Evaluation of Eustachian tube function in children with adenoid hypertrophy by nasopharyngeal digital photography and ETDQ-7 scores
-
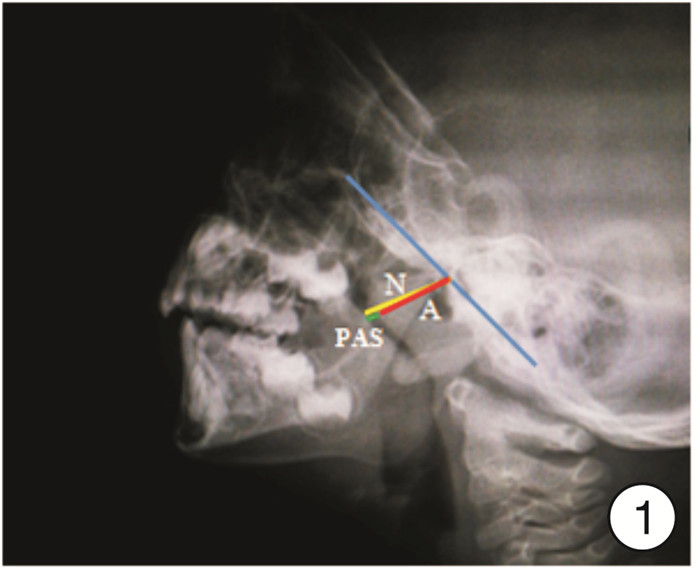
摘要: 目的 探讨鼻咽部数字化摄影及ETDQ-7量表评分在儿童腺样体肥大伴或不伴分泌性中耳炎(OME)的咽鼓管功能评估中的作用。方法 对2019年2月—2021年8月收治的60例伴或不伴OME的腺样体肥大患儿采用鼻咽部数字化摄影,对鼻咽腔有效气道宽度(PAS)、鼻咽腔宽度及腺样体指数(腺样体厚度/鼻咽腔宽度,A/N)进行测量,采用咽鼓管功能ETDQ-7评分量表进行评分。对腺样体肥大伴OME与ETDQ-7评分的相关性进行统计学分析。结果 腺样体肥大伴OME组A/N≤0.60、A/N 0.61-0.70、A/N≥0.71的ETDQ-7评分分别为4.15±1.75、14.55±6.67和23.95±6.63。腺样体肥大等级越高,ETDQ-7评分也越高。腺样体肥大伴OME组中,腺样体肥大程度与ETDQ-7评分呈正相关,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。结论 腺样体肥大也是引起儿童OME的潜在因素之一。Abstract: Objective To evaluate the Eustachian tube function of children with simple adenoid hypertrophy and adenoid hypertrophy with secretory otitis media(OME) by using the A/N value of lateral radiograph of nasopharyngeal X-ray and EDQ-7 scale scores.Methods Sixty cases of children with adenoid hypertrophy admitted from February 2019 to August 2021 were all underwent nasopharyngeal X-ray lateral radiographs to determine the adenoid/nasopharyngeal cavity ratio(A/N ratio) and then determine the size of adenoids. The Eustachian tube function ETDQ-7 survey was used to evaluate the patient's self-evaluation of the severity of the disease and ear symptoms, and the degree of influence were scored. Subsequently, the correlation between adenoid hypertrophy with OME and ETDQ-7 scores was statistically analyzed by using the Spearman rank correlation statistical method.Results In adenoid hypertrophy with OME group, the ETDQ-7 scores of A/N≤0.60, A/N 0.61—0.70 and A/N≥0.71 were 4.15±1.75, 14.55±6.67 and 23.95±6.63, respectively. The higher the grade of adenoid hypertrophy, the higher the ETDQ-7 scores. In adenoid hypertrophy with OME group, the degree of adenoid hypertrophy was positively correlated with the ETDQ-7 scores(P < 0.05).Conclusion Adenoid hypertrophy is also one of the potential factors causing OME in children.
-
Key words:
- child /
- adenoid hypertrophy /
- secretory otitis media /
- Eustachian tube function /
- X-ray lateral view /
- ETDQ-7
-

-
表 1 伴或不伴OME的腺样体肥大与A/N、PAS值的关系
例 组别 A/N值 PAS值 ≤0.60 0.61~0.70 ≥0.71 1~5 mm 6~9 mm 10~16 mm 单纯腺样体肥大组 5 15 20 18 15 7 腺样体肥大伴OME组 1 3 16 17 2 1 -
[1] Tysome JR, Sudhoff H. The Role of the Eustachian Tube in Middle Ear Disease[J]. Adv Otorhinolaryngol, 2018, 81: 146-152. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29794454/
[2] Yaman H, Yilmaz S, Guclu E, et al. Otitis media with effusion: recurrence after tympanostomy tube extrusion[J]. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, 2010, 74(3): 271-274. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2009.11.035
[3] Fujioka M, Young LW, Girdany BR. Radiographic evaluation of adenoidal size in children: adenoidal-nasopharyngeal ratio[J]. AJR Am J Roentgenol, 1979, 133(3): 401-404. doi: 10.2214/ajr.133.3.401
[4] Herrera M, Eisenberg G, Plaza G. Clinical assessment of Eustachian tube dysfunction through the Eustachian tube dysfunction questionnaire(ETDQ-7) and tubomanometry[J]. Acta Otorrinolaringol Esp(Engl Ed), 2019, 70(5): 265-271. doi: 10.1016/j.otorri.2018.05.005
[5] McCoul ED, Anand VK, Christos PJ. Validating the clinical assessment of eustachian tube dysfunction: The Eustachian Tube Dysfunction Questionnaire(ETDQ-7)[J]. Laryngoscope, 2012, 122(5): 1137-1141. doi: 10.1002/lary.23223
[6] 李东辉, 任甄华, 王晓曼, 等. 小儿腺样体肥大的X线表现(附136例总结与132例正常对照)[J]. 临床放射学杂志, 1999, 18(11): 694-697. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9324.1999.11.015
[7] Suzuki M, Wanabe T, Mogi G. Clinical, bacteriological, and histological studyof adenoids in children[J]. Am J Otolaryngol, 1999, 20(2): 85-90. doi: 10.1016/S0196-0709(99)90016-9
[8] Manno A, Iannella G, Savastano V, et al. Eustachian Tube Dysfunction in Children With Adenoid Hypertrophy: The Role of Adenoidectomy for Improving Ear Ventilation[J]. Ear Nose Throat J, 2021: 145561321989455. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33470833/
[9] 杨军, 李姝娜. 儿童分泌性中耳炎鼓膜置管的相关问题[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2020, 34(12): 1057-1059. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH202012001.htm
[10] Skoloudik L, Kalfert D, Valenta T, et al. Relation between adenoid size and otitis media with effusion[J]. Eur Ann Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Dis, 2018, 135(6): 399-402. doi: 10.1016/j.anorl.2017.11.011
[11] Ruan K, Li J, Tan S, et al. Comparison of sonotubometry, impedance, tubo-tympano-aerography, and tubomanometry to test eustachian tube function[J]. Am J Otolaryngol, 2020, 41(2): 102384. doi: 10.1016/j.amjoto.2019.102384
[12] Van Roeyen S, Van de Heyning P, Van Rompaey V. Value and discriminative power of the seven-item Eustachian Tube Dysfunction Questionnaire[J]. Laryngoscope, 2015, 125(11): 2553-2556. doi: 10.1002/lary.25316
[13] Schröder S, Lehmann M, Sauzet O, et al. A novel diagnostic tool for chronic obstructive eustachian tube dysfunction—the eustachian tube score[J]. Laryngoscope, 2015, 125(3): 703-708. doi: 10.1002/lary.24922
-




 下载:
下载:
