The relationship between clinical pathology and prognosis of chronic rhinosinusitis
-
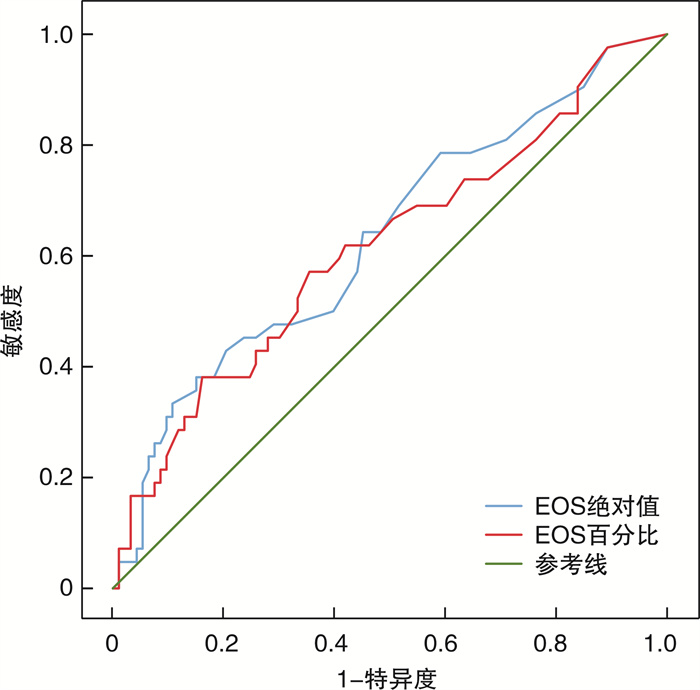
摘要: 目的 探讨慢性鼻窦炎(CRS)的病理类型、临床特征以及与预后的关系。方法 对2017年1月—2018年12月在南京医科大学附属江宁医院行鼻内镜手术的135例CRS患者进行回顾性研究。通过对病理切片逐一阅片, 将患者分为4型, 即嗜酸粒细胞型CRS(eCRS)、淋巴细胞和/或浆细胞型CRS、中性粒细胞型CRS和混合型CRS, 后三者统称为非eCRS(non-eCRS)。于2021年1—2月进行随访, 分析比较不同病理类型的分布、临床特征及预后差异。结果 ① 135例CRS患者中, eCRS共42例(31.1%), non-eCRS共93例(68.9%), 其中淋巴细胞和/或浆细胞型76例(56.3%)、中性粒细胞型4例(3.0%)、混合型13例(9.6%), 组间构成比的差异有统计学意义(n=135, P < 0.001)。②eCRS患者术前外周血嗜酸粒细胞(EOS)绝对值及百分比均较non-eCRS者高, 差异有统计学意义(n=125, P绝对值=0.030, P百分比=0.033)。受试者工作特征曲线分析结果显示EOS绝对值及百分比对eCRS均有预测价值, 截断值为EOS绝对值大于0.325×109/L, 百分比大于2.750%。术前外周血降钙素原在各组间的差异无统计学意义(n=69, P=0.647)。③eCRS患者术前鼻窦CT双侧筛窦评分与双侧上颌窦评分的比值(E/M值)为2.03±1.23, 而non-eCRS患者为1.47±0.96, 差异有统计学意义(n=112, P=0.009)。④101例有效随访患者中, eCRS共34例, 控制7例(20.6%)、部分控制18例(52.9%)、未控制9例(26.5%); non-eCRS共67例, 控制32例(47.8%)、部分控制26例(38.8%)、未控制9例(13.4%)。non-eCRS组疗效明显优于eCRS组(χ2=7.499, P=0.024)。结论 术前血常规检查EOS绝对值大于0.325×109/L或百分比大于2.750%时可初步预测eCRS, 但准确性偏低。eCRS患者CT多表现为筛窦炎症为主的影像学特征, 通常E/M>2。术后2~4年, eCRS组的疗效较non-eCRS差。Abstract: Objective To explore the pathological type, clinical features and their relationship with prognosis of chronic rhinosinusitis(CRS).Methods A retrospective study of 135 patients with CRS who underwent surgical treatment in the Affiliated Jiangning Hospital of Nanjing Medical University from January 2017 to December 2018. Review the pathological slices retrospectively and divide the CRS into 4 types, eosinophilic type(eCRS), lymphocyte or(and) plasma cell type, neutrophil type and mixed type, the latter three are collectively referred to as "non-eosinophil type(non-eCRS)". Follow-up was conducted between January and February 2021 to analyze the distribution, clinical features, and differences in prognosis of the different endotypes.Results ① Among the 135 CRS patients, 42 cases(31.1%) were eCRS and 93 cases(68.9%) were non-eCRS(76 cases[56.3%] of lymphocyte or plasma cell type, 4 cases[3.0%] of neutrophil type and 13 cases[9.6%] of mixed type). The difference in composition ratio between the groups was statistically significant(n=135, P < 0.001). ②The absolute value and percentage of preoperative peripheral blood eosinophils(EOS) in eCRS patients were higher than those of non-eCRS patients, and the difference was statistically significant(n=125, P(absolute value) =0.030, P(percentage) =0.033). The results of receiver operating characteristic curve showed that both absolute value and percentage have predictive value, and cut-off value was 0.325×109/L(absolute value) or 2.750%(percentage). There was no statistically significant difference in preoperative peripheral blood procalcitonin among the groups(n=69, P=0.647). ③The ratio(E/M value) of the bilateral ethmoid sinus scores and bilateral maxillary sinus scores of the preoperative paranasal sinus CT in eCRS patients was 2.03±1.23, while the non-eCRS patients was 1.47±0.96, and the difference was statistically significant(n=112, P=0.009). ④In total, 101 cases were effectively followed up, including 34 cases of eCRS(7 cases[20.6%] of control, 18 cases[52.9%] of partial control), 9 cases[26.5%] of non-control and 67 cases of non-eCRS(32 cases[47.8%] of control, 26 cases[38.8%] were partially controlled, 9 cases[13.4%] were not controlled), and the efficacy of the non-eCRS group was significantly better than that of the eCRS group(χ2=7.499, P=0.024).Conclusion When the absolute value of EOS in the preoperative blood examination is greater than 0.325×109/L or the percentage is greater than 2.750%, eCRS can be predicted, but the accuracy is low. CT of patients with eCRS is mostly characterized by inflammation of the ethmoid sinus and usually E/M>2. The efficacy of eCRS group is worse than that of the non-eCRS group 2—4 years after surgery.
-
Key words:
- sinusitis /
- nasal polyps /
- eosinophils /
- pathology /
- prognosis
-

-
表 1 eCRS及non-eCRS患者人口学特征及临床特征
eCRS non-eCRS T P 各类型比例/% 31.1 68.9 19.267 <0.001 年龄/岁 49.26±12.81 45.9±14.42 1.295 0.197 EOS绝对值/(×109/L) 0.18±0.19 0.12±0.16 2.195 0.030 EOS百分比/% 2.56±2.69 1.56±1.83 2.180 0.033 降钙素原/(ng·mL-1) 0.04±0.04 0.05±0.06 -0.460 0.647 E/M值 2.03±1.23 1.47±0.96 2.650 0.009 表 2 EOS绝对值及百分比对于eCRS预测价值的AUC及最佳截断值
AUC面积 标准误 P 截断值 敏感度 特异度 1-特异度 约登指数 EOS绝对值 0.631 0.053 0.015 0.325 ×109/L 0.190 0.946 0.054 0.137 EOS百分比 0.615 0.054 0.033 2.750 0.381 0.839 0.161 0.220 -
[1] 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志编辑委员会鼻科组, 中华医学会耳鼻咽喉头颈外科学分会鼻科学组. 慢性鼻-鼻窦炎诊断和治疗指南(2012年, 昆明)[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2013, 48(2): 92-94. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-0860.2013.02.002
[2] Fokkens WJ, Lund VJ, Mullol J, et al. EPOS 2012: European position paper on rhinosinusitis and nasal polyps 2012. A summary for otorhinolaryngologists[J]. Rhinology, 2012, 50(1): 1-12. doi: 10.4193/Rhino12.000
[3] Kirtsreesakul V, Atchariyasathian V. Nasal polyposis: role of allergy on therapeutic response of eosinophil-and noneosinophil-dominated inflammation[J]. Am J Rhinol, 2006, 20(1): 95-100. doi: 10.1177/194589240602000118
[4] Van Zele T, Claeys S, Gevaert P, et al. Differentiation of chronic sinus diseases by measurement of inflammatory mediators[J]. Allergy, 2006, 61(11): 1280-1289. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.2006.01225.x
[5] Cao PP, Li HB, Wang BF, et al. Distinct immunopathologic characteristics of various types of chronic rhinosinusitis in adult Chinese[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2009, 124(3): 478-484. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2009.05.017
[6] Lou H, Meng Y, Piao Y, et al. Cellular phenotyping of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps[J]. Rhinology, 2016, 54(2): 150-159. doi: 10.4193/Rhino15.271
[7] Fokkens WJ, Lund VJ, Hopkins C, et al. European Position Paper on Rhinosinusitis and Nasal Polyps 2020[J]. Rhinology, 2020, 58(Suppl S29): 1-464.
[8] Lund VJ, Kennedy DW. Staging for rhinosinusitis[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 1997, 117(3 Pt 2): S35-40.
[9] Meng Y, Lou H, Wang C, et al. Predictive significance of computed tomography in eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps[J]. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol, 2016, 6(8): 812-819. doi: 10.1002/alr.21749
[10] Yu J, Xian M, Piao Y, et al. Changes in Clinical and Histological Characteristics of Nasal Polyps in Northern China over the Past 2-3 Decades[J]. Int Arch Allergy Immunol, 2021, 182(7): 615-624. doi: 10.1159/000513312
[11] Kirtsreesakul V, Atchariyasathian V. Nasal polyposis: role of allergy on therapeutic response of eosinophil-and noneosinophil-dominated inflammation[J]. Am J Rhinol, 2006, 20(1): 95-100. doi: 10.1177/194589240602000118
[12] 张倩, 季俊峰, 张婷, 等. 慢性鼻-鼻窦炎伴双侧鼻息肉患者不同表型的临床特征[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2018, 32(23): 1774-1778. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201823002.htm
[13] Soler ZM, Sauer D, Mace J, et al. Impact of mucosal eosinophilia and nasal polyposis on quality-of-life outcomes after sinus surgery[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2010, 142(1): 64-71. doi: 10.1016/j.otohns.2009.10.005
[14] Bonfils P, Badoual C, Bonfils NA, et al. Eosinophil infiltration of nasal polyps in patients with nasal polyposis: role in clinical evolution after medical and surgical treatment [J]. J Laryngol Otol, 2009, 123(5): 509-516. doi: 10.1017/S0022215108002429
[15] Thompson CF, Price CP, Huang JH, et al. A pilot study of symptom profiles from a polyp vs an eosinophilic-based classification of chronic rhinosinusitis[J]. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol, 2016, 6(5): 500-507. doi: 10.1002/alr.21687
[16] Ho J, Hamizan AW, Alvarado R, et al. Systemic Predictors of Eosinophilic Chronic Rhinosinusitis[J]. Am J Rhinol Allergy, 2018, 32(4): 252-257. doi: 10.1177/1945892418779451
[17] 张志存, 李佩忠, 唐海燕, 等. 慢性鼻-鼻窦炎伴鼻息肉患者外周血和息肉组织中嗜酸粒细胞相关性分析[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2019, 33(1): 14-16, 22. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201901004.htm
[18] 胡万玉, 敖天, 殷敏, 等. 慢性鼻-鼻窦炎伴与不伴鼻息肉患者临床特征的比较[J]. 国际耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2020, 44(2): 63-68. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-4106.2020.02.001
[19] Turhal G, Eraslan S, Kaya, et al. Procalcitonin Levels in Chronic Rhinosinusitis[J]. Turk Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2019, 57(3): 113-116. doi: 10.5152/tao.2019.4343
[20] Bilici S, Cinar Z, Yigit O, et al. Does procalcitonin have a role in the pathogenesis of nasal polyp?[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2019, 276(5): 1367-1372. doi: 10.1007/s00405-019-05326-7
[21] Hamade B, Huang DT. Procalcitonin: Where Are We Now?[J]. Crit Care Clin, 2020, 36(1): 23-40. doi: 10.1016/j.ccc.2019.08.003
[22] Aloisio E, Dolci A, Panteghini M. Procalcitonin: Between evidence and critical issues[J]. Clin Chim Acta, 2019, 496: 7-12. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2019.06.010
[23] Tokunaga T, Sakashita M, Haruna T, et al. Novel scoring system and algorithm for classifying chronic rhinosinusitis: the JESREC Study[J]. Allergy, 2015, 70(8): 995-1003. doi: 10.1111/all.12644
[24] Tao X, Chen F, Sun Y, et al. Prediction models for postoperative uncontrolled chronic rhinosinusitis in daily practice[J]. Laryngoscope, 2018, 128(12): 2673-2680. doi: 10.1002/lary.27267
[25] Lou H, Meng Y, Piao Y, et al. Predictive significance of tissue eosinophilia for nasal polyp recurrence in the Chinese population[J]. Am J Rhinol Allergy, 2015, 29(5): 350-356. doi: 10.2500/ajra.2015.29.4231
[26] 毛弈友, 陈杰, 廖敏, 等. 慢性鼻窦炎相关内在型分类及血液标志物的研究进展[J]. 中国耳鼻咽喉颅底外科杂志, 2020, 26(3): 338-342. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZEBY202003027.htm
[27] Tsybikov NN, Egorova EV, Kuznik BI, et al. Biomarker assessment in chronic rhinitis and chronic rhinosinusitis: Endothelin-1, TARC/CCL17, neopterin, and α-defensins[J]. Allergy Asthma Proc, 2016, 37(1): 35-42. doi: 10.2500/aap.2016.37.3899
[28] Tojima I, Matsumoto K, Kikuoka H, et al. Evidence for the induction of Th2 inflammation by group 2 innate lymphoid cells in response to prostaglandin D2 and cysteinyl leukotrienes in allergic rhinitis[J]. Allergy, 2019, 74(12): 2417-2426. doi: 10.1111/all.13974
[29] 郑铭, 王敏, 李颖, 等. 慢性鼻窦炎伴鼻息肉的免疫炎性标志物表达及其对术后复发的预测价值[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2019, 54(3): 174-180.
[30] Liao B, Liu JX, Li ZY, et al. Multidimensional endotypes of chronic rhinosinusitis and their association with treatment outcomes[J]. Allergy, 2018, 73(7): 1459-1469. doi: 10.1111/all.13411
-




 下载:
下载: