-
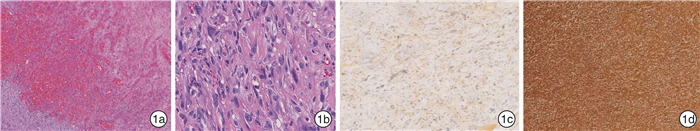
摘要: 目的 探讨头颈部肉瘤样癌的病理学特征、治疗及预后。方法 回顾性分析2013年9月—2020年9月郑州大学第一附属医院收治的17例头颈部肉瘤样癌患者的临床资料,总结其病理学特性、治疗方式及随访情况,应用Kaplan-Meier法计算其总的生存率。结果 所有患者病理组织学检查可见癌成分和肉瘤成分并存,两者之间存在过渡移行区域; 17例患者中,12例行手术治疗,5例因不能耐受手术或远处转移行姑息治疗; Kaplan-Meier法计算得到17例头颈部肉瘤样癌患者1、3、5年累积生存率分别为64.7%、26.5%、13.2%。结论 头颈部肉瘤样癌病理学检查是确诊的金标准,根治性手术是治疗的首选方式,其恶性程度高,预后差,早期诊断和根治性手术在一定程度上可提高患者的生存率。Abstract: Objective The aim of this study is to investigate the pathological features, treatment and prognosis of sarcomatoid carcinoma of head and neck.Methods The clinical data of 17 patients with sarcomatoid carcinoma of the head and neck treated in the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University from September 2013 to September 2020 were retrospectively analyzed, and the pathological characteristics, treatment and follow-up were summarized. Kaplan-Meier method was used to calculate the overall survival rate.Results The histopathological examination of all patients showed the coexistence of cancer components and sarcoma components, and there was a transitional transition area between them. In terms of treatment, 12 of the 17 patients received surgical treatment, and 5 patients received palliative treatment because they could not tolerate surgery or distant metastasis; The cumulative 1-year, 3-year and 5-year survival rates of 17 patients with head and neck sarcomatoid carcinoma calculated by Kaplan-Meier method were 64.7%, 26.5%, and 13.2%, respectively.Conclusion Pathological examination of head and neck sarcomatoid carcinoma is the gold standard for diagnosis. Radical surgery is the first choice for treatment. It has a high degree of malignancy and poor prognosis. Early diagnosis and radical surgery can improve the survival rate of patients to a certain extent.
-
Key words:
- head and neck neoplasms /
- sarcomatoid carcinoma /
- pathology /
- treatment /
- prognosis
-

-
表 1 头颈部肉瘤样癌17例患者的基本临床资料
例序 性别 年龄/岁 烟酒史 部位 症状 病程 肿瘤分期 确诊方法 放疗 化疗 随访时间/月 生存状态 1 男 51 烟酒 右上颌窦 间断鼻出血 5个月 T4aN0M0 Ⅳa期 手术 无 是 4 死亡 2a) 女 74 无 右鼻咽部 鼻塞、涕中带血 3个月 T2N0M0 Ⅱ期 手术 是 无 28 存活 3 男 71 烟酒 左上颌窦 颌面麻木、胀痛 3个月 T1N0M0 Ⅰ期 手术 是 是 25 存活 4 男 77 吸烟 左舌口底 舌口底包块 10 d T4aN0M0 Ⅳa期 活检 无 是 8 死亡 5 男 49 烟酒 下咽肿物 吞咽困难 15 d T2N2M0 Ⅳa期 活检 是 是 10 死亡 6 男 65 无 右扁桃体 咽部异物感 1个月 T2N2M0 Ⅳa期 手术 无 无 18 死亡 7b) 女 63 无 右侧外鼻 发现外鼻肿物 1年 T2N0M0 Ⅱ期 手术 是 无 15 死亡 8 女 53 无 左甲状腺 自觉颈部包块 2个月 T3aN0M0 Ⅰ期 手术 无 是 43 存活 9b) 女 47 无 右侧额窦 鼻塞、头痛 2个月 T4aN0M0 Ⅳa期 手术 是 无 16 死亡 10a) 男 57 吸烟 右上牙龈 牙龈肿物伴出血 1个月 T3N0M1 Ⅳc期 活检 无 是 6 死亡 11 女 64 无 左侧蝶窦 放射性额部头痛 1个月 T4bN0M0 Ⅳb期 手术 是 是 12 死亡 12 女 66 无 右上颌窦 鼻塞、牙区疼痛 2个月 T4bN0M0 Ⅳb期 活检 无 是 13 死亡 13 女 49 无 右下牙龈 牙龈肿物、出血 1个月 T3N0M0 Ⅲ期 手术 无 是 66 存活 14 女 73 无 右下牙龈 牙龈肿物、疼痛 1年 T3N0M0 Ⅲ期 手术 是 无 56 死亡 15 女 35 无 右侧鼻咽 鼻塞、伸舌偏斜 4个月 T4N2M0 Ⅳa期 手术 是 是 19 死亡 16 男 50 吸烟 左侧筛窦 鼻塞、涕中带血 1个月 T2N0M0 Ⅱ期 手术 是 是 36 死亡 17b) 女 44 无 左侧颈部 颈部肿块伴疼痛 2个月 T2N2M0 Ⅳa期 活检 是 是 9 死亡 注:a)表示放疗或化疗期间联合应用甲磺酸阿帕替尼片分子靶向等抗肿瘤综合治疗; b)表示发病部位既往存在射线接触史。 -
[1] 刘柱, 李笑秋, 李克鹏, 等. 鼻部肉瘤样癌9例临床分析[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2018, 32(18): 1429-1431.
[2] Antoine M, Vieira T, Fallet V, et al. [Pulmonary sarcomatoid carcinoma][J]. Ann Pathol, 2016, 36(1): 44-54. doi: 10.1016/j.annpat.2015.11.007
[3] 李永金, 李五一, 王剑, 等. 喉肉瘤样癌及癌肉瘤临床分析[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2017, 52(5): 385-387. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-0860.2017.05.013
[4] Oktay M, Kokenek-Unal TD, Ocal B, et al. Spindle cell carcinoma of the tongue: a rare tumor in an unusual location[J]. Patholog Res Int, 2011, 2011: 572381.
[5] Hasnaoui J, Anajar S, Tatari M, et al. Carcinosarcoma of the maxillary sinus: A rare case report[J]. Ann Med Surg(Lond), 2017, 19: 41-44. doi: 10.1016/j.amsu.2017.05.036
[6] Miyahara H, Tsuruta Y, Yane K, et al. Spindle cell carcinoma of the larynx[J]. Apmis, 2004, 31(2): 177-182.
[7] Onishi H, Kuriyama K, Komiyama T, et al. T1N0 laryngeal sarcomatoid carcinoma that showed rapid systemic metastases after radical radiotherapy: a case report and review of literature[J]. Am J Otolaryngol, 2005, 26(6): 400-402. doi: 10.1016/j.amjoto.2005.02.017
[8] Zidar N, Gale N. Carcinosarcoma and spindle cell carcinoma--monoclonal neoplasms undergoing epithelial-mesenchymal transition[J]. Virchows Arch, 2015, 466(3): 357-358. doi: 10.1007/s00428-014-1686-3
[9] 王延林, 刘良发, 李亚卓, 等. 11例头颈部肉瘤样癌临床分析[J]. 中国耳鼻咽喉颅底外科杂志, 2013, 19(1): 9-14.
[10] Viswanathan S, Rahman K, Pallavi S, et al. Sarcomatoid(spindle cell)carcinoma of the head and neck mucosal region: a clinicopathologic review of 103 cases from a tertiary referral cancer centre[J]. Head Neck Pathol, 2010, 4(4): 265-275. doi: 10.1007/s12105-010-0204-4
[11] 童雷, 吴国民, 陈敏芬, 等. 喉肉瘤样癌2例[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2009, 23(3): 137-138. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH200903014.htm
[12] Su HH, Chu ST, Hou YY, et al. Spindle cell carcinoma of the oral cavity and oropharynx: factors affecting outcome[J]. J Chin Med Assoc, 2006, 69(10): 478-483. doi: 10.1016/S1726-4901(09)70312-0
[13] Iqbal MS, Paleri V, Brown J, et al. Spindle cell carcinoma of the head and neck region: treatment and outcomes of 15 patients[J]. Ecancermedicalscience, 2015, 9: 594.
[14] Lin Y, Yang H, Cai Q, et al. Characteristics and Prognostic Analysis of 69 Patients With Pulmonary Sarcomatoid Carcinoma[J]. Am J Clin Oncol, 2016, 39(3): 215-222.
[15] Zhang BY, Thompson RH, Lohse CM, et al. A novel prognostic model for patients with sarcomatoid renal cell carcinoma[J]. BJU Int, 2015, 115(3): 405-411. doi: 10.1111/bju.12781
[16] Seong YW, Han SJ, Jung W, et al. Perioperative change in neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio(NLR)is a prognostic factor in patients with completely resected primary pulmonary sarcomatoid carcinoma[J]. J Thorac Dis, 2019, 11(3): 819-826. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2019.02.02
[17] 王志鹏, 蒋正举, 杨盈坡, 等. 扁桃体肉瘤样癌1例[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2020, 34(2): 183-185. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH202002021.htm
[18] Silvestri F, Bussani R, Stanta G, et al. Supraglottic versus glottic laryngeal cancer: epidemiological and pathological aspects[J]. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec, 1992, 54(1): 43-48. doi: 10.1159/000276258
-

| 引用本文: | 郭相岑, 刘丽, 王军玲, 等. 头颈部肉瘤样癌17例临床分析[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2022, 36(2): 125-129. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2022.02.010 |
| Citation: | GUO Xiangcen, LIU Li, WANG Junling, et al. Clinical analysis of 17 cases of sarcomatoid carcinoma of head and neck[J]. J Clin Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2022, 36(2): 125-129. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2022.02.010 |
- Figure 1.
- Figure 2.



 下载:
下载:
