Clinical characteristics of neuroendocrine carcinoma of nose and skull base and analysis of curative effect of endoscopic surgery
-
摘要: 目的 探讨鼻及颅底神经内分泌癌的临床特征及内镜下手术切除的疗效与预后。方法 回顾性分析7例确诊为鼻及颅底神经内分泌癌并行内镜下手术治疗的患者资料。7例均为小细胞神经内分泌癌,参照国际TNM分期:Ⅰ期1例,Ⅱ期1例,Ⅲ期1例,ⅣA期1例,ⅣB期3例。治疗方法均采用内镜下手术切除,其中术后放疗1例,化疗1例,放化疗3例。结果 随访9~58个月,2例复发后死亡,1例同侧颈部淋巴结转移(行颈淋巴结清扫术后无瘤生存),4例在最后一次随访中均为无瘤生存。结论 鼻及颅底神经内分泌癌目前并无标准治疗方案,经内镜手术彻底切除肿瘤为主的综合性治疗是有效可行的治疗方案。Abstract: Objective To investigate the clinical features of neuroendocrine carcinoma of nose and skull base and the efficacy and prognosis of endoscopic resection.Methods The clinical data of 7 patients with neuroendocrine carcinoma of nose and skull base treated by endoscopic surgery were retrospectively analyzed. According to the international TNM staging, there were 1 case of stage Ⅰ, 1 case of stage Ⅱ, 1 case of stage Ⅲ, 1 case of stage ⅣA and 3 cases of stage ⅣB. All patients were treated by endoscopic surgery, including 1 case of postoperative radiotherapy, 1 case of chemotherapy and 3 cases of radiotherapy and chemotherapy.Results During the follow-up of 9-58 months, 2 cases died after recurrence, 1 case had ipsilateral cervical lymph node metastasis(tumor-free survival after neck dissection), and 4 cases had tumor-free survival at the last follow-up.Conclusion At present, there is no standard treatment for neuroendocrine carcinoma of the nose and skull base. The comprehensive treatment based on complete resection of the tumor by endoscopic surgery is an effective and feasible treatment.
-

-
表 1 7例鼻及颅底NEC患者临床资料
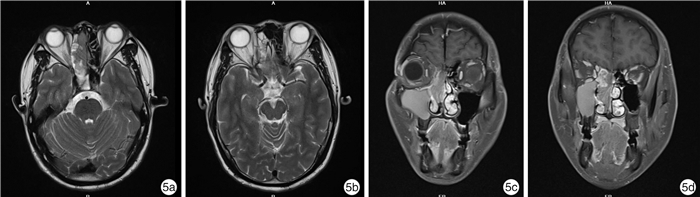
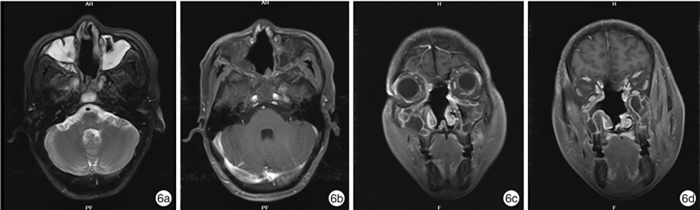
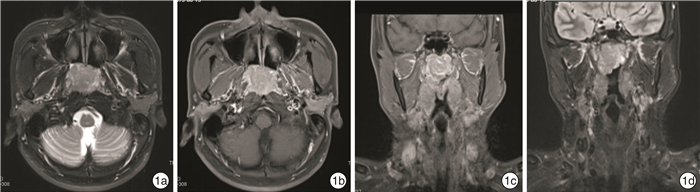
例序 性别 年龄/岁 首发症状 主要病变部位 分期 治疗方式 随访时间/月 结局 1 男 47 右鼻出血 右鼻腔、右筛窦、前颅底 ⅣA期 内镜下颅底肿瘤切除+放化疗 57 术后2年复发,再次手术+术后放化疗,3年后死亡 2 男 73 左鼻塞、左鼻出血 左鼻腔、左上颌窦、筛窦、蝶窦及额窦、硬脑膜及左侧嗅球 ⅣB期 单纯内镜下颅底肿瘤切除 9 术后8个月复发,放弃治疗后1个月死亡 3 男 37 右鼻塞伴嗅觉下降 右鼻腔、右侧筛窦 Ⅱ期 内镜下颅底肿瘤切除+放疗 58 无瘤生存 4 男 38 双鼻塞、双耳听力下降 鼻咽部 Ⅰ期 内镜下颅底肿瘤切除+放化疗 37 无瘤生存 5 男 60 右侧鼻塞伴头痛 右鼻腔、右筛窦、前颅底、硬脑膜、右嗅球及嗅束 ⅣB期 单纯内镜下颅底肿瘤切除 21 术后7个月同侧颈部淋巴结转移,行颈淋巴结清扫后无瘤生存 6 男 54 右涕中带血 右侧鼻腔、右上颌骨、右上颌窦 Ⅲ期 内镜下颅底肿瘤切除+放化疗 14 无瘤生存 7 男 60 右侧鼻塞伴嗅觉下降 右鼻腔、右筛窦、蝶窦、硬脑膜累及右嗅球、嗅束 ⅣB期 内镜下颅底肿瘤切除+化疗 15 无瘤生存 表 2 7例鼻及颅底NEC患者免疫组织化学检查结果
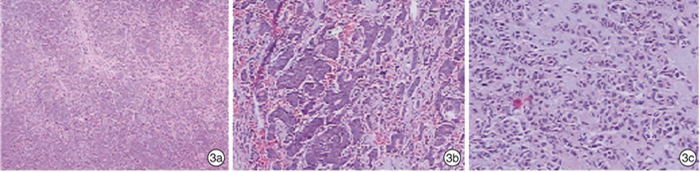
例序 CgA Syn CEA S-100 CK CD56 Ki67/% 1 + + + - 点状+ - 80 2 + + + - + + 60 3 + + - - + 未查 30 4 + + 未查 - - 未查 20 5 + + - - + - 60 6 + + + + + + 未查 7 点状+ - + - 点状+ 区域+ 50 -
[1] Baxi AJ, Chintapalli K, Katkar A, et al. Multimodality Imaging Findings in Carcinoid Tumors: A Head-to-Toe Spectrum[J]. Radiographics, 2017, 37(2): 516-536. doi: 10.1148/rg.2017160113
[2] Patel TD, Vazquez A, Dubal PM, et al. Sinonasal neuroendocrine carcinoma: a population-based analysis of incidence and survival[J]. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol, 2015, 5(5): 448-453. doi: 10.1002/alr.21497
[3] Bell D, Hanna EY. Sinonasal undifferentiated carcinoma: morphological heterogeneity, diagnosis, management and biological markers[J]. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther, 2013, 13(3): 285-296. doi: 10.1586/era.13.1
[4] Bishop JA, Guo TW, Smith DF, et al. Human papillomavirus-related carcinomas of the sinonasal tract[J]. Am J Surg Pathol, 2013, 37(2): 185-192. doi: 10.1097/PAS.0b013e3182698673
[5] Laco J, Sieglová K, Vošmiková H, et al. The presence of high-risk human papillomavirus(HPV)E6/E7 mRNA transcripts in a subset of sinonasal carcinomas is evidence of involvement of HPV in its etiopathogenesis[J]. Virchows Arch, 2015, 467(4): 405-415. doi: 10.1007/s00428-015-1812-x
[6] Su SY, Bell D, Hanna EY. Esthesioneuroblastoma, neuroendocrine carcinoma, and sinonasal undifferentiated carcinoma: differentiation in diagnosis and treatment[J]. Int Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2014, 18(Suppl 2): S149-156.
[7] Abdelmeguid AS, Bell D, Hanna EY. Neuroendocrine Carcinoma and Sinonasal Undifferentiated Carcinoma[J]. Adv Otorhinolaryngol, 2020, 84: 168-184.
[8] van der Laan TP, Iepsma R, Witjes MJ, et al. Meta-analysis of 701 published cases of sinonasal neuroendocrine carcinoma: The importance of differentiation grade in determining treatment strategy[J]. Oral Oncol, 2016, 63: 1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2016.10.002
[9] Adnan A, Basu S. Combined 177Lu-DOTATATE Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy and Platinum-Based Chemotherapy in Recurrent, Metastatic Sinonasal Neuroendocrine Carcinoma: A Promising Therapeutic Option[J]. J Nucl Med Technol, 2020, 48(3): 292-294. doi: 10.2967/jnmt.119.237354
[10] Fitzek MM, Thornton AF, Varvares M, et al. Neuroendocrine tumors of the sinonasal tract. Results of a prospective study incorporating chemotherapy, surgery, and combined proton-photon radiotherapy[J]. Cancer, 2002, 94(10): 2623-2634. doi: 10.1002/cncr.10537
[11] 危维, 张秋航, 严波, 等. 内镜经鼻手术治疗前中颅底神经内分泌癌[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2015, 50(5): 357-361. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-0860.2015.05.003
[12] 张娜, 黄谦, 崔顺九, 等. 鼻腔鼻窦恶性肿瘤经鼻内镜手术治疗效果和生活质量评价[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2020, 55(1): 21-28.
[13] 孙敬武, 汪银凤, 郭涛, 等. 经鼻内镜切除侵犯前颅底鼻腔恶性肿瘤的疗效分析[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2018, 32(10): 778-781. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201810015.htm
[14] Spadigam A, Dhupar A, Syed S, et al. Small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the paranasal sinus with intraoral involvement: Report of a rare case and review of the literature[J]. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol, 2017, 21(2): 286-295. doi: 10.4103/jomfp.JOMFP_205_15
-




 下载:
下载: