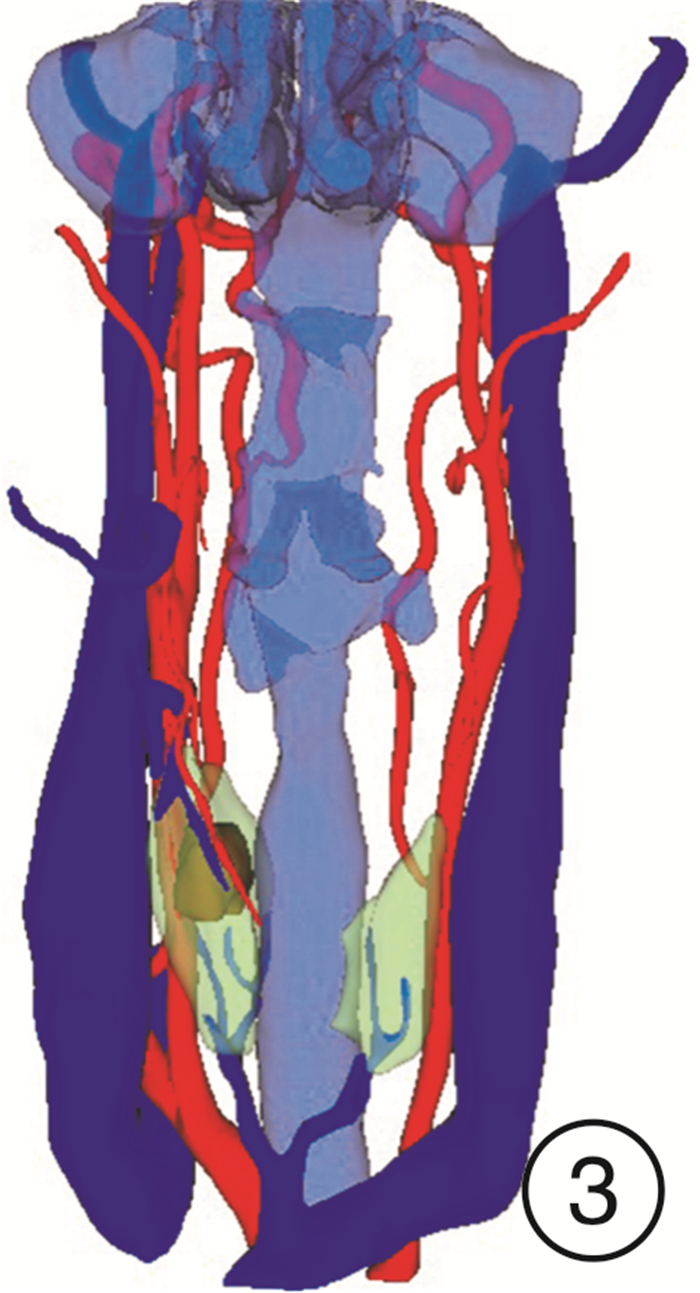
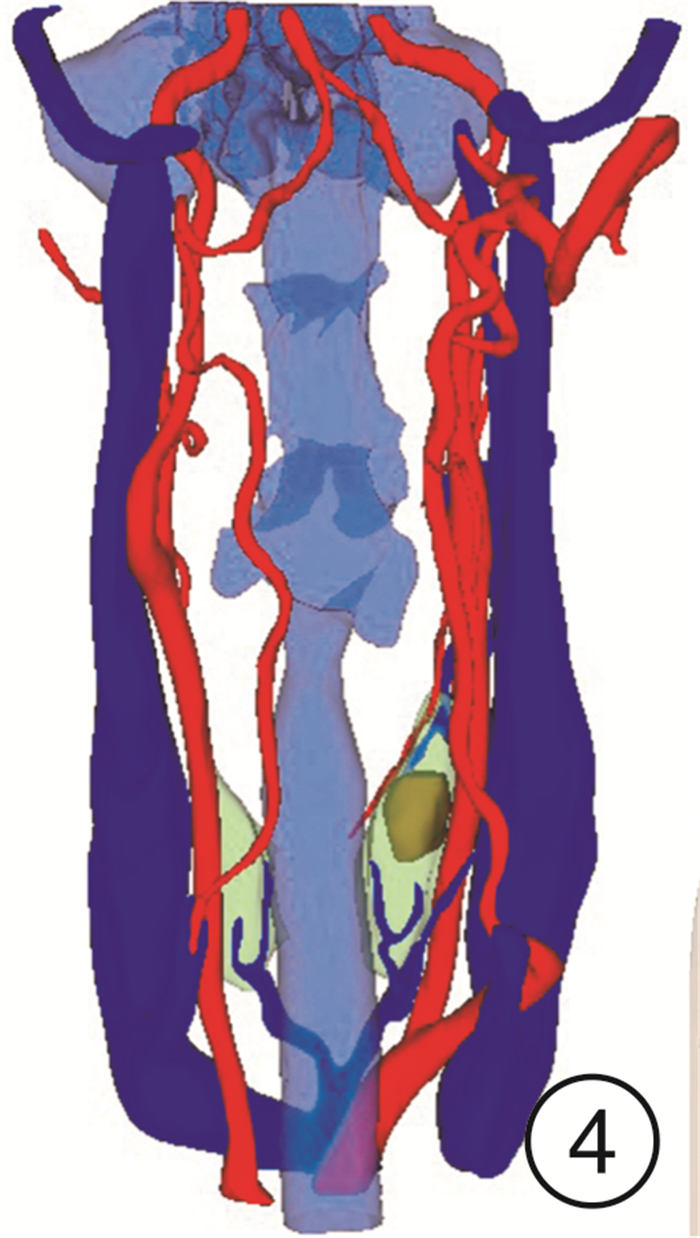
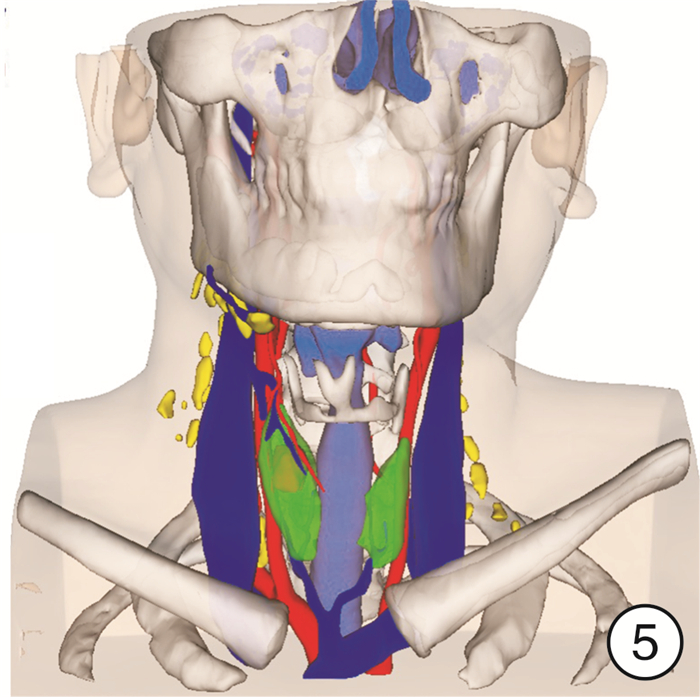
-
摘要: 目的 探讨三维可视化技术在腔镜甲状腺手术中的应用价值。方法 将术前细针穿刺明确为甲状腺乳头状癌的50例患者随机分为联合组(20例)和单纯手术组(30例),联合组采用腔镜甲状腺手术联合三维可视化模型制作,单纯手术组采用单纯腔镜甲状腺手术。比较两组术前与患者的沟通时间及沟通满意度、术中出血量及手术时间、术后并发症等指标。结果 联合组和单纯手术组术前与患者的沟通时间分别为(23.05±6.83) min和(28.83±8.57) min,联合组沟通时间更短,沟通交流后患者对病情知晓满意度更高,两组比较差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。联合组和单纯手术组的手术时间分别为(104.30±13.06) min和(130.46±17.01) min,联合组手术时间更短(P<0.05);术中出血量分别为(12.80±6.10) mL和(17.60±5.19) mL,联合组术中出血量更少(P<0.05)。两组在术后并发症方面的差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。结论 三维可视化模型的重建有助于改善医患沟通,提高腔镜甲状腺手术的安全性,加快患者术后康复,值得推广。Abstract: Objective To explore the application value of three dimensional(3D) visualization in the endoscopic thyroidectomy.Methods Fifty patients with thyroid papillary carcinoma confirmed by preoperative fine needle aspiration(FNA) were randomly divided into the combined group (20 cases) and the simple operation group (30 cases). Endoscopic thyroid surgery combined with three-dimensional visualization model was used in the combined group. Simple operation group was treated with simple endoscopic thyroid surgery. The communication time and communication satisfaction, intraoperative blood loss, operation time and postoperative complications between the two groups were compared.Results The communication time with patients in the combined group and the simple operation group before operation was (23.05±6.83) min and (28.83±8.57) min. The communication time in the combined group was shorter, and the patients' satisfaction with disease awareness was higher after communication. There was a statistically significant difference between the two groups (P < 0.05). The operation time of combined group and simple operation group was (104.30±13.06) min and (130.46±17.01) min respectively, and the operation time of combined group was shorter (P < 0.05). The intraoperative bleeding volume of combined group and simple operation group was (12.80±6.10) mL and (17.60±5.19) mL, and the combined group had less intraoperative bleeding volume (P < 0.05). There was no significant difference in postoperative complications between the two groups (P > 0.05).Conclusion 3D visualization technology will benefit to improve the efficiency of doctor-patient communication, enhance the safety of the endoscopic thyroidectomy, and then accelerate the postoperative rehabilitation of patients, which worthy of clinical promotion and practice.
-

-
表 1 两组患者基本情况比较
组别 例数 年龄/岁 身高/cm 体重/kg 肿瘤长径/mm 联合组 20 33.40±6.83 164.15±5.99 53.90±7.49 6.92±2.93 单纯手术组 30 32.73±6.79 164.56±6.03 54.5±7.56 7.37±2.72 t值 0.339 -0.240 -0.276 -0.556 P值 0.736 0.811 0.784 0.580 95%CI -3.28~4.61 -3.90~3.07 -4.97~3.77 -2.08~1.17 -
[1] 中华医学会数字医学分会, 中国研究型医院学会数字智能化外科专业委员会, 中国医师协会肝癌专业委员会. 中央型肝癌三维可视化精准诊疗中国专家共识(2020版)[J]. 中国实用外科杂志, 2020, 40(4): 361-368. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGWK202004001.htm
[2] 中华医学会数字医学分会, 中国医师协会肝癌专业委员会, 中国医师协会临床精准医学专业委员会, 等. 复杂性肝脏肿瘤三维可视化精准诊治指南(2019版)[J]. 中国实用外科杂志, 2019, 39(8): 766-774. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGWK201908002.htm
[3] 支修益, 胡坚, 刘伦旭, 等. 人工智能平台下肺结节的三维可视化定位与手术规划专家共识[J]. 中国胸心血管外科临床杂志, 2019, 26(12): 1161-1166. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZXYX201912001.htm
[4] 吕继连, 钟克涛, 郑永红, 等. 3D打印技术联合三维重建在下颌骨骨折中的应用[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2019, 33(11): 1057-1059, 1064. https://lceh.cbpt.cnki.net/WKC/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=d0dabc2d-48af-4d21-a8d1-c57afab5e2e1
[5] 王平, 吴国洋, 田文, 等. 经口腔前庭入路腔镜甲状腺手术专家共识(2018版)[J]. 中国实用外科杂志, 2018, 38(10): 1104-1107. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGWK201810002.htm
[6] 王登欢, 张冉, 冯恩梓, 等. 经口腔前庭入路腔镜手术在甲状腺癌中央区淋巴结清扫中的有效性研究[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2022, 36(7): 540-544, 558. https://lceh.cbpt.cnki.net/WKC/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=a6218384-c343-4b55-aa85-4727ebdc421e
[7] 彭文, 彭小伟, 李赞, 等. 经口入路腔镜手术在较大甲状腺良性肿瘤中的应用[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2018, 32(13): 972-975. https://lceh.cbpt.cnki.net/WKC/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=69caa8a8-def0-474a-9aeb-2f347dc63acf
[8] Hong YT, Ahn JH, Kim JH, et al. Bi-institutional experience of transoral endoscopic thyroidectomy: Challenges and outcomes[J]. Head Neck, 2020, 42(8): 2115-2122.
[9] 岳阳, 辛华. 三维可视化技术在精准肺切除术中的应用进展[J]. 中国胸心血管外科临床杂志, 2022, 29(2): 262-266. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZXYX202202016.htm
[10] 王朝晖, 伏桂明, 陈锦, 等计算机辅助设计三维可视化技术在侵犯气管的甲状腺癌手术中的应用[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2017, 52(10): 774-776.
[11] 陈灵勰, 宣明, 丁昊, 等. 三维可视化模型经乳晕单通道腔镜切除甲状腺大结节(附33例报告)[J]. 外科理论与实践, 2020, 25(4): 331-335. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WKLL202004017.htm
[12] Hong D, Lee S, Kim T, et al. Usefulness of a 3D-Printed Thyroid Cancer Phantom for Clinician to Patient Communication[J]. World J Surg, 2020, 44(3): 788-794.
[13] Seok J, Yoon S, Ryu CH, et al. A Personalized 3D-Printed Model for Obtaining Informed Consent Process for Thyroid Surgery: A Randomized Clinical Study Using a Deep Learning Approach with Mesh-Type 3D Modeling[J]. J Pers Med, 2021, 11(6): 574.
[14] Carter John L, Ankura P, Gabriel H, et al. Thyroid gland visualization with 3D/4D ultrasound: integrated hands-on imaging in anatomical dissection laboratory[J]. Surg Radiol Anat, 2017, 39(5): 567-572.
-

| 引用本文: | 陈征, 张青松, 赵亚通, 等. 三维可视化技术在腔镜甲状腺手术中的应用价值[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2023, 37(1): 31-35. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2023.01.006 |
| Citation: | CHEN Zheng, ZHANG Qingsong, ZHAO Yatong, et al. The application of three-dimensional visualization in the endoscopic thyroidectomy[J]. J Clin Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2023, 37(1): 31-35. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2023.01.006 |
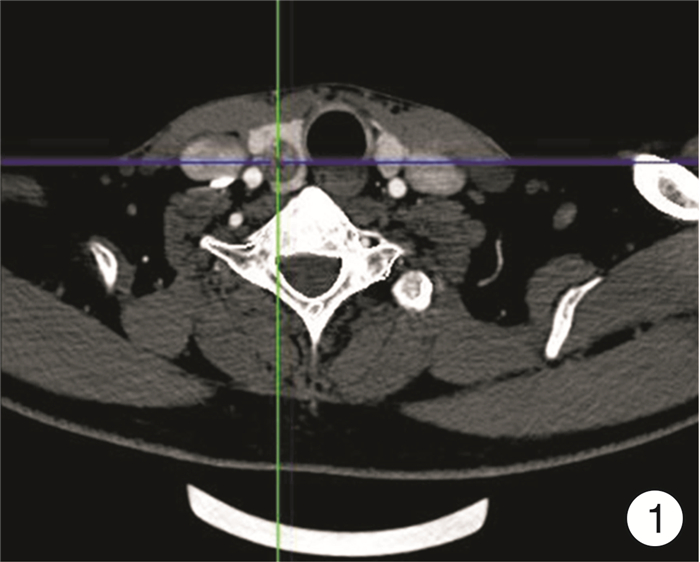
- Figure 1.
- Figure 2.
- Figure 3.
- Figure 4.
- Figure 5.
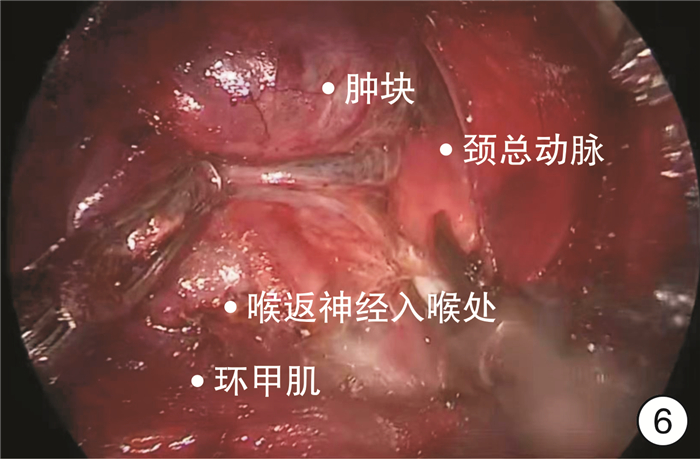
- Figure 6.
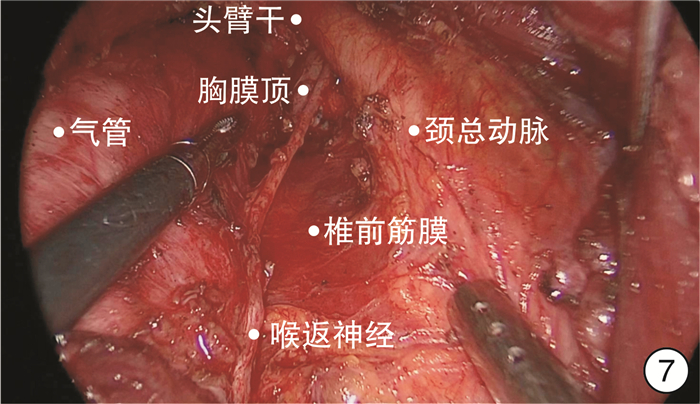
- Figure 7.
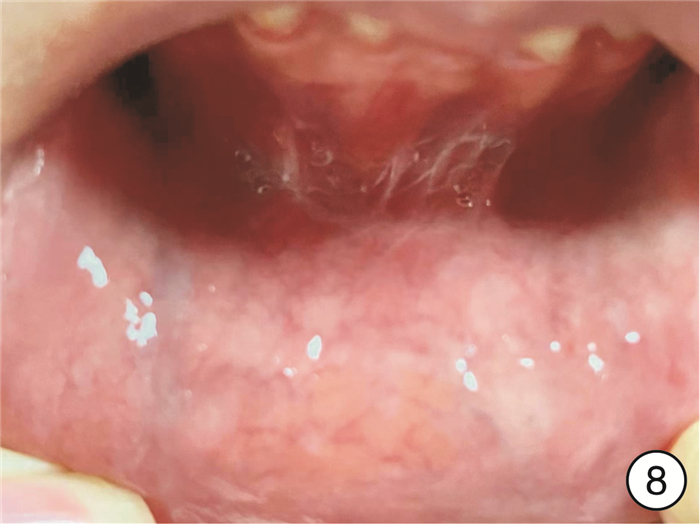
- Figure 8.



 下载:
下载: