Diagnosis and treatment of the fourth branchial fissure: a clinical report of 1 case and literature review
-
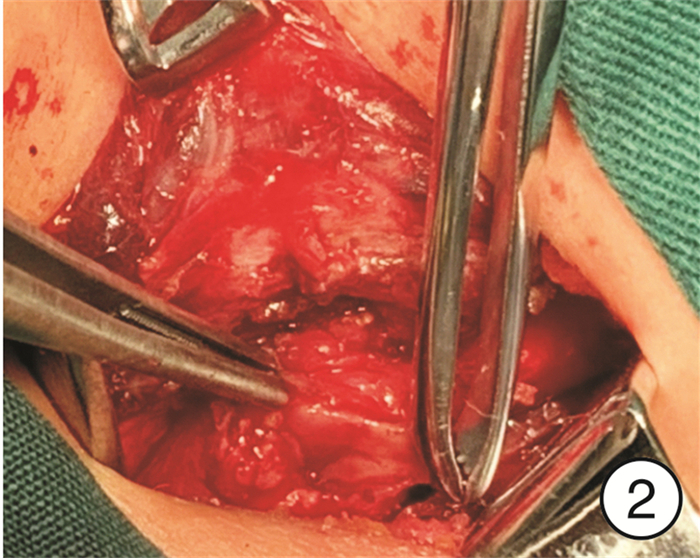
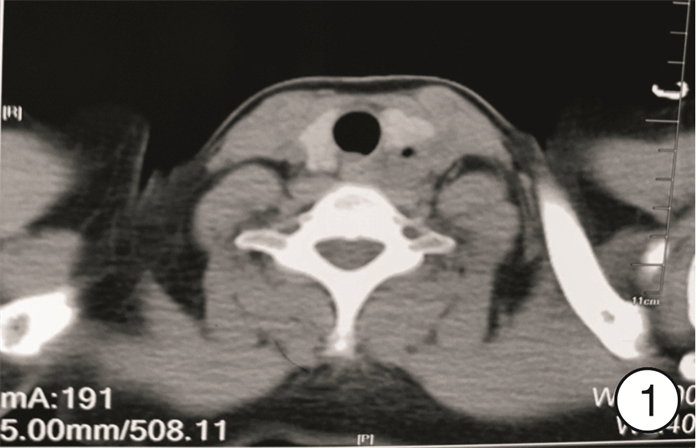
Abstract: The patient repeatedly suffer from pain in the left side neck for 4 years and had 1-2 recurrence per year. We used neck ultrasound and neck CT examination to find an abnormal soft tissue lumps exist in the patient′s left neck root to the trachea esophageal ditch. Diagnostic analysis combines embryogenesis and anatomy, and the diagnosis results are infection with the fourth branchial fissure. The lesion site was completely excisioned with full hemp surgery, the incision showed Ⅰ type healing after surgery, and there was no recurrence after six months of follow-up.
-

-
[1] 黄选兆, 汪吉宝. 实用耳鼻咽喉科学[M]. 2版. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2008: 42-47.
[2] Kenealy JF, Torsiglieri AJ Jr, Tom LW. Branchial cleft anomalies: a five-year retrospective review[J]. Trans Pa Acad Ophthalmol Otolaryngol, 1990, 42: 1022-1025.
[3] 黄选兆, 汪吉宝. 实用耳鼻咽喉科学[M]. 2版. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2008: 3-6, 609-615.
[4] 邹仲之, 李继承. 组织学与胚胎学[M]. 7版. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2010: 224-225, 231-232.
[5] Zhang P, Tian X. Recurrent neck lesions secondary to pyriform sinus fistula[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2016, 273(3): 735-739. doi: 10.1007/s00405-015-3572-2
[6] Snow JB, Wackym PA, 李大庆, 译. 耳鼻咽喉头颈外科学[M]. 17版. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2012: 937-938.
[7] Mandell DL. Head and neck anomalies related to the branchial apparatus[J]. Otolaryngol Clin North Am, 2000, 33(6): 1309-1332. doi: 10.1016/S0030-6665(05)70283-8
[8] Garrel R, Jouzdani E, Gardiner Q, et al. Fourth branchial pouch sinus: from diagnosis to treatment[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2006, 134(1): 157-163. doi: 10.1016/j.otohns.2005.05.653
[9] Yang C, Cohen J, Everts E, et al. Fourth branchial arch sinus: clinical presentation, diagnostic workup, and surgical treatment[J]. Laryngoscope, 1999, 109(3): 442-446. doi: 10.1097/00005537-199903000-00019
[10] Shrime M, Kacker A, Bent J, et al. Fourth branchial complex anomalies: a case series[J]. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, 2003, 67(11): 1227-1233. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2003.07.015
[11] Zhu H, Xiao X, Zheng S, et al. Diagnosis and management of pyriform sinus cyst in neonates: 16-year experience at a single center[J]. J Pediatr Surg, 2017, 52(12): 1989-1993.
[12] Li Y, Lyu K, Wen Y, et al. Third or fourth branchial pouch sinus lesions: a case series and management algorithm[J]. J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2019, 48(1): 61-61.
[13] Liberman M, Kay S, Emil S, et al. Ten years of experience with third and fourth branchial remnants[J]. J Pediatr Surg, 2002, 37(5): 685-690.
[14] Burge D, Middleton A. Persistent pharyngeal pouch derivatives in the neonate[J]. J Pediatr Surg, 1983, 18(3): 230-234.
[15] Prosser JD, Myer CM 3rd. Branchial cleft anomalies and thymic cysts[J]. Otolaryngol Clin North Am, 2015, 48(1): 1-14.
[16] Zaifullah S, Yunus MR, See GB. Diagnosis and treatment of branchial cleft anomalies in UKMMC: a 10-year retrospective study[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2013, 270(4): 1501-1506.
[17] Zatoński T, Inglot J, Krecicki T. Torbiel boczna szyi[Brachial cleft cyst][J]. Pol Merkur Lekarski, 2012, 32(191): 341-344.
[18] Cai Q, Pan Y, Xu Y, et al. Resection of recurrent branchial cleft deformity using selective neck dissection technique[J]. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, 2014, 78(7): 1071-1073.
-




 下载:
下载: