Surgical technique and risk control of tumor resection in parapharyngeal space via transoral endoscopic parapterygomandibular ligament internal approach
-
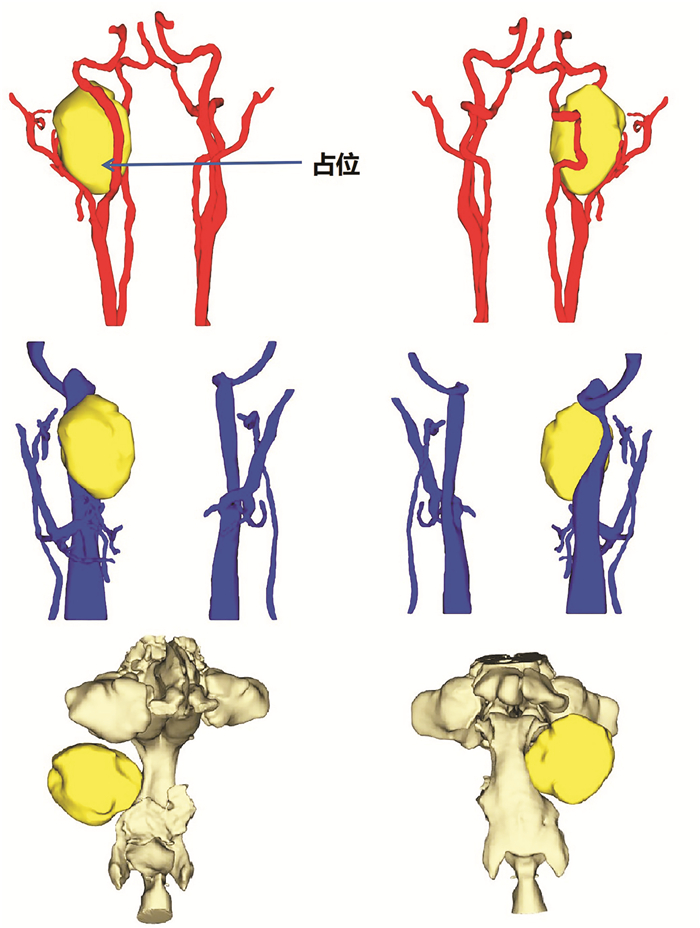
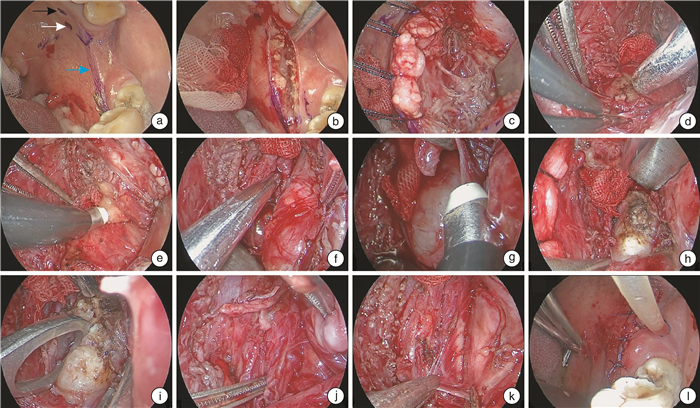
摘要: 由于咽旁间隙位置深在,解剖结构复杂,探索改良的咽旁间隙肿瘤手术进路成为近年来头颈外科的热点之一。经口内镜进路具有创伤小、路径短的优点,逐渐广泛应用于咽旁间隙肿瘤的切除。然而,由于手术空间有限,肿瘤暴露困难,导致经口内镜进路手术难度大,风险控制十分关键。经口内镜翼下颌韧带旁内进路可以充分暴露咽旁间隙肿瘤的上、下极,避免损伤腭大、腭小神经和血管,同时对口腔和软腭黏膜以及腭帆张肌和腭帆提肌的功能有良好的保护作用,手术创伤小,术后并发症少。Abstract: Due to the deep location and complex anatomy of the parapharyngeal space, the exploration of improved surgical approach for tumors in the parapharyngeal space is one of the hotspots in the head and neck surgery in recent years. Transoral endoscopic approach has the advantages of small trauma and short path, which is gradually widely used in the resection of tumors in the parapharyngeal space. However, due to the limited operation space and the difficulty of tumor exposure, it is laborious to operate through transoral approach, and the risk control is rather critical. The transoral endoscopic parapterygomandibular ligament internal approach can fully expose the upper and lower poles of tumors in the parapharyngeal space, and avoid damage to the greater and lesser palatine nerve and blood vessels. This surgical approach has a satisfactory protective effect on the sensory function of oral and soft palate mucosa, as well as the tensor velum palatine muscle and levator velum palatine muscle with less surgical trauma and fewer postoperative complications.
-

-
[1] Olsen KD. Tumors and surgery of the parapharyngeal space[J]. Laryngoscope, 1994, 104(5 Pt 2 Suppl 63): 1-28.
[2] Bradley PJ, Bradley PT, Olsen KD. Update on the management of parapharyngeal tumours[J]. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2011, 19(2): 92-98. doi: 10.1097/MOO.0b013e328342b9b4
[3] Goodwin WJ Jr, Chandler JR. Transoral excision of lateral parapharyngeal space tumors presenting intraorally[J]. Laryngoscope, 1988, 98(3): 266-269.
[4] 杨征, 陈晓红. 经口内镜高位咽旁间隙良性肿瘤切除术临床分析[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2017, 31(15): 1187-1190. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201715013.htm
[5] Li L, London NR Jr, Gao Y, et al. Endoscopic transoral approach for resection of retrostyloid parapharyngeal space tumors: Retrospective analysis of 16 patients[J]. Head Neck, 2020, 42(12): 3531-3537. doi: 10.1002/hed.26415
[6] Paderno A, Piazza C, Nicolai P. Recent advances in surgical management of parapharyngeal space tumors[J]. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2015, 23(2): 83-90. doi: 10.1097/MOO.0000000000000134
[7] Battaglia P, Turri-Zanoni M, Dallan I, et al. Endoscopic endonasal transpterygoid transmaxillary approach to the infratemporal and upper parapharyngeal tumors[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2014, 150(4): 696-702. doi: 10.1177/0194599813520290
[8] Larson AR, Ryan WR. Transoral Excision of Parapharyngeal Space Tumors[J]. Otolaryngol Clin North Am, 2021, 54(3): 531-541. doi: 10.1016/j.otc.2021.03.001
[9] Hussain A, Ah-See KW, Shakeel M. Trans-oral resection of large parapharyngeal space tumours[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2014, 271(3): 575-582. doi: 10.1007/s00405-013-2550-9
[10] Chen Z, Chen YL, Yu Q, et al. Excision of tumors in the parapharyngeal space using an endoscopically assisted transoral approach: a case series and literature review[J]. J Int Med Res, 2019, 47(3): 1103-1113. doi: 10.1177/0300060518816190
[11] De Virgilio A, Costantino A, Mercante G, et al. Trans-oral robotic surgery in the management of parapharyngeal space tumors: A systematic review[J]. Oral Oncol, 2020, 103: 104581. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2020.104581
[12] Chan JY, Tsang RK, Eisele DW, et al. Transoral robotic surgery of the parapharyngeal space: a case series and systematic review[J]. Head Neck, 2015, 37(2): 293-298. doi: 10.1002/hed.23557
[13] Araneda N, Parra M, González-Arriagada WA, et al. Morphological Analysis of the Human Maxillary Sinus Using Three-Dimensional Printing[J]. Contemp Clin Dent, 2019, 10(2): 294-298.
[14] Li L, Xu H, Chen X, et al. Management of Multiple Head and Neck Paragangliomas With Assistance of a 3-D Model[J]. Ear Nose Throat J, 2021: 1455613211009441.
-




 下载:
下载: