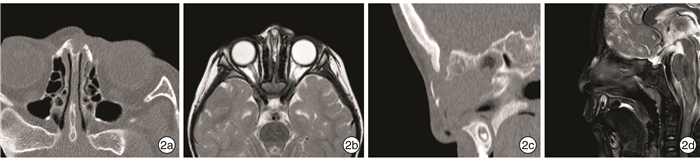
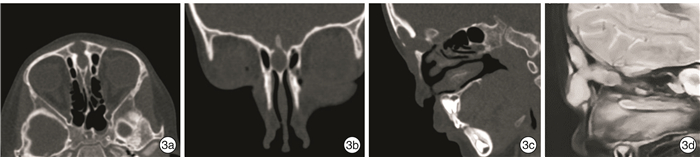
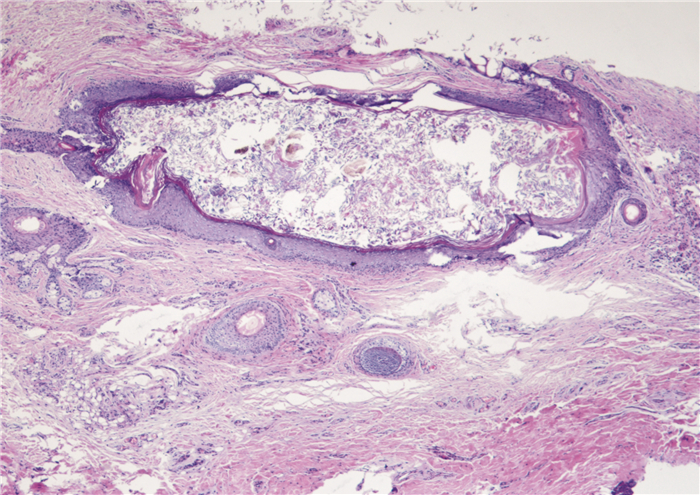
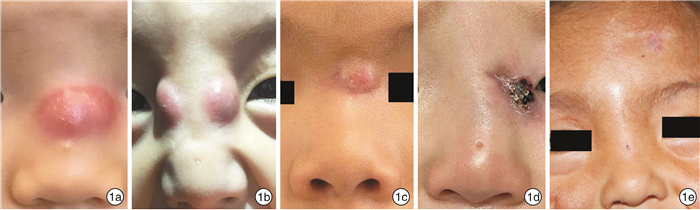
Clinical analysis of 59 cases of pediatric nasal dermal sinus cysts with midfacial infection as the first symptom
-
摘要: 目的总结以面中部感染为首发症状的儿童鼻中线囊肿及瘘管(NDSC)的临床特点及诊疗经验。方法收集2007年1月—2021年12月就诊于北京儿童医院的59例NDSC继发额鼻眶区感染患儿的临床资料。均完善薄层CT及MRI检查,并进行全身麻醉内镜辅助下囊肿及瘘管切除术。结果59例病例包括囊肿1例,瘘管58例。NDSC主要部位包括鼻根20例(33.9%),鼻梁34例(57.6%),鼻尖4例(6.8%),鼻尖及鼻根1例(1.7%)。病变深度包括鼻额骨浅表型6例(10.2%),鼻额骨型33例(55.9%),颅内硬膜外型19例(32.2%),颅内硬膜内型1例(1.7%)。感染灶主要部位包括内眦15例(25.4%),鼻背22例(37.3%),鼻根16例(27.1%),前额部6例(10.2%)。59例患儿中,合并其他疾病7例(11.9%),外鼻畸形4例(6.8%)。手术入路包括横行小切口12例(20.3%),纵行小切口41例(69.5%),开放式整形切口4例(6.8%),双顶冠状切口2例(3.4%)。病变范围与MRI结果均完全符合。所有患儿手术过程顺利,未行一期鼻背重建术。术后随访7~173个月(平均52.2个月),复发6例,均为鼻梁瘘管原位复发,再次手术,随访至今无复发。全部患儿外鼻无畸形,外观满意。结论以面中部感染为首发症状的儿童NDSC感染临床少见,表现多样。早期诊断及合理化治疗对于提高治愈率至关重要。高分辨率MRI辅以CT扫描对于判断NDSC的走行,尤其是与颅内贯通情况具有重要意义。治疗目标是在彻底切除病灶的前提下尽量做到微创、个体化,并兼顾美容需求。Abstract: ObjectiveTo review the clinical and radiological presentation and management of infected nasal dermal sinus cysts(NDSC) in children.MethodsClinical data were collected from 59 NDSC children with secondary fronto-orbital area infection who presented to Beijing Children's Hospital from January 2007 to December 2021. All patients underwent preoperative imaging workup, including MRI and CT. All patients underwent endoscopic excision of a NDSC under general anesthesia.ResultsA total of 59 patients were included in the study, while 58 presented with a sinus, 1 presented with a cyst.The main lesions of NDSC included nasal root in 20 cases (33.9%), nasal bridge in 34 cases (57.6%), nasal tip in 4 cases (6.8%), and nasal tip and nasal root in 1 case (1.7%). The depth of lesions included 6 cases (10.2%) of superficial type of nasal frontal bone, 33 cases (55.9%) of nasal frontal bone, 19 cases (32.2%) of intracranial epidural type, and 1 case (1.7%) of intracranial epidural type. The main sites of infection included inner canthus in 15 cases (25.4%), nasal dorsum in 22 cases (37.3%), nasal root in 16 cases (27.1%), and forehead in 6 cases (10.2%). Among 59 cases, 7 cases (11.9%) were complicated with other diseases, and 4 cases(6.8%) had external nasal deformities. Surgical approaches included transverse incision in 12 cases(20.3%), minimal midline vertical incision in 41 cases (69.5%), external rhinoplasty in 4 cases (6.8%) and bicoronal incision with vertical incision in 2 cases (3.4%). The range of lesions was completely consistent with MRI results.All cases were successfully operated without one-stage nasal dorsum reconstruction. All patients were followed up from 7 to 173 months(average 52.2 months). There were 6 cases of recurrence, all of which were in situ recurrence. The operation was performed again, and no recurrence has occurred since the follow-up, No nasal deformity was noted, and cosmetic outcome were favorable for all patients.ConclusionNDSC infection in children with midfacial infection as the first symptom is rare in clinical practice, and its manifestations are diverse. Early diagnosis and rational treatment are very important to improve the cure rate.Preoperative high resolution MRI combined with CT scanning is of great significance in judging the course of NDSC, especially the intracranial extension. The treatment goal is to achieve minimally invasive and individualized treatment under the premise of complete excision of the lesion, and take into account the cosmetic needs.
-
Key words:
- child /
- nasal dermoid /
- sinus /
- surgical procedures
-

-
表 1 59例儿童NDSC继发感染的临床特征
临床特征 例数(%)/ X±S 临床特征 例数(%)/ X±S 性别 感染部位 男 34(57.6) 内眦 15(25.4) 女 25(42.4) 鼻背 22(37.3) 年龄/月 38.14±31.67 鼻根 16(27.1) 外鼻畸形 前额 4(6.8) 有 4(6.8) 鼻根+前额 1(1.7) 无 55(93.2) 前额+双上睑 1(1.7) 瘘管部位 合并疾病 鼻梁 34(57.6) 有 7(11.9) 鼻根 20(33.9) 无 52(88.1) 鼻尖 4(6.8) 手术切口 鼻尖+鼻根 1(1.7) 纵行 41(69.5) 瘘管深度 横行 12(20.3) 浅表型 6(10.2) 双顶冠状切口 2(3.4) 鼻额骨型 33(55.9) 整形切口 4(6.8) 硬膜外型 19(32.2) 随访时间/月 52.19±45.39 硬膜内型 1(1.7) 预后 复发 6(10.2) 无 53(89.8) -
[1] Sessions RB. Nasal dermal sinuses--new concepts and explanations[J]. Laryngoscope, 1982, 92(8 Pt 2 Suppl 29): 1-28.
[2] El-Fattah AM, Naguib A, El-Sisi H, et al. Midline nasofrontal dermoids in children: A review of 29 cases managed at Mansoura University Hospitals[J]. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, 2016, 83: 88-92. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2016.01.005
[3] Naina P, Jonathan GE, Prabhakar M, et al. Pediatric nasal dermoid-a decade's experience from a South Indian tertiary care centre[J]. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, 2020, 139: 110418. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2020.110418
[4] 赵长青, 安云芳, 赵海亮, 等. 鼻背皮样囊肿合并颅内病变一例[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉科杂志, 2004, 39(11): 57-58. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHEB200411016.htm
[5] 刘卫一, 张亚梅, 张振英. 先天性鼻正中瘘管及皮样囊肿10例[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2007, 21(15): 709-710. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH200715014.htm
[6] 杨小健, 张杰, 唐力行, 等. 儿童先天性鼻中线囊肿及瘘管切除术[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2020, 55(3): 230-235. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-0860.2020.03.008
[7] 张亚梅, 倪鑫, 张天宇. 实用儿童耳鼻咽喉头颈科学[M]. 2版. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2021: 424-428.
[8] Rahbar R, Shah P, Mulliken JB, et al. The presentation and management of nasal dermoid: a 30-year experience[J]. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2003, 129(4): 464-471. doi: 10.1001/archotol.129.4.464
[9] Herrington H, Adil E, Moritz E, et al. Update on current evaluation and management of pediatric nasal dermoid[J]. Laryngoscope, 2016, 126(9): 2151-2160. doi: 10.1002/lary.25860
[10] Hartley BE, Eze N, Trozzi M, et al. Nasal dermoids in children: a proposal for a new classification based on 103 cases at Great Ormond Street Hospital[J]. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, 2015, 79(1): 18-22. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2014.10.020
[11] Hedlund G. Congenital frontonasal masses: developmental anatomy, malformations, and MR imaging[J]. Pediatr Radiol, 2006, 36(7): 647-662; quiz 726-727. doi: 10.1007/s00247-005-0100-3
[12] Winterton RI, Wilks DJ, Chumas PD, et al. Surgical correction of midline nasal dermoid sinus cysts[J]. J Craniofac Surg, 2010, 21(2): 295-300. doi: 10.1097/SCS.0b013e3181cf5f44
[13] 易彬, 石润杰, 王珮华, 等. 鼻背中线瘘管及先天性皮样囊肿的治疗[J]. 中国耳鼻咽喉头颈外科, 2013, 20(7): 356-359. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-EBYT201307010.htm
[14] Ortlip T, Ambro BT, Pereira KD. Midline approach to pediatric nasofrontal dermoid cysts[J]. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2015, 141(2): 174-177. doi: 10.1001/jamaoto.2014.3185
[15] Makhdoom N, Abo El Ezz TA, Abdel-Haleem M. Management of midline nasal dermoid lesions in children by external rhinoplasty[J]. J Taibah Univ Med Sci, 2017, 12(4): 324-328.
[16] Holzmann D, Huisman TA, Holzmann P, et al. Surgical approaches for nasal dermal sinus cysts[J]. Rhinology, 2007, 45(1): 31-35.
[17] Purnell CA, Skladman R, Alden TD, et al. Nasal dermoid cysts with intracranial extension: avoiding coronal incision through midline exposure and nasal bone osteotomy[J]. J Neurosurg Pediatr, 2019: 1-7.
[18] Adil E, Rahbar R. Paediatric nasal dermoid: evaluation and management[J]. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2021, 29(6): 487-491.
-




 下载:
下载: