-
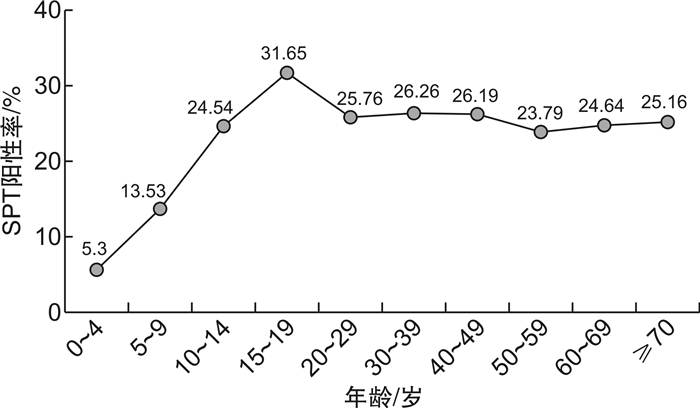
摘要: 目的了解北京地区变应性鼻炎(AR)和/或过敏性哮喘患者蟑螂致敏特点,为蟑螂致敏患者的防治提供依据。方法回顾性分析2017年1月—2019年12月就诊于北京世纪坛医院变态反应科门诊的AR和/或哮喘患者,采用蟑螂过敏原试剂进行皮肤点刺试验(SPT),比较不同年龄和疾病患者蟑螂致敏情况,观察蟑螂致敏的人群分布特征。采用SAS 9.4软件进行统计学分析。结果纳入9915例患者,蟑螂SPT总阳性率达24.79%(2458/9915),其中15~19岁年龄组阳性率最高(31.65%),0~14岁的患儿SPT阳性率随着年龄的增长逐渐增加,>20岁的患者随着年龄的增长SPT阳性率基本持平。AR患者蟑螂SPT阳性率24.83%(2355/9484),过敏性哮喘患者蟑螂SPT阳性率26.38%(410/1554),AR伴哮喘患者蟑螂SPT阳性率27.34%(307/1123); 单一蟑螂SPT阳性者占9.64%(237/2458),蟑螂合并其他室内吸入性过敏原SPT阳性者占90.36%(2221/2458),合并粉尘螨、屋尘螨、尘土、猫毛和狗毛的SPT阳性率分别为74.25%(1825/2458)、66.27%(1629/2458)、58.99%(1450/2458)、43.08%(1059/2458)和40.85%(1004/2458)。在AR、哮喘、AR伴哮喘3种疾病中,成年组蟑螂SPT阳性率均高于未成年组,其中AR组有统计学差异(25.81% vs.19.07%,P < 0.001)。未成年组中,AR伴哮喘患儿的SPT阳性率高于AR和哮喘。结论北京地区AR和/或过敏性哮喘患者蟑螂致敏性较高,多合并多重吸入过敏原致敏,成人致敏程度高于未成年人。Abstract: ObjectiveTo investigate the sensitization characteristics of cockroach in patients with allergic rhinitis(AR) and/or allergic asthma in Beijing area, and to provide basis for the prevention and treatment of cockroach sensitized population.MethodsClinical data of patients with allergic rhinitis and/or asthma from January 2017 to December 2019 treated in the outpatient Department of Allergy of Beijing Shijitan Hospital were retrospectively analyzed.Skin prick test (SPT) was performed with cockroach allergen reagents. The cockroach sensitization of patients with different ages and diseases was compared, and the population distribution characteristics of cockroach sensitization were observed.Statistical analysis was performed using SAS 9.4 software.ResultsA total of 9915 patients were enrolled in the end.The total positive rate of cockroach SPT was 24.79%(2458/9915), with the highest positive rate (31.65%) in 15-19 years old group. The positive rate of SPT increased with age in patients less than 14 years old, while the positive rate of SPT was basically flat with age in patients more than 20 years old.The positive rate of cockroach SPT was 24.83% (2355/9484) in allergic rhinitis patients, 26.38% (410/1554) in allergic asthma patients, and 27.34% (307/1123) in allergic rhinitis combined with asthma patients. Single cockroach SPT positive accounted for 9.64% (237/2458), cockroach with other indoor inhalation allergens SPT positive accounted for 90.36% (2221/2458). The positive SPT rates for combined Der f, Der p, house dust, cat dander, and dog dander were 74.25% (1825/2458), 66.27% (1629/2458), 58.99% (1450/2458), 43.08% (1059/2458), and 40.85% (1004/2458), respectively.In allergic rhinitis, asthma, and allergic rhinitis combined with asthma, the cockroach SPT positive rate was higher in the adult group than that in juvenile group, and the difference of positive rate in allergic rhinitis group was statistically significant(25.81% vs 19.07%, P < 0.001).In the juvenile group, the positive rate of SPT in AR combined with asthma was higher than that in AR and that in asthma.ConclusionCockroach allergy in patients with AR and/or allergic asthma in Beijing is relatively high, most of them are sensitized by multiple inhalation allergens, and the sensitization degree of adults is higher than that of juvenile.
-
Key words:
- rhinitis, allergic /
- allergic asthma /
- cockroach /
- skin prick test /
- cross-reaction
-

-
表 1 9915例患者的基本资料
特征 例数 百分率/% 性别 男 3890 39.23 女 6025 60.77 年龄/岁 0~4 132 1.33 5~9 584 5.89 10~14 485 4.89 15~19 357 3.60 20~29 1879 18.95 30~39 2909 29.34 40~49 1428 14.40 50~59 1215 12.25 60~69 767 7.74 ≥70 159 1.60 疾病类型 AR 9484 95.65 过敏性哮喘 1554 15.67 AR伴哮喘 1123 11.33 单一ARa) 8361 84.33 单一过敏性哮喘b) 431 4.35 注:a)指AR为临床唯一诊断; b)指过敏性哮喘为临床唯一诊断。 表 2 单一蟑螂致敏与多重过敏原致敏患者的基本特征比较
基本特征 单一蟑螂致敏(n=237) 多重过敏原致敏(n=2221) χ2 P值 性别 1.66 0.197 6 男 120(50.63) 1027(46.24) 女 117(49.37) 1194(53.76) 平均年龄/岁 38.86±15.14 36.26±15.33 2.48 0.013 2 年龄/岁 15.24 0.084 6 0~4 0(0) 7(0.32) 5~9 6(2.53) 73(3.29) 10~14 4(1.69) 115(5.18) 15~19 12(5.06) 101(4.55) 20~29 38(16.03) 446(20.08) 30~39 77(32.49) 687(30.93) 40~49 47(19.83) 327(14.72) 50~59 29(12.24) 260(11.71) 60~69 17(7.17) 172(7.74) ≥70 7(2.95) 33(1.49) 疾病类型 AR 228(96.20) 2127(95.77) 0.10 0.750 8 过敏性哮喘 29(12.24) 381(17.15) 3.73 0.053 5 AR伴哮喘 20(8.44) 287(12.92) 3.94 0.047 2 单一AR 208(87.76) 1840(82.85) 3.73 0.053 5 单一过敏性哮喘 9(3.80) 94(4.23) 0.10 0.750 8 表 3 蟑螂SPT阳性患者合并其他吸入性过敏原情况(n=2458)
过敏原 阳性例数 阳性率/% 粉尘螨 1825 74.25 屋尘螨 1629 66.27 尘土 1450 58.99 猫毛 1059 43.08 狗毛 1004 40.85 表 4 年龄分组在不同疾病中蟑螂SPT阳性率比较
疾病 未成年组 成年组 χ2 P值 例数 阳性例数(%) 例数 阳性例数(%) AR 1374 262(19.07) 8110 2093(25.81) 28.589 < 0.001 哮喘 183 39(21.31) 1371 371(27.06) 2.747 0.097 AR伴哮喘 137 34(24.82) 986 273(27.69) 0.499 0.480 -
[1] 贺盼, 马强. 国内卫生害虫蜚蠊的危害、种类、分布及其防制研究进展[J]. 中国保健营养, 2017, 27(23): 62-64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7484.2017.23.078
[2] Kumar M, Gupta RK, Kumar R, et al. Cockroach exposure and its allergy sensitization in asthma patients[J]. Monaldi Arch Chest Dis, 2021, 91(3).
[3] 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志编辑委员会鼻科组, 中华医学会耳鼻咽喉头颈外科学分会鼻科学组. 中国变应性鼻炎诊断和治疗指南(2022年, 修订版)[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2022, 57(2): 106-129.
[4] Bousquet J, Hellings PW, Agache I, et al. Allergic Rhinitis and its Impact on Asthma(ARIA)Phase 4(2018): Change management in allergic rhinitis and asthma multimorbidity using mobile technology[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2019, 143(3): 864-879. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2018.08.049
[5] 中华医学会变态反应分会呼吸过敏学组(筹), 中华医学会呼吸病学分会哮喘学组. 中国过敏性哮喘诊治指南(第一版, 2019年)[J]. 中华内科杂志, 2019, 58(9): 636-655.
[6] 王洪田, 马琳, 王成硕, 等. 过敏原皮肤点刺试验的专家共识[J]. 北京医学, 2020, 42(10): 966-985. doi: 10.15932/j.0253-9713.2020.10.912
[7] Weinberg, EG. The WAO white book on allergy 2011-2012: Review article[J]. Curr Allergy Clin Immunol, 2011, 24: 156-157.
[8] Gelfand EW. Inflammatory mediators in allergic rhinitis[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2004, 114(5 Suppl): S135-138.
[9] da Silva Antunes R, Sutherland A, Frazier A, et al. Heterogeneity of magnitude, allergen immunodominance, and cytokine polarization of cockroach allergen-specific T cell responses in allergic sensitized children[J]. Clin Transl Allergy, 2021, 11(8): e12073.
[10] 赵飞, 李丹, 孙庆山, 等. 皮肤点刺试验诊断过敏性鼻炎效能及过敏原检出率的临床分析[J]. 中国实验诊断学, 2022, 26(1): 14-16. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZSZD202201005.htm
[11] 李春林, 谢伟伟, 刘硕, 等. 海南省500例蟑螂过敏皮肤点刺试验分析[J]. 海南医学, 2011, 22(10): 16-17.
[12] 张少杰, 班莫璐, 王瑢, 等. 南宁地区变应性鼻炎与天气因素相关性的探讨[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2021, 35(1): 1-8.
[13] 张楠楠, 吴云文, 张庆丰, 等. 深圳地区的变应性鼻炎患者吸入性变应原分布特点及结果分析[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2022, 36(6): 467-472.
[14] 秦嘉, 于春水, 杨和荣, 等. 川中地区2975例过敏性疾病患者过敏原筛查结果分析[J]. 国际检验医学杂志, 2020, 41(12): 1448-1452.
[15] Do DC, Zhao Y, Gao P. Cockroach allergen exposure and risk of asthma[J]. Allergy, 2016, 71(4): 463-474.
[16] Gruchalla RS, Pongracic J, Plaut M, et al. Inner City Asthma Study: relationships among sensitivity, allergen exposure, and asthma morbidity[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2005, 115(3): 478-485.
[17] Kwizera R, Wadda V, Mugenyi L, et al. Skin prick reactivity among asthmatics in East Africa[J]. World Allergy Organ J, 2020, 13(6): 100130.
[18] AlKhater SA. Sensitization to Common Aeroallergens in Asthmatic Children in the Eastern Region of Saudi Arabia[J]. Saudi J Med Med Sci, 2017, 5(2): 136-141.
[19] Kulalert P, Sritipsukho P, Nanthapisal S, et al. Concordance of skin test reactivity between indoor inhalant allergens among children with allergic respiratory disease[J]. BMC Pediatr, 2021, 21(1): 338.
[20] Svendsen ER, Gonzales M, Commodore A. The role of the indoor environment: Residential determinants of allergy, asthma and pulmonary function in children from a US-Mexico border community[J]. Sci Total Environ, 2018, 616-617: 1513-1523.
[21] 孙金, 张锡平, 赵庆武. 支气管哮喘与过敏性鼻炎患者对蟑螂变应原的反应性研究[J]. 中国医药导刊, 2010, 12(12): 2120-2120, 2123.
[22] 孙宝清, 李靖, 钟南山. 全国多中心支气管哮喘与过敏性鼻炎门诊患者对蟑螂变应原皮肤反应性的调查[J]. 中华哮喘杂志(电子版), 2009, 3(1): 1-5.
[23] Luo W, Chen H, Wu Z, et al. A new trend in sensitization to cockroach allergen: A cross-sectional study of indoor allergens and food allergens in the inland region of Southwest China[J]. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol, 2020.
[24] Matricardi PM, Kleine-Tebbe J, Hoffmann HJ, et al. EAACI Molecular Allergology User's Guide[J]. Pediatr Allergy Immunol, 2016, 27 Suppl 23: 1-250.
[25] Lee MF, Song PP, Hwang GY, et al. Sensitization to Per a 2 of the American cockroach correlates with more clinical severity among airway allergic patients in Taiwan[J]. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol, 2012, 108(4): 243-248.
[26] Liu T, He SH, Zheng PY, et al. Staphylococcal enterotoxin B increases TIM4 expression in human dendritic cells that drives naïve CD4 T cells to differentiate into Th2 cells[J]. Mol Immunol, 2007, 44(14): 3580-3587.
[27] Xu ZQ, Zhu LX, Lu C, et al. Identification of Per a 13 as a novel allergen in American cockroach[J]. Mol Immunol, 2022, 143: 41-49.
[28] Barbosa MC, Santos AB, Ferriani VP, et al. Efficacy of recombinant allergens for diagnosis of cockroach allergy in patients with asthma and/or rhinitis[J]. Int Arch Allergy Immunol, 2013, 161(3): 213-219.
[29] Arruda LK, Barbosa MC, Santos AB, et al. Recombinant allergens for diagnosis of cockroach allergy[J]. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep, 2014, 14(4): 428.
-

| 引用本文: | 索爽, 马婷婷, 王洪田, 等. 北京地区蟑螂致敏的特征分析[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2022, 36(11): 835-840. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2022.11.005 |
| Citation: | SUO Shuang, MA Tingting, WANG Hongtian, et al. Sensitization characteristics of cockroach in Beijing area[J]. J Clin Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2022, 36(11): 835-840. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2022.11.005 |
- Figure 1.



 下载:
下载: