-
摘要: 目的 探讨婴幼儿声门下血管瘤(SGH)的临床特征,观察普萘洛尔治疗SGH的安全性和有效性。方法 回顾性分析2015年11月—2020年3月于上海市儿童医院确诊为SGH并使用普萘洛尔治疗的13例患儿的基本资料并进行随访。13例患儿均行纤维喉镜检查,10例行颈部增强CT检查。2例全身麻醉下行喉探查术。心电监测下给药,起始剂量1 mg/(kg·d),分3次口服,如无不良反应,第2天调整剂量为1.5 mg/(kg·d),并维持该剂量(不随体重增加而增加)直至疗程结束。结果 治疗结束年龄9~38个月,仅2例超过2岁,平均(19.3±7.7)个月;治疗时间6~21.3个月,平均(13.3±4.9)个月;随访21~71个月,平均(46.8±14.9)个月。13例患儿全部治愈。结论 2岁以内的婴幼儿喉喘鸣经常规治疗效果不佳或者病情反复,应考虑SGH的可能。纤维喉镜检查并结合颈部增强CT值得推荐。口服普萘洛尔治疗SGH安全有效,建议临床用药至19月龄以上以减少复发,2岁龄可能是停药的最佳时机。Abstract: Objective To investigate the clinical characteristics of infantile subglottic hemangioma(SGH), and to observe the safety and efficacy of propranolol in the treatment of SGH.Methods The data of 13 children diagnosed with SGH and treated with propranolol in Shanghai Children's Hospital from November 2015 to March 2020 were retrospectively analyzed and followed up. All 13 cases underwent laryngoscopy and 10 cases underwentcontrastenhanced CT. Laryngeal exploration under general anesthesia was performed in 2 cases. Propranolol was started at 1 mg/(kg·d) divided into 3 doses. Heart rate and blood pressure were monitored during treatment. If no side effects were observed, then the dose was increased to 1.5 mg/(kg·d) on the second day. It was suggested to maintain this starting dose at diagnosis(1.5 mg/kg body weight), and not increase the number of milligrams as the child gained weight.Results The age at therapy termination ranged from 9 months to 38 months, only 2 cases beyond 2 years old, with an average of (19.3±7.7) months. The treatmentduration ranged from 6 to 21.3 months, with an average of (13.3±4.9) months. The follow-up time ranged from 21 to 71 months, with an average of (46.8±14.9) months. All 13 cases were cured.Conclusion Infants under 2 years old with stridor have poor effect or repeated condition after routine treatment, SGH should be considered at this moment. Laryngoscopy combined with contrastenhanced CT is recommended. Oral propranolol is safe and effective in the treatment of SGH. It is suggested to oral propranololbeyond 19 months old to reduce recurrence, furthermore, 2 years old may be the best time for therapy termination.
-
Key words:
- propranolol /
- infant /
- subglottic hemangioma
-

-
表 1 SGH患儿一般资料
例序 性别 部位 临床表现 误诊漏诊史 出现临床症状时年龄/d 确诊时年龄/月 治疗结束时年龄/月 治疗时间/月 其他部位血管瘤 结果 1 男 左 喉喘鸣 喉肿物、喉软化 1 3.0 9.0 6.0 无 治愈 2 男 左 喉喘鸣、犬吠样咳嗽 支气管炎 33 2.0 13.0 11.0 无 治愈 3 男 右 喉喘鸣、紫绀、呼吸窘迫 支气管炎 1 6.2 23.2 17.0 无 治愈 4 女 右 喉喘鸣、喂养困难、三凹征 支气管炎 79 3.6 18.6 15.0 背部 治愈 5 女 右 喉喘鸣 无 58 3.0 13.0 10.0 无 治愈 6 女 右 喉喘鸣、犬吠样咳嗽、喂养困难 支气管炎、喉软化 36 1.6 11.6 10.0 无 治愈 7 女 右 喉喘鸣、声嘶、呼吸窘迫、三凹征、紫绀 肺炎 16 1.3 19.3 18.0 双手 治愈 8 男 右 喉喘鸣、犬吠样咳嗽 哮喘 240 13.2 25.2 12.0 无 治愈 9 女 左 喉喘鸣、喂养困难 支气管炎 30 2.4 21.0 18.0 上臂 治愈 10 女 右 喉喘鸣、呼吸窘迫 肺炎 28 28.0 38.0 10.0 无 治愈 11 男 左 喉喘鸣、犬吠样咳嗽、呼吸窘迫、三凹征 肺炎 60 7.0 13.0 6.0 肩背、双臂、臀部 治愈 12 女 左 喉喘鸣、犬吠样咳嗽、呼吸窘迫 支气管炎 20 2.7 24.0 21.3 无 治愈 13 女 右 喉喘鸣、喂养困难、三凹征、呼吸窘迫 肺炎、喉软化 30 4.0 22.0 18.0 颈部、舌、眼睑 治愈 -
[1] Piram M, Hadj-Rabia S, Boccara O, et al. Beard infantile hemangioma and subglottic involvement: are median pattern and telangiectatic aspect the clue?[J]. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol, 2016, 30(12): 2056-2059. doi: 10.1111/jdv.13812
[2] Liu Z, Yeo YH, Jackson C, et al. Treatment failure with propranolol for subglottic haemangioma[J]. BMJ Case Rep, 2019, 12(5): e227135. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2018-227135
[3] Léauté-Labrèze C, Dumas de la Roque E, Hubiche T, et al. Propranolol for severe hemangiomas of infancy[J]. N Engl J Med, 2008, 358(24): 2649-2651. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc0708819
[4] Denoyelle F, Leboulanger N, Enjolras O, et al. Role of Propranolol in the therapeutic strategy of infantile laryngotracheal hemangioma[J]. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, 2009, 73(8): 1168-1172. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2009.04.025
[5] Parkes WJ, Propst EJ. Advances in the diagnosis, management, and treatment of neonates with laryngeal disorders[J]. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med, 2016, 21(4): 270-276. doi: 10.1016/j.siny.2016.03.003
[6] Schwartz T, Faria J, Pawar S, et al. Efficacy and rebound rates in propranolol-treated subglottic hemangioma: A literature review[J]. Laryngoscope, 2017, 127(11): 2665-2672. doi: 10.1002/lary.26818
[7] McCormick AA, Tarchichi T, Azbell C, et al. Subglottic hemangioma: Understanding the association with facial segmental hemangioma in a beard distribution[J]. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, 2018, 113: 34-37. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2018.07.019
[8] Ajmi H, Mama N, Hassayoun S, et al. Life-threatening subglottic hemangioma in an infant successfully treated with propranolol[J]. Arch Pediatr, 2018, 5. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0929693X18301143
[9] Kumar P, Kaushal D, Garg PK, et al. Subglottic hemangioma masquerading as croup and treated successfully with oral propranolol[J]. Lung India, 2019, 36(3): 233-235. https://europepmc.org/article/MED/31031345
[10] Li XY, Wang Y, Jin L, et al. Role of oral propranolol in the treatment of infantile subglottic hemangioma[J]. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther, 2016, 54(9): 675-681. doi: 10.5414/CP202536
[11] Yang W, Wolter NE, Cushing SL, et al. Propranolol versus nadolol for treatment of pediatric subglottic hemangioma[J]. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, 2021, 144: 110688. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2021.110688
[12] Darrow DH. Management of Infantile Hemangiomas of the Airway[J]. Otolaryngol Clin North Am, 2018, 51(1): 133-146. doi: 10.1016/j.otc.2017.09.001
[13] Hardison S, Wan W, Dodson KM. The use of propranolol in the treatment of subglottic hemangiomas: A literature review and meta-analysis[J]. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, 2016, 90: 175-180. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2016.09.012
[14] Ozeki M, Nozawa A, Hori T, et al. Propranolol for infantile hemangioma: Effect on plasma vascular endothelial growth factor[J]. Pediatr Int, 2016, 58(11): 1130-1135. doi: 10.1111/ped.12981
[15] 王桂香, 张丰珍, 张亚梅, 等. 普萘洛尔治疗婴幼儿声门下血管瘤临床疗效及远期随访观察[J]. 中国耳鼻咽喉头颈外科, 2020, 27(8): 464-468. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-EBYT202008011.htm
[16] Ting M, Roseby R, McAdam C. Subglottic infantile haemangioma: A rare but important consideration in young infants presenting with stridor[J]. J Paediatr Child Health, 2016, 52(12): 1111-1113. doi: 10.1111/jpc.13327
[17] 孙晓卫, 刘小芳, 房玉辉, 等. 彩色多普勒血流显像技术在婴幼儿先天性声门下血管瘤中的应用[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2021, 35(4): 321-324. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH202104008.htm
[18] Andersen IG, Rechnitzer C, Charabi B. Effectiveness of propanolol for treatment of infantile haemangioma[J]. Dan Med J, 2014, 61(2): A4776.
-

| 引用本文: | 陈伟, 陈佳瑞, 陈淑梅, 等. 普萘洛尔治疗婴幼儿声门下血管瘤的疗效分析[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2022, 36(1): 55-58. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2022.01.012 |
| Citation: | CHEN Wei, CHEN Jiarui, CHEN Shumei, et al. Treatment for infantile subglottic hemangioma with oral propranolol[J]. J Clin Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2022, 36(1): 55-58. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2022.01.012 |
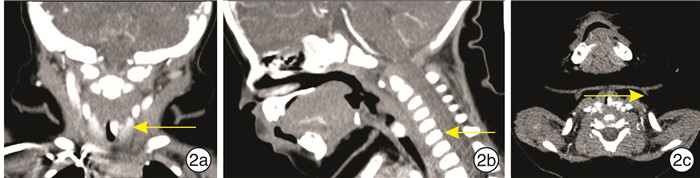
- Figure 1.
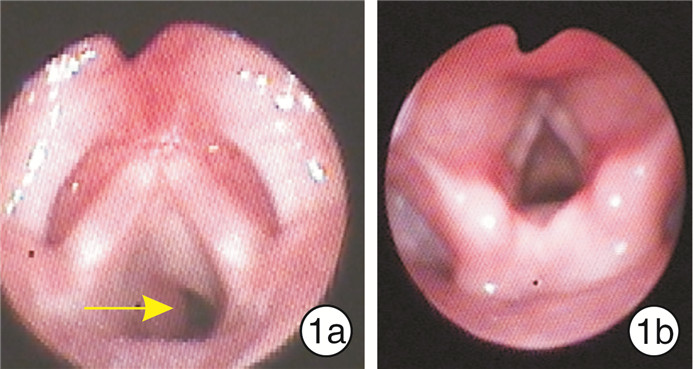
- Figure 2.



 下载:
下载: