-
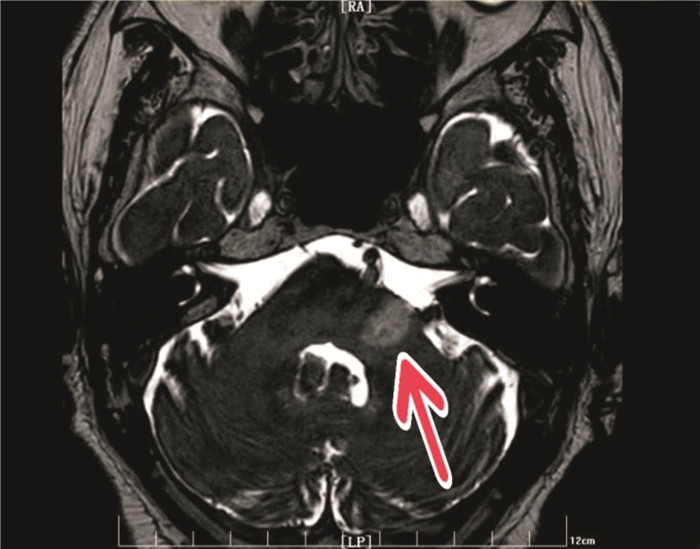
摘要: 脑梗死是临床上常见的疾病之一。本文报道1例脑桥臂梗死的患者,主要临床表现有听力下降、眩晕及面瘫等,颅脑MRI提示脑桥臂区新发梗死。该患者经治疗后面瘫及听力、眩晕状况恢复良好。Abstract: Cerebral infarction is one of the common clinical diseases. This article reported that one patient with pontine brachial infarction had hearing loss, vertigo, facial paralysis, etc., and cranial MRI showed new infarction in the pontine brachial region. The patient recovered well after treatment with paralysis, hearing and vertigo.
-
Key words:
- deafness, sudden /
- vertigo /
- facial paralysis /
- cerebral infarction
-

-
[1] 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志编辑委员会, 中华医学会耳鼻咽喉头颈外科学分会. 突发性聋诊断和治疗指南(2015)[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2015, 50(6): 443-447. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHEB200608004.htm
[2] Ozkan A, Balcı Ç, Sen HM, et al. Bilateral Anterior Inferior Cerebellar Artery Infarction[J]. Turk Beyin Damar Hast Derg, 2016, 22 (1): 41-44. doi: 10.5505/tbdhd.2016.85047
[3] Yoshimura C, Kikuchi A, Takahashi Y, et al. [Trigeminal neuralgia caused by cerebellopontine angle lipoma: a case report and review of the literature][J]. No Shinkei Geka, 2014, 42(12): 1131-1136.
[4] Lee H, Whitman GT, Lim JG, et al. Bilateral sudden deafness as a prodrome of anterior inferior cerebellar artery infarction[J]. Arch Neurol, 2001, 58(8): 1287-1289. doi: 10.1001/archneur.58.8.1287
[5] Liqun Z, Park KH, Kim HJ, et al. Acute Unilateral Audiovestibulopathy due to Embolic Labyrinthine Infarction[J]. Front Neurol, 2018, 9: 311. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2018.00311
[6] Wang XL, Sun M, Wang XP. Cerebellar artery infarction with sudden hearing loss and vertigo as initial symptoms: A case report[J]. World J Clin Cases, 2021, 9(11): 2519-2523. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i11.2519
[7] Deng Y, Shi J, Zhang M, et al. Clinical characteristics of cerebral hemorrhage with bilateral sudden deafness as the first symptom[J]. Neurol Sci, 2021, 42(1): 141-150. doi: 10.1007/s10072-020-04515-1
[8] 李智慧, 吕佳蕙, 陈纲, 等. 突发性感音神经性听力损失与内听道MRI中面听神经及小脑前下动脉血管袢的相关性研究[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2022, 36(6): 435-440. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH202206006.htm
[9] 鲍凤香, 杨成俊, 周国辉. 突发性聋并发缺血性脑卒中风险预测模型的构建及验证[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2021, 35(12): 1078-1084. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH202112005.htm
[10] 吴晓清, 张宝荣. 双侧椎动脉闭塞致双侧急性桥臂梗死一例[J]. 浙江大学学报(医学版), 2014, 43(5): 583-587. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZJYB201405018.htm
[11] Ogawa K, Suzuki Y, Takahashi K, et al. Clinical Study of Seven Patients with Infarction in Territories of the Anterior Inferior Cerebellar Artery[J]. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis, 2017, 26(3): 574-581. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2016.11.118
[12] 李涛, 邱梓瀚, 刘向一, 等. 以单侧突发性耳聋为首发症状的急性脑梗塞一例报告[J]. 中国听力语言康复科学杂志, 2020, 18(1): 35-36. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TLKF202001012.htm
[13] Kinouchi T, Ishitani K, Uyama S, et al. Basilar artery occlusion presenting as sudden bilateral deafness: a case report[J]. J Med Case Rep, 2021, 15(1): 111.
[14] Pihl CE, Back CF, Iversen HK, Amin FM. Sudden Bilateral Deafness in a Patient with Transient Ischemic Attack: A Case Report[J]. Case Rep Neurol, 2021, 13(1): 119-122.
-

| 引用本文: | 赵博, 张文, 刘晖, 等. 1例以突聋伴眩晕为首发症状的“桥臂梗死”[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2022, 36(12): 964-965. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2022.12.015 |
| Citation: | ZHAO Bo, ZHANG Wen, LIU Hui, et al. A case of pontine infarction with sudden deafness and vertigo as the first symptom[J]. J Clin Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2022, 36(12): 964-965. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2022.12.015 |
- Figure 1.



 下载:
下载: