The changes in subjective visual vertical after otolith reduction in patients with BPPV
-
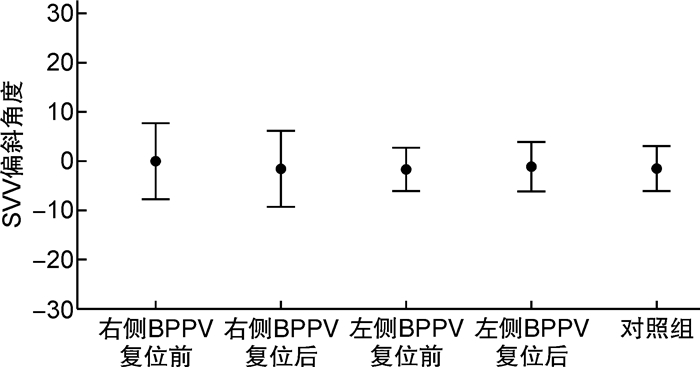
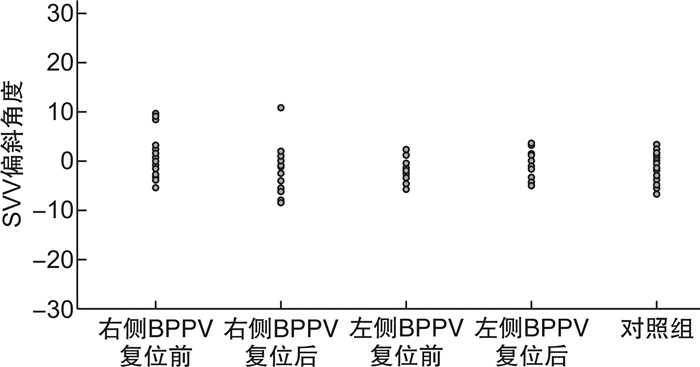
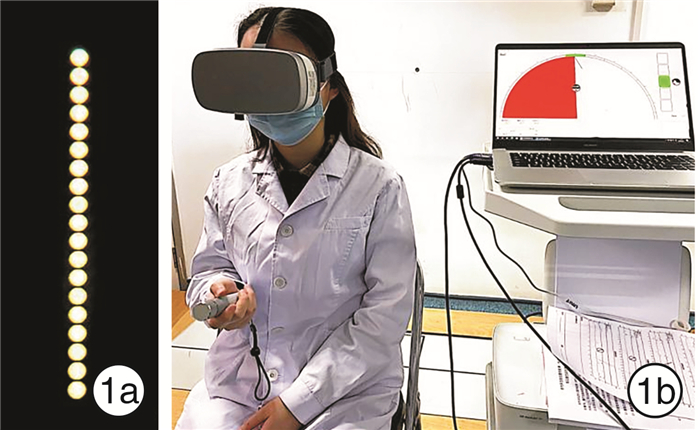
摘要: 目的观察分析良性阵发性位置性眩晕(BPPV)患者耳石复位后主观视觉垂直线(SVV)的变化特点。方法选取确诊BPPV且耳石复位成功的46例患者为试验组(后半规管BPPV管石症31例、水平半规管BPPV管石症15例,右耳29例、左耳17例),健康青年志愿者50例为对照组。利用虚拟现实SVV检查系统,分别对试验组患者耳石复位前后和对照组进行正头位0° SVV检测,分析试验组患者耳石复位前后SVV的偏斜角度。结果对照组的SVV为(-1.57±2.28)°; 试验组右耳及左耳BPPV患者复位前的SVV分别为(0.08±3.83)°和(-1.69±2.23)°,复位后的SVV分别为(-1.52±3.74)°和(-1.04±2.50)°。组间分析,仅右耳BPPV复位前与对照组、右耳BPPV复位前后的SVV偏斜角度的差异有统计学意义。试验组耳石复位后18例偏斜角度变大,28例偏斜角度变小,其中偏斜角度变小甚至转向对侧偏斜的有13例。结论BPPV患者椭圆囊功能障碍导致对重力垂直线的判断误差,复位耳石可对椭圆囊产生新刺激、影响其功能状态,SVV检测可为BPPV患者的椭圆囊功能评估提供帮助。Abstract: ObjectiveTo observe and analyze the changes in subjective visual vertical(SVV) after otolith reduction in patients with BPPV.Methods46 patients with confirmed BPPV recieving successful otolith reduction were selected as the test group. 31 cases of posterior canal stones and 15 cases of horizontal semicircular canal stones, 29 cases of right ear and 17 cases of left ear. Fifty cases of healthy young volunteers were in the control group. Using the virtual reality SVV examination system, 0° SVV in the positive head were tested in the test group patients before and after the reduction of SVV, and were tested in the control group.The deviation angle of the SVV before and after the otolith reduction in the test group were analyzed.ResultsBefore otoliths reduction, the SVV was (0.08±3.83)° of right BPPV and was (-1.69±2.23)° of left BPPV. After otoliths reduction, the SVV was (-1.52±3.74)° of right BPPV and was (-1.04±2.50)° of left BPPV. In the control group, the SVV was(-1.57±2.28)°. The changes of SVV deflection angle between the control group and the right BPPV before the otolith reduction, and before and after the otolith reduction in the right BPPV were analyzed, and the differences were all statistically significant. There was no significant difference in SVV deflection angle between the left BPPV(before and after reduction) and the control group. In the test group, after the otolith reduction, 18 cases had larger bias angles, 28 cases had smaller bias angle among which 13 cases the deviation angle even turned to the contralateral side.ConclusionUtriculare dysfunction in patients with BPPV leads to the judgment error of SVV. Reduction of otolithoid can cause new stimulation to the eutricule and affect its functional status. SVV detection can provide help for the evaluation of utricular function in patients with BPPV.
-
Key words:
- vertigo /
- subjective visual vertical /
- utricle
-

-
表 1 有残余症状组和无残余症状组复位前后的SVV与对照组比较
组别 SVV偏斜角度/(°) P值 对照组 -1.57±2.28 无残余症状组 复位前 -0.61±3.46 0.17 复位后 -0.84±3.40 0.29 有残余症状组 复位前 -0.50±3.42 0.23 复位后 -2.40±2.96 0.35 注:P值为不同组别SVV偏斜角度与对照组比较。 -
[1] Ji L, Zhai S. Aging and the peripheral vestibular system[J]. J Otol, 2018, 13(4): 138-140.
[2] Chetana N, Jayesh R. Subjective Visual Vertical in Various Vestibular Disorders by Using a Simple Bucket Test[J]. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2015, 67(2): 180-184.
[3] 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志编辑委员会, 中华医学会耳鼻咽喉头颈外科学分会. 良性阵发性位置性眩晕诊断和治疗指南(2017)[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2017, 52(3): 173-177. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-0860.2017.03.003
[4] 谷李欣, 陈建勇, 张勤, 等. 后半规管良性阵发性位置性眩晕病程对复位成功后残余症状的影响[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2021, 35(11): 976-980. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2021.11.004
[5] 刘晓薇, 孙敬武, 张波, 等. 良性阵发性位置性眩晕成功复位后残余头晕的危险因素分析[J]. 听力学及言语疾病杂志, 2018, 26(2): 148-151. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7299.2018.02.008
[6] 王兆霞, 张新江, 刘斌, 等. 良性发作性位置性眩晕患者残余头晕的危险因素分析[J]. 中华神经科杂志, 2013, 46(8): 527-530. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1006-7876.2013.08.008
[7] Faralli M, Manzari L, Panichi R, et al. Subjective visual vertical before and after treatment of a BPPV episode[J]. Auris Nasus Larynx, 2011, 38(3): 307-311. doi: 10.1016/j.anl.2010.10.005
[8] Faralli M, Lapenna R, Giommetti G, et al. Residual dizziness after the first BPPV episode: role of otolithic function and of a delayed diagnosis[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2016, 273(10): 3157-3165. doi: 10.1007/s00405-016-3947-z
[9] 成颖, 张玉忠, 陈飞云, 等. 虚拟现实辅助下的主观视觉垂直线与主观视觉水平线检测[J]. 中华耳科学杂志, 2019, 17(6): 895-899. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2922.2019.06.018
[10] 贾宏博, 郭世俊, 谢溯江, 等. 主观重力垂直线知觉检查及其常值标准[J]. 中华航空航天医学杂志, 2005, 16(1): 29-33. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHHK200501009.htm
[11] Imai T, Okumura T, Nishiike S, et al. Recovery of positional nystagmus after benign paroxysmal positional vertigo fatigue[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2018, 275(12): 2967-2973.
[12] 贾宏博, 于立身, 王奎年, 等. 椭圆囊和球囊在线加速度前庭知觉中的相互作用[J]. 中华航空医学杂志, 1996, 7(4): 222-224. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHHK604.010.htm
[13] Lee SK, Kim SJ, Park MS, et al. Otolith organ function according to subtype of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo[J]. Laryngoscope, 2014, 124(4): 984-988.
[14] Halmagyi GM, Colebatch JG, Curthoys IS. New tests of vestibular function[J]. Baillieres Clin Neurol, 1994, 3(3): 485-500.
[15] Hong SM, Park MS, Cha CI, et al. Subjective visual vertical during eccentric rotation in patients with benign paroxysmal positional vertigo[J]. Otol Neurotol, 2008, 29(8): 1167-1170.
[16] 汪晓锋, 周燚, 苏文玲, 等. 主观视觉垂直线/水平线对良性阵发性位置性眩晕患者耳石器功能的评估作用[J]. 中国耳鼻咽喉头颈外科, 2022, 29(1): 37-40, 51. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-EBYT202201009.htm
[17] Kobayashi H, Hayashi Y, Higashino K, et al. Dynamic and static subjective visual vertical with aging[J]. Auris Nasus Larynx, 2002, 29(4): 325-328.
[18] Ferreira MM, Cunha F, Ganança CF, et al. Subjective visual vertical with the bucket method in Brazilian healthy individuals[J]. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol, 2016, 82(4): 442-446.
[19] Böhmer A, Rickenmann J. The subjective visual vertical as a clinical parameter of vestibular function in peripheral vestibular diseases[J]. J Vestib Res, 1995, 5(1): 35-45.
[20] Gall RM, Ireland DJ, Robertson DD. Subjective visual vertical in patients with benign paroxysmal positional vertigo[J]. J Otolaryngol, 1999, 28(3): 162-165.
[21] Ferreira MM, Ganança MM, Caovilla HH. Subjective visual vertical after treatment of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo[J]. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol, 2017, 83(6): 659-664.
[22] 李斐, 肖本杰, 陈瑛, 等. 良性阵发性位置性眩晕复位后残余症状持续时间和病因分析[J]. 第二军医大学学报, 2018, 39(2): 216-219. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DEJD201802019.htm
[23] Van Nechel C, Toupet M, Bodson I. The subjective visual vertical[J]. Adv Otorhinolaryngol, 2001, 58: 77-87.
[24] 赵媛, 陈太生, 王巍, 等. 主观视觉重力线在前庭代偿评定中的应用初探[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2016, 51(5): 355-360.
[25] 黄爱萍, 顾东胜, 冯爱凤, 等. 良性阵发性位置性眩晕残余症状的影响因素及oVEMP分析[J]. 浙江医学, 2020, 42(23): 2511-2515. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZJYE202023008.htm
[26] 陈太生, 李姗姗, 董红, 等. 良性阵发性位置性眩晕半规管功能分析[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2012, 47(10): 793-798. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHER202102012.htm
[27] Doménech Campos E, Armengot Carceller M, Barona de Guzmán R. [Oculographic findings in 145 patients with benign paroxysmal positional vertigo][J]. Acta Otorrinolaringol Esp, 2006, 57(8): 339-344.
[28] 高铭媛, 王冬梅, 丁雷. 730例原发性良性阵发性位置性眩晕患者双温试验回顾性分析[J]. 中华耳科学杂志, 2022, 20(1): 72-77. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHER202201014.htm
-





 下载:
下载: