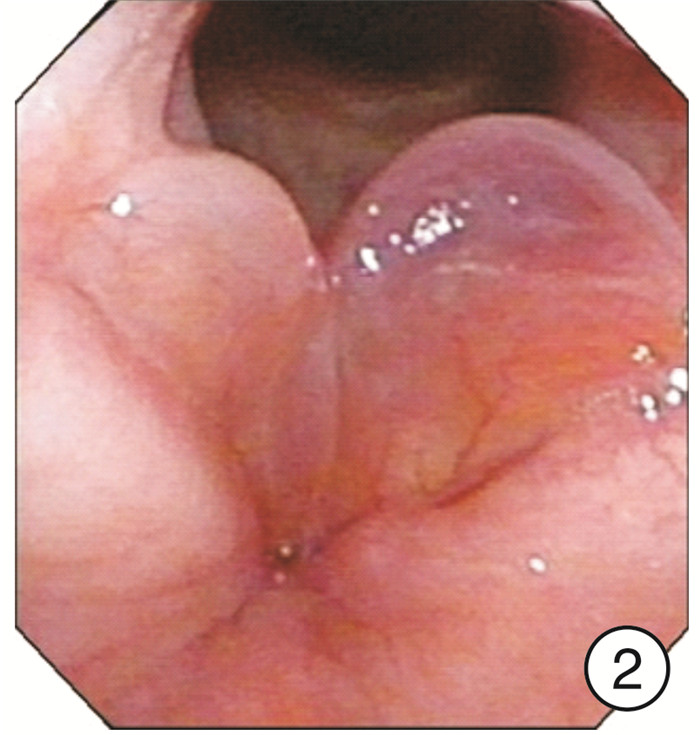
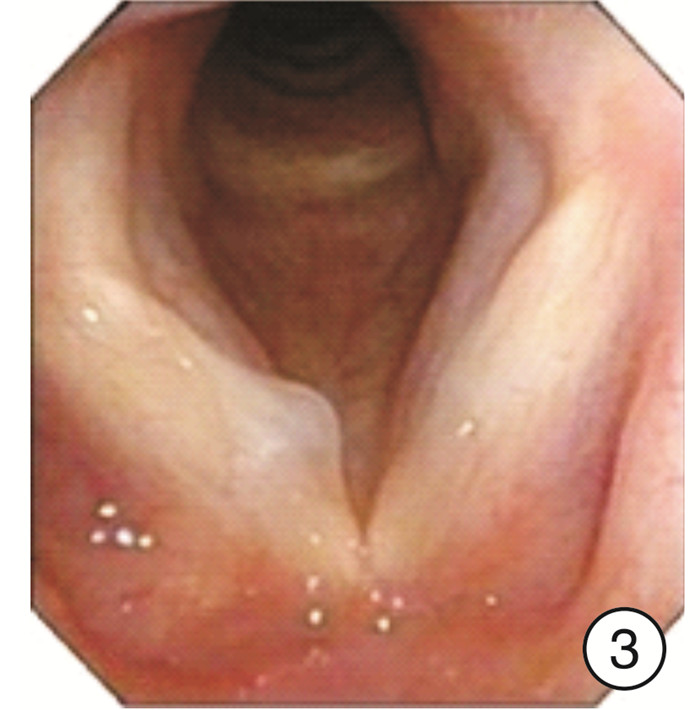
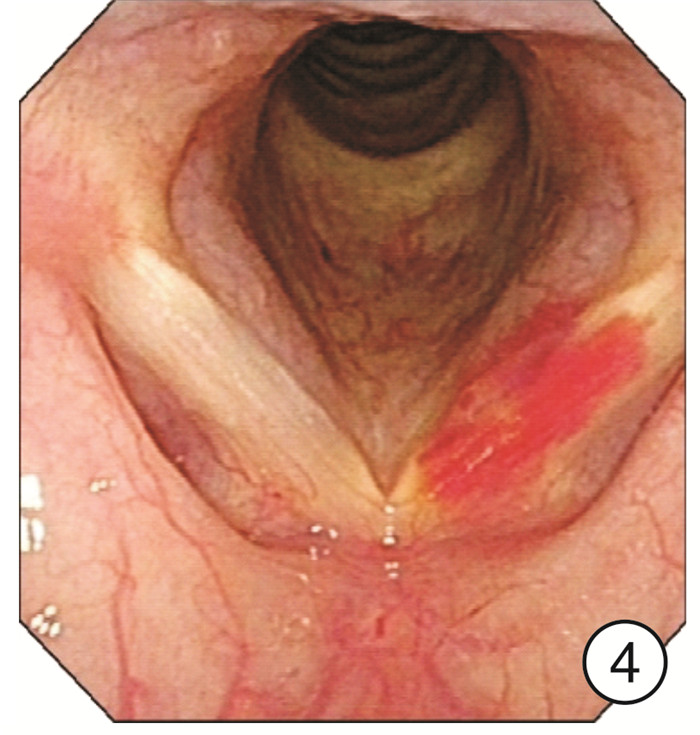
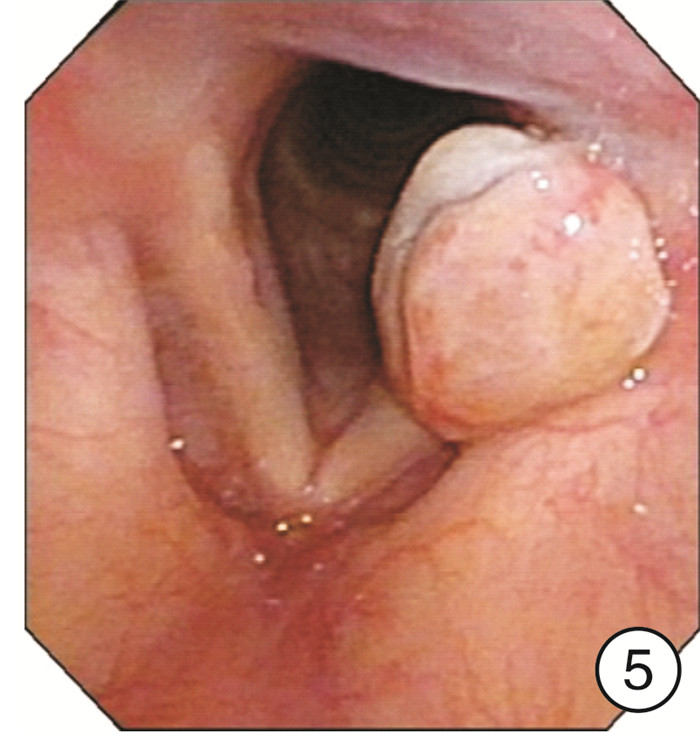
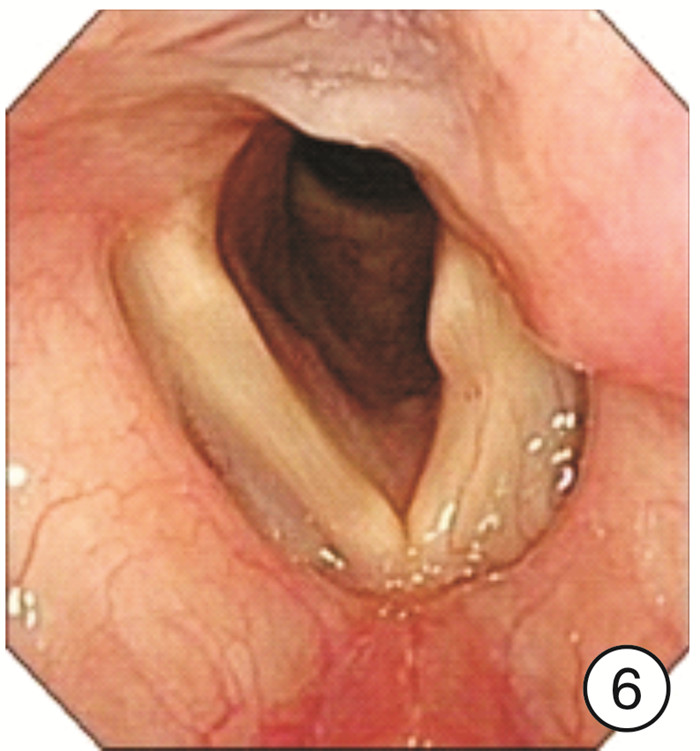
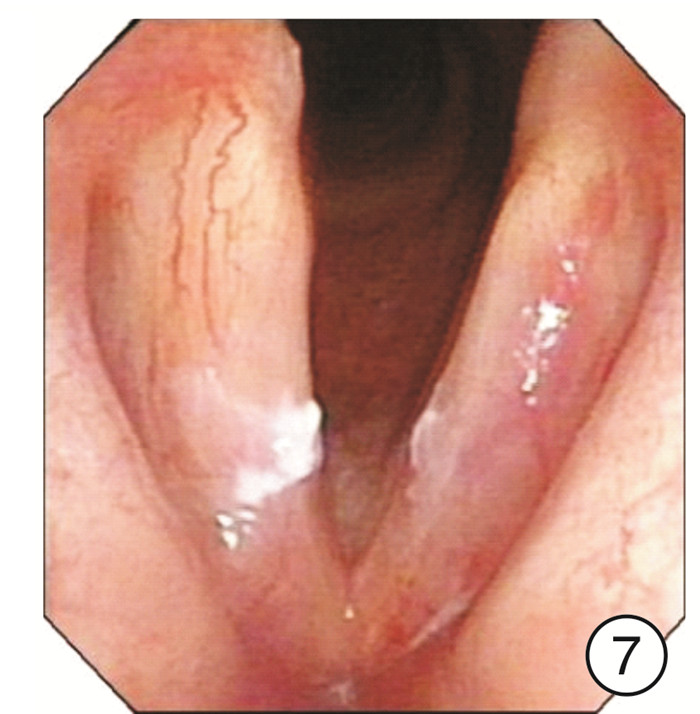
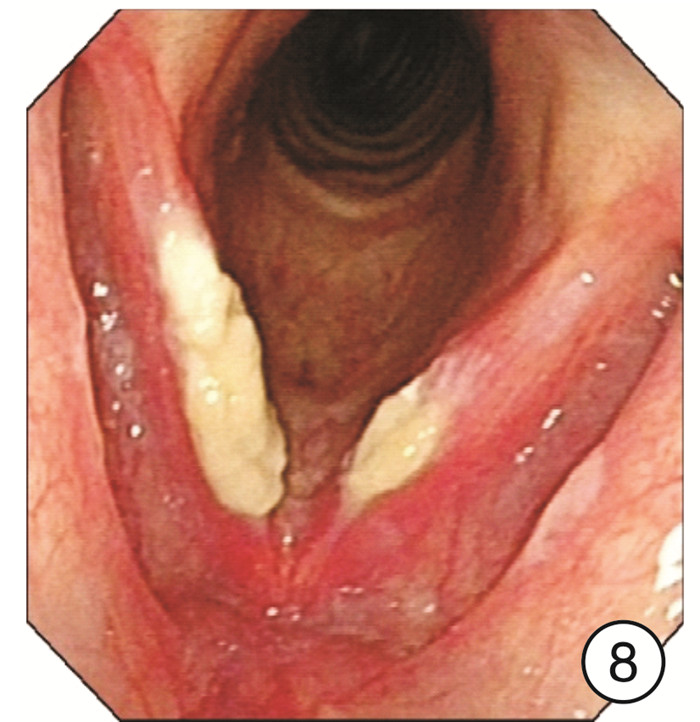
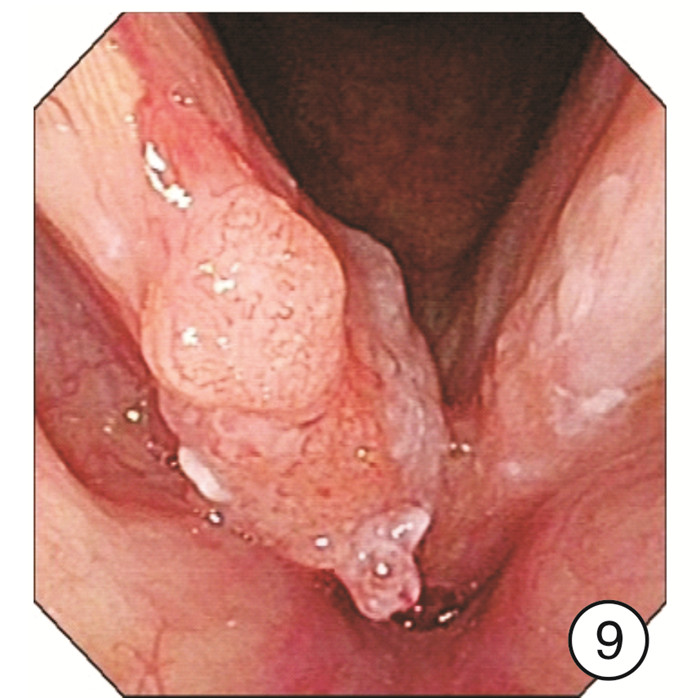
Clinical characteristics of 1330 elderly patients with voice diseases diagnosed by electronic laryngoscope
-
摘要: 目的 探讨电子喉镜对老年性嗓音疾病的诊断价值及老年嗓音疾病的临床特征。方法 收集2014年9月-2018年9月在南京大学医学院附属鼓楼医院耳鼻咽喉头颈外科门诊就诊且以声嘶为主诉的老年患者的临床资料,常规采用电子喉镜检查进行诊断,并分析检查结果。结果 纳入1330例年龄≥60岁的老年患者,其中男924例,女406例。各类嗓音疾病在男女不同性别中的分布有显著差异(P< 0.05),在老年男性患者中,占比前3位的分别是咽喉部恶性肿瘤239例(25.87%)、声带良性增生性疾病182例(19.70%)、声带白斑147例(15.91%);在老年女性患者中,占比前3位的分别是声带良性增生性疾病183例(45.07%)、喉炎70例(17.24%)、声带麻痹66例(16.26%)。在3组不同年龄段的老年患者中,不同嗓音疾病的分布有显著差异,60~69岁占比前3位的分别是声带良性增生性疾病298例(35.06%)、咽喉部恶性肿瘤132例(15.53%)、声带麻痹104例(12.24%);70~79岁占比前3位的分别是咽喉部恶性肿瘤91例(24.20%)、声带良性增生性疾病57例(15.16%)、声带麻痹55例(14.63%);在≥80岁老年患者中嗓音疾病占前3位的分别是咽喉部恶性肿瘤25例(24.04%)、声带麻痹21例(20.19%)、声带闭合不全16例(15.38%)。各类嗓音疾病在是否吸烟的患者中的分布也有显著差异(P< 0.05)。结论 随着社会老龄化的进程加快,老年人的嗓音问题应得到充分重视,声带良性增生性疾病在老年女性声嘶患者中最常见,咽喉部恶性肿瘤在吸烟的老年男性声嘶患者中高发,尤其值得关注。电子喉镜在诊断老年患者的嗓音疾病中发挥着重要的作用。Abstract: Objective To investigate the clinical features of electronic laryngoscope in the diagnosis of senile voice diseases.Methods Elderly patients who visited the outpatient department of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery, Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital from September 2014 to September 2018 were collected. All patients came in with hoarseness. All patients were routinely diagnosed by electronic laryngoscopy and the results were analyzed.Results A total of 1330 elderly patients aged 60 years and over were enrolled in this study, including 924 males and 406 females. There are significant differences in the distribution of various voice diseases in different genders(P< 0.05). Among male elderly patients, the top three were: 239 cases of throat malignant tumor(25.87%), 182 cases of vocal cord benign proliferative disease(19.70%), 147 cases of vocal cord leukoplakia(15.91%). Among female elderly patients, the top three diseases were: 183 cases(45.07%) of vocal cord benign proliferative disease, 70 cases(17.24%) of laryngitis, 66 cases(16.26%) of vocal cord paralysis. There were significant differences in the distribution of different voice disorders among the three different age groups of elderly patients. The top three elderly patients aged 60-69 years were: 298 cases(35.06%) of vocal cord benign proliferative diseases, 132 cases(15.53%) of laryngopharyngeal malignant tumors, 104 cases(12.24%) of vocal cord paralysis. The top three elderly patients aged 70-79 years were: 91 cases(24.20%) of laryngopharyngeal malignant tumors, 57 cases(15.16%) of vocal cord benign proliferative diseases, 55 cases(14.63%) of vocal cord paralysis. The top three elderly patients aged 80 years and above were: 25 cases(24.04%) of laryngopharyngeal malignant tumors, 21 cases(20.19%) of vocal cord paralysis, 16 cases(15.38%) of the vocal cords are not closed completely. There were also significant differences in the distribution of various voice diseases among smokers(P< 0.05).Conclusion With the acceleration of the aging of society, we should pay more attention to the voice of the elderly. The most common disease in elderly women with hoarseness is benign hyperplastic vocal cord disease. The high incidence of laryngeal malignant tumors in elderly male hoarseness patients who smoke should be paid special attention to. Electronic laryngoscope plays an important role in the diagnosis of voice diseases in elderly patients.
-
Key words:
- electronic laryngoscope /
- old age voice /
- hoarseness /
- polyp of vocal cord /
- laryngeal neoplasms
-

-
表 1 不同年龄组患者的疾病分布
例(%) 病因 60~69岁组 70~79岁组 ≥80岁组 总计 声带小结、息肉、囊肿 298(35.06) 57(15.16) 10(9.62) 365(27.44) 喉癌、下咽癌 132(15.53) 91(24.20) 25(24.04) 248(18.65) 声带麻痹 104(12.24) 55(14.63) 21(20.19) 180(13.53) 喉炎 98(11.53) 49(13.03) 14(13.46) 161(12.11) 声带白斑 94(11.06) 50(13.30) 9(8.65) 153(11.50) 声带闭合不全 44(5.18) 43(11.44) 16(15.38) 103(7.74) 声带任克水肿 41(4.82) 11(2.93) 2(1.92) 54(4.06) 声带后联合肉芽肿 7(0.82) 4(1.06) 2(1.92) 13(0.98) 声带沟 5(0.59) 1(0.27) 3(2.88) 9(0.68) 其他 27(3.18) 15(3.99) 2(1.92) 44(3.31) 表 2 不同性别及吸烟与否的疾病分布
例(%) 病因 性别 吸烟 男 女 是 否 声带小结、息肉、囊肿 182(19.70) 183(45.07) 106(14.15) 259(44.58) 喉癌、下咽癌 239(25.87) 9(2.22) 231(30.84) 17(2.93) 声带麻痹 114(12.34) 66(16.26) 101(13.48) 79(13.60) 喉炎 91(9.85) 70(17.24) 66(8.81) 95(16.35) 声带白斑 147(15.91) 6(1.48) 134(17.89) 19(3.27) 声带闭合不全 63(6.82) 40(9.85) 35(4.67) 68(11.70) 声带任克水肿 45(4.87) 9(2.22) 53(7.08) 1(0.17) 声带肉芽肿 8(0.87) 5(1.23) 3(0.40) 10(1.72) 声带沟 8(0.87) 1(0.25) 3(0.40) 6(1.03) 其他 27(2.92) 17(4.19) 17(2.27) 27(4.65) 合计 924(100.0) 406(100.0) 749(100.0) 581(100.0) -
[1] 段勇, 乔梁, 臧艳姿, 等. 儿童声嘶498例电子喉镜结果分析[J]. 中国临床医生杂志, 2021, 49(5): 596-598. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-8552.2021.05.029
[2] 唐守英, 王建波, 陈建东. 2580例声嘶患者临床分析和诊断[J]. 中国中西医结合耳鼻咽喉科杂志, 2014, 22(3): 203-205. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-4856.2014.03.014
[3] 侯丽珍, 韩德民, 徐文, 等. 儿童声嘶及良性增生性声带疾病的嗓音频谱分析[J]. 中国耳鼻咽喉头颈外科, 2005, 12(12): 771-774. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7002.2005.12.008
[4] 张晓莉, 张伶俐, 谭建国, 等. 1328例成人声嘶患者纤维喉镜检查结果分析[J]. 重庆医学, 2016, 45(3): 405-407. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-8348.2016.03.039
[5] Speyer R. Effects of voice therapy: a systematic review[J]. J Voice, 2008, 22(5): 565-580. doi: 10.1016/j.jvoice.2006.10.005
[6] 李翠娥, 周涛, 陶泽璋. 老年嗓音[J]. 听力学及言语疾病杂志, 2011, 19(1): 87-90. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TLXJ201101031.htm
[7] Pelucchi C, Gallus S, Garavello W, et al. Cancer risk associated with alcohol and tobacco use: focus on upper aero-digestive tract and liver[J]. Alcohol Res Health, 2006, 29(3): 193-198.
[8] Panwar A, Lindau R 3 rd, Wieland A. Management of permalignant lesions of the larynx[J]. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther, 2013, 13(9): 1045-1051. doi: 10.1586/14737140.2013.829643
[9] 张晴晴, 张宝根, 倪晓光. 窄带成像内镜对喉癌诊断价值的Meta分析[J]. 癌症进展, 2018, 16(14): 1719-1723. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-AZJZ201814008.htm
[10] 倪鑫, 王晓晔, 张玉焕, 等. 声带白斑与胃食管反流的相关性分析[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2008, 88(19): 1323-1326. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0376-2491.2008.19.008
[11] 时海波, 张亮, 刘业海. 老年反流性咽喉炎的诊断与治疗[J]. 实用老年医学, 2014, 28(5): 363-367. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYLA201405005.htm
[12] Poelmans J, Tack J. Determinants of long-term out-come of patients with reflux related ear, nose and throat symptoms[J]. Dig Dis Sci, 2006, 51(2): 282-288. doi: 10.1007/s10620-006-3126-y
[13] 赵宁军, 祝江才, 孙臻锋, 等. 368例声带麻痹病因分析[J]. 听力学及言语疾病杂志, 2005, 13(2): 105-107. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TLXJ200502012.htm
[14] 王瑜, 王存德, 江波, 等. 老年人肺癌诊治特点(附200例临床分析)[J]. 中华实用医学, 2003, 5(7): 66-67. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYZZ200203023.htm
[15] 苏惠芹. 老年人单侧声带麻痹39例病因分析[J]. 中国眼耳鼻喉科杂志, 2015, 15(6): 423-424. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YRBH201506019.htm
[16] Rukhman N, Silverberg A. Thyroid cancer in older men[J]. Aging Male, 2011, 14(2): 91-98.
[17] 龚建平, 张仁希. 老年人甲状腺癌88例临床分析[J]. 中华肿瘤杂志, 2007, 29(2): 150. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYQY200602009.htm
[18] 王淑芬, 王智楠, 徐忠强. 4668例声嘶儿童电子鼻咽喉镜检查结果分析[J]. 听力学及言语疾病杂志, 2014, 22(6): 613-615. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TLXJ201406015.htm
[19] Hirano S, Sugiyama Y, Kaneko M, et al. Intracordal Injection of Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor in 100 Cases of Vocal Fold Atrophy and Scar[J]. Laryngoscope, 2021, 131(9): 2059-2064.
[20] Allen J. Cause of vocal fold scar[J]. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2010, 18(6): 475-480.
-




 下载:
下载: