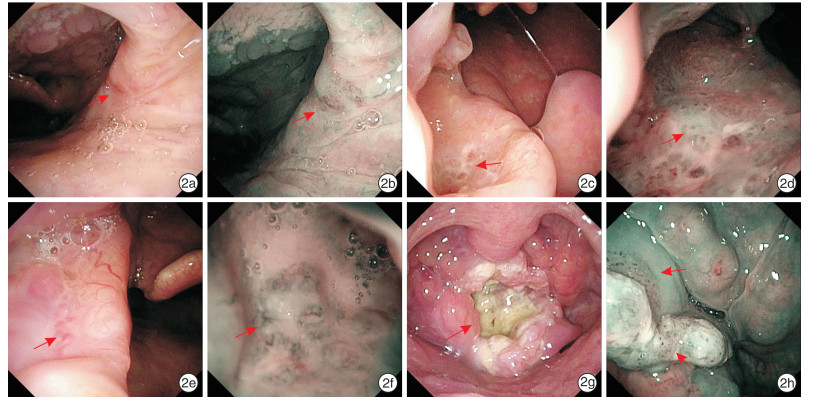
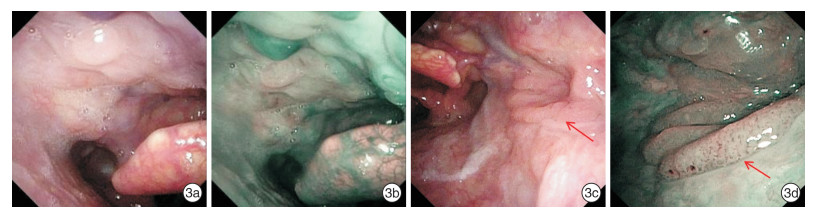
The application of NBI endoscopy in finding concealed primary lesions of misdiagnosis of oropharyngeal cancer
-
摘要: 目的 探讨窄带成像技术(NBI)内镜在寻找漏诊的口咽癌隐匿原发病灶中的应用价值。方法 回顾性研究自2018年5月-2021年6月就诊于西安交通大学第二附属医院耳鼻咽喉头颈外科的漏诊口咽癌患者的临床资料,结合NBI内镜检查结果,分析漏诊原因。结果 漏诊的31例患者临床诊断均为口咽恶性肿瘤,其中男25例,女6例,两者在年龄、BMI、病程及TNM分期方面比较差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05)。临床首发症状主要为咽痛(17例)、咽部异物感(4例)和单侧颈部局部肿物(10例)。初诊时21例未行喉镜检查,10例行喉镜检查未发现病灶。17例给予抗炎对症治疗无效或手术切除可疑病变部位,9例行CT、MRI及PET-CT,5例行颈部淋巴结穿刺活检。根据结果提示,2例再行普通喉镜,29例再行NBI内镜检查,在可疑病变处定位活检后证实为口咽部鳞状细胞癌,结果提示NBI内镜筛查漏诊的口咽癌隐匿原发病灶的准确率(93.55%)显著高于普通电子喉镜(6.45%),两者比较差异有统计学意义(χ2=43.613,P<0.01)。结论 NBI内镜在寻找扁桃体、舌根、软腭及口咽侧壁等隐匿部位的口咽癌具有独特优势,可减少口咽癌的漏诊。Abstract: Objective The aim of this study is to analyze the application value of NBI endoscopy in finding the concealed primary lesions of misdiagnosis of oropharyngeal cancer.Methods The clinical data of patients with missed oropharyngeal cancer treated in the Department of Otolaryngology Head and neck surgery, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Xi'an Jiaotong University from May 2018 to June 2021, were retrospectively studied, and the missed diagnosis was also analyzed combined with results of NBI endoscopy.Results In 31 cases of misdiagnosis of oropharyngeal cancer patients, including 25 males and 6 females, there was no significant difference in age, BMI index, course of disease and TNM stage (P> 0.05), and the pharyngeal or cervical symptoms were the first clinical manifestations of them, containing pharyngeal pain in 17 cases(54.8%), pharyngeal foreign body sensation in 4 cases(12.9%) and unilateral cervical mass in 10 cases (32.3%). No laryngoscopy was performed (21 cases) or no primary lesion was found by laryngoscopy (10 cases) at initial diagnosis. Among them, "inflammatory lesions" were given anti-inflammatory treatment with ineffective results or surgical resection was explored for suspicious lesions (17 cases), or imaging examination (9 cases, including 6 cases with CT and MRI, 3 cases with PET-CT) and cervical lymph node biopsy (5 cases) were carried out for further diagnosis. According to these results, they were given ordinary laryngoscope (2 cases) or NBI endoscopy (29 cases) subsequently, finally they were confirmed as oropharyngeal squamous cellcarcinoma after localized biopsy at the suspicious lesions, indicating that the accuracy of NBI endoscopy in finding the concealed primary lesions of oropharyngeal cancer (93.55%) is significantly higher than that of ordinary electronic laryngoscope (6.45%)(χ2=43.613, P < 0.01).Conclusion NBI endoscopy has unique advantages in finding oropharyngeal cancer in concealed parts such as tonsil, root of tongue, soft palate and lateral wall of oropharynx, which could reduce misdiagnosis of oropharyngeal cancer.
-

-
表 1 31例漏诊口咽癌患者的临床特征分析
指标 性别 t/Z P值 男 女 年龄/岁 62.6±9.8 59.0±11.8 0.768 0.777 BMI 24.0±3.2 24.1±1.3 -0.03 0.093 病程/月 4.0(5.5) 2.5(4.6) -0.504 0.643 TNM分期 — 0.654 Ⅰ~Ⅱ期 12(48.0) 4(66.7) Ⅲ~Ⅳ期 13(52.0) 2(33.3) 表 2 31例漏诊口咽癌患者隐匿原发病灶的部位及寻找方法
漏诊口咽癌原发病灶的寻找方法 单侧扁桃体 舌根 口咽侧壁/软腭 其他部位a) 对症治疗无效或手术后完善NBI内镜 7 4 1 5 影像学检查 2 2 1 4 颈部淋巴结穿刺活检 1 0 2 2 合计 10 6 4 11 a)包括合并累及口咽侧壁、口咽后壁、软腭、舌根及同侧扁桃体等多个部位。 -
[1] 刘良发, 袁硕卿. 口咽癌诊断治疗进展[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2019, 33(11): 1009-1013. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201911001.htm
[2] 周梁. 口咽癌诊断与治疗发展现状[J]. 中国耳鼻咽喉头颈外科, 2017, 24(11): 582-585. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-EBYT201711009.htm
[3] Hegde P, Roy S, Shetty T, et al. Tumor Infiltration Depth as a Prognostic Parameter for Nodal Metastasis in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma[J]. Int J Appl Basic Med Res, 2017, 7(4): 252-257. doi: 10.4103/ijabmr.IJABMR_66_17
[4] 张宝根, 倪晓光. 窄带成像内镜在头颈部肿瘤诊断中的应用[J]. 癌症进展, 2019, 17(2): 125-127. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-AZJZ201902001.htm
[5] Ansari UH, Wong E, Smith M, et al. Validity of narrow band imaging in the detection of oraland oropharyngeal malignant lesions: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Head Neck, 2019, 41(7): 2430-2440. doi: 10.1002/hed.25724
[6] Piazza C, Del Bon F, Paderno A, et al. The diagnostic value of narrow band imaging in different oral and oropharyngeal subsites[J]. Eur Arch of Otorhinol, 2016, 273(10): 3347-3353. doi: 10.1007/s00405-016-3925-5
[7] 倪晓光, 程荣荣, 赖少清, 等. 窄带成像内镜在原发灶不明的颈部转移性鳞状细胞癌诊断中的作用[J]. 中华肿瘤杂志, 2013, 35(9): 698-702. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-3766.2013.09.012
[8] Muto M, Nakane M, Katada C, et al. Squamous cell carcinoma in situ at oropharyngeal and hypopharyngeal mucosal sites[J]. Cancer, 2004, 101(6): 1375-1381. doi: 10.1002/cncr.20482
[9] Muto M, Katada C, Sano Y, et al. Narrow band imaging: a new diagnostic approach to visualize angiogenesis in superficial neoplasia[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2005, 3(7 Suppl 1): S16-S20.
[10] Tanaka S, Morita Y, Fujita T, et al. Clinicopathological characteristics of abnormal micro-lesions at the oro-hypopharynx detected by a magnifying narrow band imaging system[J]. Dig Endosc, 2012, 24(2): 100-109. doi: 10.1111/j.1443-1661.2011.01177.x
[11] 吴俊华, 骆献阳. 窄带成像内镜在口咽癌和下咽癌及癌前病变诊断中的应用[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2018, 32(9): 665-669. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201809007.htm
[12] Arens C, Piazza C, Andrea M, et al. Proposal for a descriptive guideline of vascular changes in lesions of the vocal folds by the committee on endoscopic laryngeal imaging of the European Laryngological Society[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2016, 273(5): 1207-1214.
[13] Lin YC, Wang WH, Lee KF, et al. Value of narrow band imaging endoscopy in early mucosal head and neck cancer[J]. Head Neck, 2012, 34(11): 1574-1579. doi: 10.1002/hed.21964
[14] Nonaka S, Saito Y. Endoscopic diagnosis of pharyngeal carcinoma by NBI[J]. Endoscopy, 2008, 40(4): 347-351. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-995433
[15] Randall DA, Johnstone PA, Foss RD, et al. Tonsillectomy in diagnosis of the unknown primary tumor of the head and neck[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2000, 122(1): 52-55. doi: 10.1016/S0194-5998(00)70143-4
-




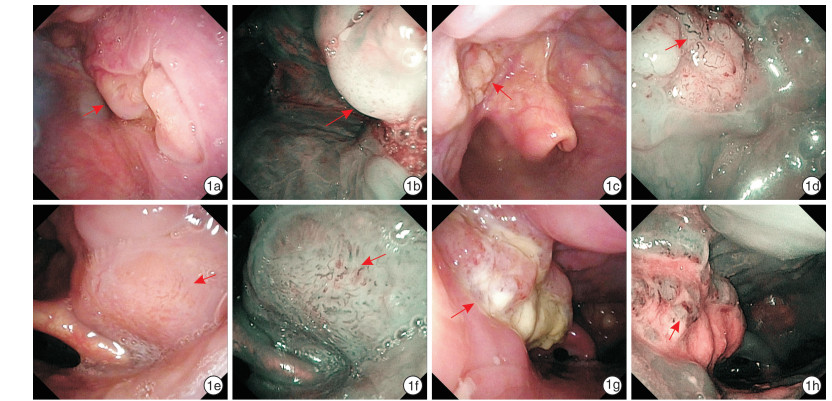
 下载:
下载: