Sensory organization test results for maintaining an upright balance in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and patients with peripheral vestibular disorders
-
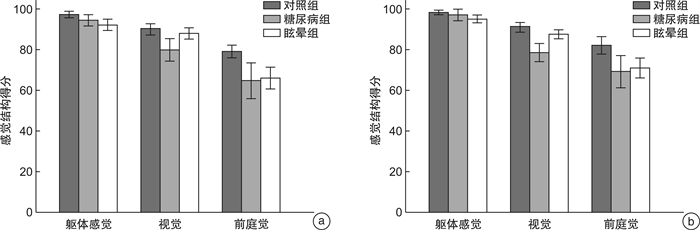
摘要: 目的 通过动静态姿势描记仪对2型糖尿病和外周性眩晕患者进行直立姿势稳定性测试,分析其利用感觉结构维持平衡的差异。 方法 研究对象分为对照组(52例)、糖尿病组(45例)和眩晕组(47例),所有受试者均进行6种条件下的直立姿势稳定性测试和感觉结构分析。 结果 糖尿病组在条件1(睁眼、硬平板)、条件4(睁眼、泡沫板)、条件6(视觉干扰、泡沫板)的身体压力中心晃动的姿势包络面积较眩晕组大,差异有统计学意义(P<0.01)。通过感觉结构分析发现,在前后方向和侧方,糖尿病组的视觉评分较眩晕组低,差异有统计学意义(P<0.01)。 结论 2型糖尿病患者和外周性眩晕患者保持直立姿势平衡能力下降,其中2型糖尿病患者利用视觉维持平衡的能力比外周性眩晕患者更差。Abstract: Objective To research the differences of sensory organization testing in maintaining postural stability between patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and patients with peripheral vertigo using computerized posturography. Methods Participants were divided into the control group (52 cases), the type 2 diabetes mellitus group (T2DM) (45 cases), and the peripheral vertigo group (PV) (47 cases). All participants were examined under six conditions by computerized posturography: The sensory organization test, a part of computerized dynamic posturography, was used to assess the abilities of vision, somatosensory and vestibular systems in maintaining postural stability. Results The scores of statokinesiogram (SKG) of the T2DM group in condition 1 (standing on static platform with eye open), condition 4(standing on foam platform with eyes open) and condition 6(standing on foam platform with servo-controlled vision) were significantly greater than that in the vertigo group (P<0.01). The visual scores in the T2DM group were lower than those of the PV group(P<0.01) in the anteroposterior and lateral directions. Conclusion Patients with type 2 diabetes and peripheral vertigo have a decreased ability to maintain balance in the upright position. Patients with type 2 diabetes have a poorer ability to maintain balance with visual systems than patients with peripheral vertigo.
-
Key words:
- vertigo /
- type 2 diabetes mellitus /
- sensory organization test
-

-
表 1 各组在6种直立条件下的SKG面积
mm2 直立条件 糖尿病组 眩晕组 对照组 条件1 406.57±287.282)3) 230.65±101.98 263.24±143.49 条件2 461.61±439.87 417.64±383.42 279.30±144.95 条件3 447.23±634.87 326.28±250.40 232.49±141.69 条件4 1511.46±837.112)3) 718.01±467.02 739.93±428.75 条件5 2343.87±1653.742) 2096.16±1689.661) 1168.47±476.72 条件6 2231.68±2599.353) 829.31±476.52 758.61±334.97 与对照组比较,1)P<0.05;2)P<0.01;与眩晕组比较,3)P<0.01。 -
[1] IDF Diabetes Atlas Group. Update of mortality attributable to diabetes for the IDF Diabetes Atlas: Estimates for the year 2013[J]. Diabetes Res Clin Pract, 2015, 109(3) : 461-465. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2015.05.037
[2] World Health Organization. Global Report on Diabetes [R]. Geneva: WHO, 2016.
[3] Alyono JC. Vertigo and Dizziness: Understanding and Managing Fall Risk[J ]. Otolaryngol Clin North Am, 2018, 51(4) : 725-740. doi: 10.1016/j.otc.2018.03.003
[4] Herdman SJ, Blatt P, Schubert MC, et al. Falls in patients with vestibular deficits[J]. AmJ Otol, 2000, 21 (6) : 847- 851.
[5] 黄小兵, 刘博, 孙敬武, 等. 2型糖尿病患者平衡功能的分析与评价[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2016, 30 (1) : 27-30. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201601008.htm
[6] 刘博, 黄小兵, 陈秀伍, 等. 外周性眩晕患者的感觉结构与稳定极限能力分析[J]. 中华耳科学杂志, 2010, 8(2) : 137-140. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2922.2010.02.005
[7] Gioacchini FM, Albera R, Re M, et al. Hyperglycemia and diabetes mellitus are related to vestibular organs dysfunction: truth or suggestion? A literatu rereview[J]. Acta Diabetol, 2018, 55(12) : 1201-1207. doi: 10.1007/s00592-018-1183-2
[8] De Kegel A, DhoogeI, Cambier D, et al. Test-retest reliability of the assessment of postural stability in typically developing children and in hearing impaired children[J]. Gait Posture, 2011, 33(4) : 679-685. doi: 10.1016/j.gaitpost.2011.02.024
[9] 黄小兵, 刘博. 平衡三联及中枢整合在人体平衡中的作用[J]. 听力学及言语疾病杂志, 2009, 17(6) : 534-536. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7299.2009.06.007
[10] Hewston P, Deshpande N. Falls and Balance Impairments in Older Adults with Type 2 Diabetes: Thinking Beyond Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy[J]. CanJ Diabetes, 2016, 40(1) : 6-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jcjd.2015.08.005
[11] Schwartz AV, Vittinghoff E, Sellmeyer DE, et al. Diabetes-related complications, glycemic control, and falls in older adults[J]. Diabetes Care, 2008, 31(3) : 391-396. doi: 10.2337/dc07-1152
[12] Chau RM, Ng TK, Kwan RL, et al. Risk of fall for people with diabetes[J ]. Disabil Rehabil, 2013, 35 (23) : 1975- 1980. doi: 10.3109/09638288.2013.770079
[13] Morimoto A, Sonoda N, Ugi S, et al. Association between symptoms of bilateral numbness and/or paresthesia in the feet and postural instability in Japanese patients with diabetes[J]. Diabetol Int, 2016, 7(1) : 69-76.
[14] Li J, Jiang J, Zhang Y, et al. Impairment of Vestibular Function and Balance Control in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes[J]. Audiol Neurootol, 2019, 24(3) : 154-160. doi: 10.1159/000501291
[15] Ward BK, Wenzel A, Kalyani RR, et al. Characterization of Vestibulopathy in Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2015, 153(1) : 112-118. doi: 10.1177/0194599815576717
[16] Elangovan S, Spankovich C. Diabetes and Auditory-Vestibular Pathology[J]. Semin Hear, 2019, 40(4) : 292-299. doi: 10.1055/s-0039-1697033
[17] Konukseven O, Polat SB, Karahan S, et al. Electrophysiologic vestibular evaluation in type 2 diabetic and prediabetic patients: Air conduction ocular and cervical vestibular evoked myogenic potentials[J]. Int J Audiol, 2015, 54 (8) : 536-543. doi: 10.3109/14992027.2014.971887
[18] Hegemann S, Bockisch CJ. Otoconial loss or lack of otoconia-An overlooked or ignored diagnosis of balance deficits[J]. Med Hypotheses, 2019, 128: 17-20. doi: 10.1016/j.mehy.2019.05.002
[19] Martínez Pascual P, Amaro Merino P. Otolithic damage study in patients with benign paroxysmal positional vertigo with vestibular evoked myogenic potentials[J]. Acta Otorrinolaringol Esp(Engl Ed), 2019, 70(3) : 131-135. doi: 10.1016/j.otorri.2018.04.003
[20] Oliva Domínguez M, Bartual Magro J, Dañino González JL, et al. [Postural control related to age in patients with benign positional paroxysmal vertigo][J]. Acta Otorrinolaringol Esp, 2005, 56(8) : 354-360. doi: 10.1016/S0001-6519(05)78629-5
[21] Cohen-Shwartz Y, Nechemya Y, Kalron A. Canalith repositioning procedure improves gait and static balance in people with posterior semicircular canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo[J]. J Vestib Res, 2020, 30(5) : 335- 343. doi: 10.3233/VES-200713
[22] Fujimoto C, Egami N, Kinoshita M, et al. Factors affecting postural instability in Meniere's disease[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2013, 149(5) : 759-765. doi: 10.1177/0194599813501625
[23] Daneshi A, Bozorgzadeh N, Asghari A, et al. Dynamic posturography for staging of patients with Ménière's disease[J]. J Laryngol Otol, 2009, 123(8) : 863-867. doi: 10.1017/S0022215109004423
[24] Soto A, Labella T, Santos S, et al. The usefulness of computerized dynamic posturography for the study of equilibrium in patients with Meniere's disease: correlation with clinical and audiologic data[J]. Hear Res, 2004, 196 (1/ 2) : 26-32.
[25] Zhou YJ, Li QZ, Gao YQ, et al. Are Meniere's disease patients with otolith organ impairment more likely to have balance dysfunction?[J ]. Acta Otolaryngol, 2019, 139 (11) : 977-981. doi: 10.1080/00016489.2019.1663923
-




 下载:
下载: