-
Abstract: Structural nasal obstruction(SNO) is a series of diseases caused by congenital or acquired structural anatomical abnormalities of nasal airway and its surrounding tissues, which leads to increased nasal ventilation resistance. The effect of medication drugs for SNO is poor and surgical intervention is often needed. However, the abnormal structure of nasal airway is very complex, including the periphery of nasal airway, internal nasal airway, the front and rear of nasal airway and complex factors. These abnormal structures may interfere with the nasal airflow mechanics by changing the nasal ventilation volume and disrupting the symmetry of the bilateral nasal cavity, and finally lead to subjective feeling of nasal obstruction. In addition, the structure of nasal airway has plasticity. After the abnormal structure appears, the corresponding compensation of nasal airway can occur to ensure normal nasal ventilation and bilateral nasal cavity symmetry. Therefore, the SNO is the result of the failure of nasal airway remodeling after the appearance of abnormal structures. The etiology of SNO is complex, involving original structural abnormalities, nasal symmetry changing and nasal airway structure remodeling. Therefore, accurate identification of the main factors leading to SNO is the vitalpremise of making personalized nasal ventilation surgery.
-
Key words:
- nasal obstruction /
- nasal airway /
- etiology
-

-
[1] Schuman TA, Senior BA. Treatment Paradigm for Nasal Airway Obstruction[J]. Otolaryngol Clin North Am, 2018, 51(5): 873-882. doi: 10.1016/j.otc.2018.05.003
[2] 张罗, 韩德民, 王琪. 鼻炎概述[J]. 中国耳鼻咽喉头颈外科, 2007, 14(1): 19-24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7002.2007.01.007
[3] 张革化, Fenton RS, Rival R, 等. 鼻阻塞的主观评价与客观鼻测量的相关性研究[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2008, 43(7): 484-489. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1673-0860.2008.07.002
[4] Esmaili A, Acharya A. Clinical assessment, diagnosis and management of nasal obstruction[J]. Aust Fam Physician, 2017, 46(7): 499-503.
[5] 袁晓培, 马有祥, 邢志敏, 等. 鼻内镜下鼻腔成形术治疗结构性鼻炎[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2007, 21(17): 782-785. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH200717007.htm
[6] Liu JF, Yan ZF, Zhang ZJ, et al. Septoplasty alone is not suitable for most structural nasal obstructions[J]. World J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surgery, 2020.
[7] Hsu DW, Suh JD. Anatomy and Physiology of Nasal Obstruction[J]. Otolaryngol Clin North Am, 2018, 51(5): 853-865. doi: 10.1016/j.otc.2018.05.001
[8] Whyte A, Boeddinghaus R. Imaging of adult nasal obstruction[J]. Clin Radiol, 2020, 75(9): 688-704. doi: 10.1016/j.crad.2019.07.027
[9] Zhao K, Blacker K, Luo Y, et al. Perceiving nasal patency through mucosal cooling rather than air temperature or nasal resistance[J]. PLoS One, 2011, 6(10): e24618. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0024618
[10] Sozansky J, Houser SM. Pathophysiology of empty nose syndrome [J]. Laryngoscope, 2015, 125(1): 70-74. doi: 10.1002/lary.24813
[11] Baraniuk JN, Merck SJ. Neuroregulation of human nasal mucosa[J]. Ann N Y Acad Sci, 2009, 1170: 604-609. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2009.04481.x
[12] Williams R, Patel V, Chen YF, et al. The Upper Airway Nasal Complex: Structural Contribution to Persistent Nasal Obstruction[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2019, 161(1): 171-177. doi: 10.1177/0194599819838262
[13] 张柳青, 孙艺渊, 王珮华, 石润杰, 陈东. 2881例鼻骨骨折患者流行病学分析[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2020, 34(3): 239-243. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH202003014.htm
[14] Rao A, Godehal SM, Patil AR, et al. Congenital nasal pyriform aperture stenosis: a rare cause of neonatal nasal airway obstruction[J]. BJR Case Rep, 2015, 1(1): 20150006.
[15] 刘锦峰, 闫占峰, 郝鹏鹏, 等. 上颌窦后部气化程度对鼻腔形态影响的CT观察[J]. 中国医学文摘(耳鼻咽喉科学), 2018, 33(1): 66-69. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYEB201801019.htm
[16] 陈威, 徐啟. 青少年口呼吸伴腺样体面容者硬腭形态的研究[J]. 浙江实用医学, 2019, 24(4): 250-253. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZJSA201904006.htm
[17] 刘继远, 桂雄斌, 陆灵娟, 等. 成人大筛泡与鼻塞及鼻源性头痛和嗅觉障碍的关系[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉科杂志, 2005, 19(20): 950-951. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1781.2005.20.016
[18] Janovic N, Janovic A, Milicic B, et al. Is Computed Tomography Imaging of Deviated Nasal Septum Justified for Obstruction Confirmation?[J]. Ear Nose Throat J, 2021, 100(2): NP131-NP136. doi: 10.1177/0145561319871533
[19] 邱小雯, 胡建道. 鼻中隔偏曲伴下鼻甲肥大患者的鼻窦CT分析[J]. 中国耳鼻咽喉头颈外科, 2017, 24(7): 365-367. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-EBYT201707013.htm
[20] 何婷, 邓刚, 黄喜, 江远明, 师洪. 以划分鼻中隔偏曲单元为基础的个体化鼻中隔矫正手术[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2020, 34(8): 706-709. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH202008007.htm
[21] Koo SK, Kim JD, Moon JS, et al. The incidence of concha bullosa, unusual anatomic variation and its relationship to nasal septal deviation: A retrospective radiologic study[J]. Auris Nasus Larynx, 2017, 44(5): 561-570. doi: 10.1016/j.anl.2017.01.003
[22] Jun BC, Kim SW, Kim SW, et al. Is turbinate surgery necessary when performing a septoplasty?[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2009, 266(7): 975-980. doi: 10.1007/s00405-008-0855-x
[23] Tomblinson CM, Cheng MR, Lal D, et al. The Impact of Middle Turbinate Concha Bullosa on the Severity of Inferior Turbinate Hypertrophy in Patients with a Deviated Nasal Septum[J]. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol, 2016, 37(7): 1324-1330. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A4705
[24] Camacho M, Zaghi S, Certal V, et al. Inferior turbinate classification system, grades 1 to 4: development and validation study[J]. Laryngoscope, 2015, 125(2): 296-302. doi: 10.1002/lary.24923
[25] Ozcan KM, Selcuk A, Ozcan I, et al. Anatomical variations of nasal turbinates[J]. J Craniofac Surg, 2008, 19(6): 1678-1682. doi: 10.1097/SCS.0b013e318188a29d
[26] Yiǧit O, Acioǧlu E, Cakir ZA, et al. Concha bullosa and septal deviation[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2010, 267(9): 1397-1401. doi: 10.1007/s00405-010-1228-9
[27] Neskey D, Eloy JA, Casiano RR. Nasal, septal, and turbinate anatomy and embryology[J]. Otolaryngol Clin North Am, 2009, 42(2): 193-205. doi: 10.1016/j.otc.2009.01.008
[28] 段丙志, 崔顺九. 副中鼻甲和第二中鼻甲鼻内镜手术切除1例[J]. 中国耳鼻咽喉头颈外科, 2006, 13(1): 20-20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7002.2006.01.021
[29] Demir D, Asil K, Güven M, et al. Assessment of the correlation between nasal septal deviation and compensatory hypertrophy of the middle turbinate[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2015, 272(10): 2847-2851. doi: 10.1007/s00405-014-3387-6
[30] Demir D, Asil K, Güven M, et al. Does septoplasty change the dimensions of compensatory hypertrophy of the middle turbinate?[J]. J Laryngol Otol, 2016, 130(6): 554-559. doi: 10.1017/S0022215116001055
[31] Rhee JS, Weaver EM, Park SS, et al. Clinical consensus statement: Diagnosis and management of nasal valve compromise[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2010, 143(1): 48-59. doi: 10.1016/j.otohns.2010.04.019
[32] Osborn JL, Sacks R. Chapter 2: Nasal obstruction[J]. Am J Rhinol Allergy, 2013, 27 Suppl 1: S7-8.
[33] Suh MW, Jin HR, Kim JH. Computed tomography versus nasal endoscopy for the measurement of the internal nasal valve angle in Asians[J]. Acta Otolaryngol, 2008, 128(6): 675-679. doi: 10.1080/00016480701663391
[34] Wang Y, Bonaparte JP. Diagnosis and management of septal deviation and nasal valve collapse-a survey of Canadian otolaryngologists[J]. J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2019, 48(1): 71-71. doi: 10.1186/s40463-019-0394-z
[35] Chambers KJ, Horstkotte KA, Shanley K, et al. Evaluation of Improvement in Nasal Obstruction Following Nasal Valve Correction in Patients With a History of Failed Septoplasty[J]. JAMA Facial Plast Surg, 2015, 17(5): 347-350. doi: 10.1001/jamafacial.2015.0978
[36] Li L, Zang H, Han D, et al. Impact of a Concha Bullosa on Nasal Airflow Characteristics in the Setting of Nasal Septal Deviation: A Computational Fluid Dynamics Analysis[J]. Am J Rhinol Allergy, 2020, 34(4): 456-462.
[37] Han D, Zhang L. Nasal cavity ventilation expansion techniques[J]. Acta Otolaryngol, 2011, 131(12): 1244-1248.
[38] Aslan G, Uzun L, Ugur MB, et al. Unilateral inferior turbinate bone hypertrophy: is it compensatory or congenital?[J]. Am J Rhinol Allergy, 2013, 27(4): 255-259.
-

| 引用本文: | 张郅瑾, 杨旭雯, 李绚, 等. 结构性鼻塞的病因学及机制研究进展[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2021, 35(7): 666-672. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2021.07.021 |
| Citation: | ZHANG Zhijin, YANG Xuwen, LI Xuan, et al. Advances in etiology and mechanism of structural nasal obstruction[J]. J Clin Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2021, 35(7): 666-672. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2021.07.021 |
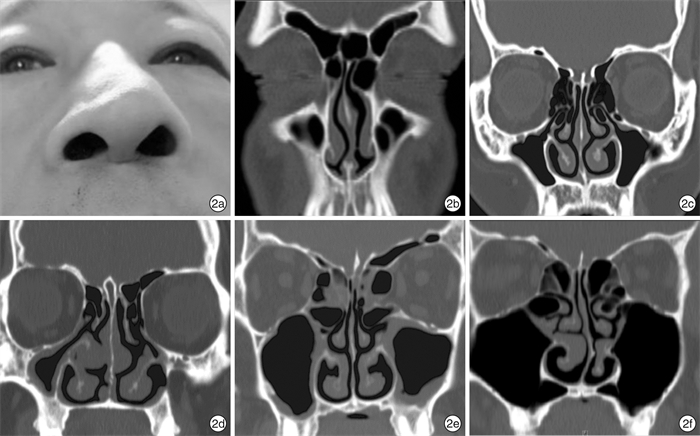
- Figure 1.
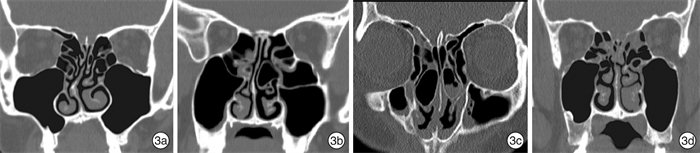
- Figure 2.
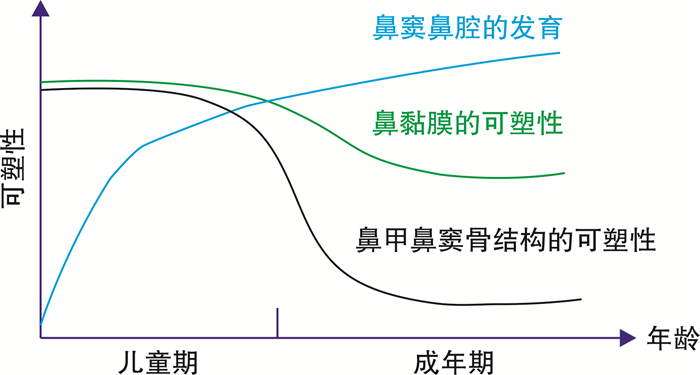
- Figure 3.
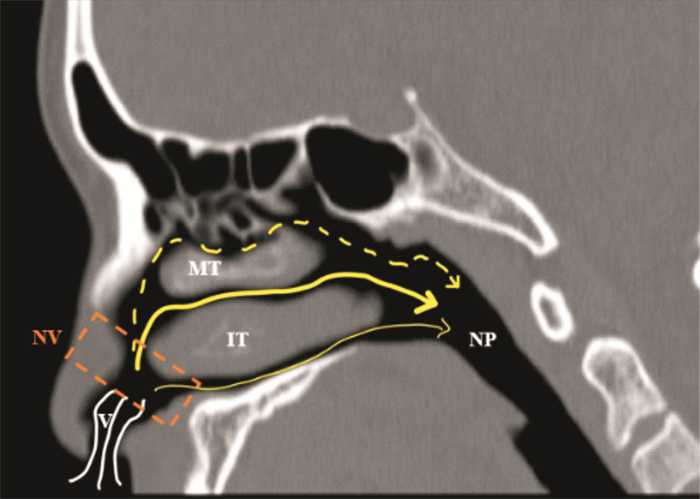
- Figure 4.



 下载:
下载: