Research progress of cancer stem cell biomarkers in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
-
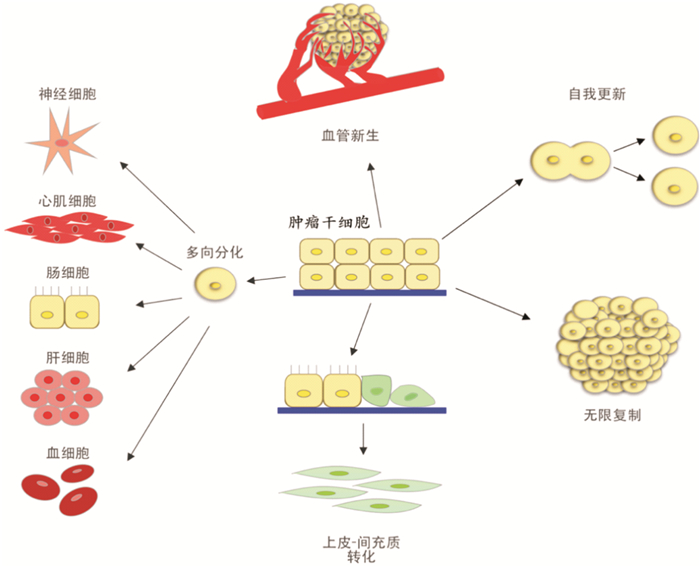
Abstract: Summary Cancer stem cells (CSCs), as a few amount of tumors, have infinite replication, self-renewal, differentiation and regeneration of cell subsets with tumorigenicity, have close relationship with tumor occurrence and recurrence, which can be found in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). One of the important measures to improve the patient prognosis is monitoring cancer stem cells and timely clinical intervention. Biomarker detection of cancer stem cells is an important method for clinical monitoring of cancer stem cells. This article reviews the biomarkers of CSCs in HNSCC, which is consist of membrane surface markers, non-coding RNAs, target genes and proteins.
-
Key words:
- head and neck neoplasms /
- neoplastic stem cells /
- biomarker
-

-
[1] Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2018, 68(6): 394-424. doi: 10.3322/caac.21492
[2] Hildebrand LC, Carvalho AL, Lauxen IS, et al. Spatial distribution of cancer stem cells in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas[J]. J Oral Pathol Med, 2014, 43(7): 499-506. doi: 10.1111/jop.12169
[3] Mannelli G, Gallo O. Cancer stem cells hypothesis and stem cells in head and neck cancers[J]. Cancer Treat Rev, 2012, 38(5): 515-39. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2011.11.007
[4] Eun K, Ham SW, Kim H. Cancer stem cell heterogeneity: origin and new perspectives on CSC targeting[J]. BMB Rep, 2017, 50(3): 117-125. doi: 10.5483/BMBRep.2017.50.3.222
[5] Featherston T, Brasch HD, Siljee SD, et al. Cancer Stem Cells in Head and Neck Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma Express Cathepsins[J]. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open, 2020, 8(8): e3042.
[6] Xiao M, Liu L, Zhang S, et al. Cancer stem cell biomarkers for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: A bioinformatic analysis[J]. Oncol Rep, 2018, 40(6): 3843-3851.
[7] Saghravanian N, Anvari K, Ghazi N, et al. Expression of p63 and CD44 in oral squamous cell carcinoma and correlation with clinicopathological parameters[J]. Arch Oral Biol, 2017, 82: 160-165. doi: 10.1016/j.archoralbio.2017.06.011
[8] Lu S, Tian J, Lv Z, et al. The probable role of tumor stem cells for lymph node metastasis in supraglottic carcinoma[J]. Pathol Oncol Res, 2011, 17(1): 33-8. doi: 10.1007/s12253-010-9271-9
[9] Wang J, Wu Y, Gao W, et al. Identification and characterization of CD133+CD44+ cancer stem cells from human laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma cell lines[J]. J Cancer, 2017, 8(3): 497-506. doi: 10.7150/jca.17444
[10] Lv B, Li F, Liu X, et al. The tumor-suppressive role of microRNA-873 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma correlates with downregulation of ZIC2 and inhibition of AKT signaling pathway[J]. Cancer Gene Ther, 2021, 28(1-2): 74-88. doi: 10.1038/s41417-020-0185-8
[11] Zhao Q, Zheng X, Guo H, et al. Serum Exosomal miR-941 as a promising Oncogenic Biomarker for Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma[J]. J Cancer, 2020, 11(18): 5329-5344. doi: 10.7150/jca.45394
[12] Gao W, Wu Y, He X, et al. MicroRNA-204-5p inhibits invasion and metastasis of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma by suppressing forkhead box C1[J]. J Cancer, 2017, 8(12): 2356-2368. doi: 10.7150/jca.19470
[13] Gao W, An C, Xue X, et al. Mass Spectrometric Analysis Identifies AIMP1 and LTA4H as FSCN1-Binding Proteins in Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma[J]. Proteomics, 2019, 19(21-22): e1900059. doi: 10.1002/pmic.201900059
[14] Sun Z, Hu W, Xu J, et al. MicroRNA-34a regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer stem cell phenotype of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma in vitro[J]. Int J Oncol, 2015, 47(4): 1339-1350. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2015.3142
[15] Wang R, Ma Z, Feng L, et al. LncRNA MIR31HG targets HIF1A and P21 to facilitate head and neck cancer cell proliferation and tumorigenesis by promoting cell-cycle progression[J]. Mol Cancer, 2018, 17(1): 162. doi: 10.1186/s12943-018-0916-8
[16] Yuan Z, Xiu C, Liu D, et al. Long noncoding RNA LINC-PINT regulates laryngeal carcinoma cell stemness and chemoresistance through miR-425-5p/PTCH1/SHH axis[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2019, 234(12): 23111-23122. doi: 10.1002/jcp.28874
[17] Sun P, Feng Y, Guo H, et al. MiR-34a Inhibits Cell Proliferation and Induces Apoptosis in Human Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma by Targeting lncRNA MCM3AP-AS1[J]. Cancer Manag Res, 2020, 12: 4799-4806. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S245520
[18] 赵雷, 池伟伟, 曹欢, 等. 长链非编码RNA LINC00152在喉鳞状细胞癌中的表达及其临床意义[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2019, 33(8): 721-725. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201908010.htm
[19] Yan N, Xu H, Zhang J, Xu L, Zhang Y, Zhang L, Xu Y, Zhang F. Circular RNA profile indicates circular RNA VRK1 is negatively related with breast cancer stem cells[J]. Oncotarget, 2017, 8(56): 95704-95718. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.21183
[20] Wu Y, Zhang Y, Niu M, et al. Whole-Transcriptome Analysis of CD133+CD144+ Cancer Stem Cells Derived from Human Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells[J]. Cell Physiol Biochem, 2018, 47(4): 1696-1710. doi: 10.1159/000490992
[21] Lee SH, Do SI, Lee HJ, et al. Notch1 signaling contributes to stemness in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Lab Invest, 2016, 96(5): 508-516. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.2015.163
[22] 申丽君, 黄茂凌, 李祥攀, 等. Notch1基因敲除后鼻咽癌细胞放疗敏感性的变化及分子机制[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2020, 34(1): 64-69. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH202001017.htm
[23] Ma G, Dai W, Sang A, et al. Roles of ZIC family genes in human gastric cancer[J]. Int J Mol Med, 2016, 38(1): 259-266. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2016.2587
[24] Wang J, Fan J, Gao W, et al. LY6D as a Chemoresistance Marker Gene and Therapeutic Target for Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma[J]. Stem Cells Dev, 2020, 29(12): 774-785. doi: 10.1089/scd.2019.0210
[25] Szafarowski T, Sierdziński J, Ludwig N, et al. Assessment of cancer stem cell marker expression in primary head and neck squamous cell carcinoma shows prognostic value for aldehyde dehydrogenase(ALDH1A1)[J]. Eur J Pharmacol, 2020, 867: 172837. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2019.172837
[26] Luo WR, Gao F, Li SY, et al. Tumour budding and the expression of cancer stem cell marker aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma[J]. Histopathology, 2012, 61(6): 1072-1081. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.2012.04350.x
[27] Bourguignon LY, Earle C, Wong G, et al. Stem cell marker(Nanog)and Stat-3 signaling promote MicroRNA-21 expression and chemoresistance in hyaluronan/CD44-activated head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells[J]. Oncogene, 2012, 31(2): 149-160. doi: 10.1038/onc.2011.222
[28] Keysar SB, Le PN, Miller B, et al. Regulation of Head and Neck Squamous Cancer Stem Cells by PI3K and SOX2[J]. J Natl Cancer Inst, 2016, 109(1): djw189.
[29] Wang X, He C, Li C, et al. IQGAP1 silencing suppresses the malignant characteristics of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma cells[J]. Int J Biol Markers, 2018, 33(1): 73-78. doi: 10.5301/ijbm.5000287
[30] Bessède E, Molina S, Acuña-Amador L, et al. Deletion of IQGAP1 promotes Helicobacter pylori-induced gastric dysplasia in mice and acquisition of cancer stem cell properties in vitro[J]. Oncotarget, 2016, 7(49): 80688-80699. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12486
[31] Carmon KS, Gong X, Yi J, et al. LGR5 receptor promotes cell-cell adhesion in stem cells and colon cancer cells via the IQGAP1-Rac1 pathway[J]. J Biol Chem, 2017, 292(36): 14989-15001. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.786798
[32] Zheng D, Zhu G, Liao S, et al. Dysregulation of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway affects cell cycle and apoptosis of side population cells in nasopharyngeal carcinoma[J]. Oncol Lett, 2015, 10(1): 182-188. doi: 10.3892/ol.2015.3218
[33] Wang J, Guo LP, Chen LZ, et al. Identification of cancer stem cell-like side population cells in human nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell line[J]. Cancer Res, 2007, 67(8): 3716-3724. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-4343
[34] Hoe SL, Tan LP, Jamal J, et al. Evaluation of stem-like side population cells in a recurrent nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell line[J]. Cancer Cell Int, 2014, 14(1): 101. doi: 10.1186/s12935-014-0101-0
[35] Wu CP, Zhou L, Xie M, et al. Identification of cancer stem-like side population cells in purified primary cultured human laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma epithelia[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(6): e65750. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0065750
-




 下载:
下载: