-
-
关键词:
- 锥形束计算机体层摄影术 /
- 耳蜗植入术 /
- 颞骨影像
Abstract: Cochlear implant, as the most successful artificial auditory implant, brings tens of thousands of patients with severe or profound sensorineural hearing loss back to the world of sound every year.With the expansion of surgical indications, a large number of difficult cases bring new challenges for cochlear implantation.As a new technology, cone beam CT has the double advantages of high spatial resolution and low radiation.It is considered as the second revolution of CT technology, which shows unique value in the application of cochlear implantation.This article reviews the basic principles of cone beam CT and its application and research progress in cochlear implantation. -

-
[1] 许晓飞, 张丽, 尹红霞. 锥形束CT在颞骨检查中的应用与进展[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2018, 98(23): 1887-1889. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0376-2491.2018.23.018
[2] Pauwels R, Araki K, Siewerdsen JH, et al. Technical aspects of dental CBCT: state of the art[J]. Dentomaxillofac Radiol, 2015, 44(1): 20140224. doi: 10.1259/dmfr.20140224
[3] Nemtoi A, Czink C, Haba D, et al. Cone beam CT: a current overview of devices[J]. Dentomaxillofac Radiol, 2013, 42(8): 20120443. doi: 10.1259/dmfr.20120443
[4] Theunisse HJ, Joemai RM, Maal TJ, et al. Cone-beam CT versus multi-slice CT systems for postoperative imaging of cochlear implantation--a phantom study on image quality and radiation exposure using human temporal bones[J]. Otol Neurotol, 2015, 36(4): 592-599. doi: 10.1097/MAO.0000000000000673
[5] Guberina N, Dietrich U, Arweiler-Harbeck D, et al. Comparison of radiation doses imparted during 128-, 256-, 384-multislice CT-scanners and cone beam computed tomography for intra-and perioperative cochlear implant assessment[J]. Am J Otolaryngol, 2017, 38(6): 649-653. doi: 10.1016/j.amjoto.2017.09.005
[6] Dierckx D, Saldarriaga Vargas C, Rogge F, et al. Dosimetric analysis of the use of CBCT in diagnostic radiology: sinus and middle ear[J]. Radiat Prot Dosimetry, 2015, 163(1): 125-132. doi: 10.1093/rpd/ncu117
[7] 谢晓艳, 张祖燕, 王争, 等. 锥形束CT与螺旋CT应用于颞骨显像的辐射剂量分析[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2018, 98(23): 1837-1840. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0376-2491.2018.23.006
[8] 方军杰, 胡宝华, 王建锋, 等. 人工耳蜗植入术后锥体束CT影像评估[J]. 中国耳鼻咽喉颅底外科杂志, 2019, 25(1): 55-59. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZEBY201901014.htm
[9] Haghanifar S, Yousefi S, Moudi E, et al. Accuracy of densitometry of two cone beam computed tomography equipment in comparison with computed tomography[J]. Electron Physician, 2017, 9(5): 4384-4390. doi: 10.19082/4384
[10] 王争, 尹红霞, 张征宇, 等. 锥形束CT与多层螺旋CT对前庭导水管显示能力的比较分析[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2018, 98(41): 3328-3331. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0376-2491.2018.41.007
[11] Jacobs R, Salmon B, Codari M, et al. Cone beam computed tomography in implant dentistry: recommendations for clinical use[J]. BMC Oral Health, 2018, 18(1): 88. doi: 10.1186/s12903-018-0523-5
[12] 赖若沙, 伍伟景, 李葳, 等. 内耳畸形人工耳蜗植入手术难点及其处理[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2020, 34(10): 919-924. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH202010014.htm
[13] Gupta R, Bartling SH, Basu SK, et al. Experimental flat-panel high-spatial-resolution volume CT of the temporal bone[J]. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol, 2004, 25(8): 1417-1424.
[14] Zou J, Lähelmä J, Koivisto J, et al. Imaging cochlear implantation with round window insertion in human temporal bones and cochlear morphological variation using high-resolution cone beam CT[J]. Acta Otolaryngol, 2015, 135(5): 466-472. doi: 10.3109/00016489.2014.993090
[15] Barker E, Trimble K, Chan H, et al. Intraoperative use of cone-beam computed tomography in a cadaveric ossified cochlea model[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2009, 140(5): 697-702. doi: 10.1016/j.otohns.2008.12.046
[16] Würfel W, Lanfermann H, Lenarz T, et al. Cochlear length determination using Cone Beam Computed Tomography in a clinical setting[J]. Hear Res, 2014, 316: 65-72. doi: 10.1016/j.heares.2014.07.013
[17] Nateghifard K, Low D, Awofala L, et al. Cone beam CT for perioperative imaging in hearing preservation Cochlear implantation-a human cadaveric study[J]. J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2019, 48(1): 65. doi: 10.1186/s40463-019-0388-x
[18] 张征宇, 尹红霞, 王振常, 等. 锥形束CT面神经管成像的可行性分析[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2018, 98(23): 1832-1836. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0376-2491.2018.23.005
[19] Zhang Z, Yin H, Wang Z, et al. Imaging re-evaluation of the tympanic segment of the facial nerve canal using cone-beam computed tomography compared with multi-slice computed tomography[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2019, 276(7): 1933-1941. doi: 10.1007/s00405-019-05419-3
[20] Komori M, Yamada K, Hinohira Y, et al. Width of the normal facial canal measured by high-resolution cone-beam computed tomography[J]. Acta Otolaryngol, 2013, 133(11): 1227-1232. doi: 10.3109/00016489.2013.816443
[21] Diogo I, Walliczeck U, Taube J, et al. Possibility of differentiation of cochlear electrodes in radiological measurements of the intracochlear and chorda-facial angle position[J]. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital, 2016, 36(4): 310-316. doi: 10.14639/0392-100X-878
[22] Hiraumi H, Suzuki R, Yamamoto N, et al. The sensitivity and accuracy of a cone beam CT in detecting the chorda tympani[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2016, 273(4): 873-877. doi: 10.1007/s00405-015-3647-0
[23] Zou J, Lähelmä J, Arnisalo A, et al. Clinically relevant human temporal bone measurements using novel high-resolution cone-beam CT[J]. J Otol, 2017, 12(1): 9-17. doi: 10.1016/j.joto.2017.01.002
[24] 杨仕明, 侯昭晖, 李佳楠. 疑难复杂人工耳蜗植入术中CT导航[J]. 中国医学文摘(耳鼻咽喉科学), 2015, 30(5): 245-248. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYEB201505004.htm
[25] 张德军, 高搏, 戴朴. 术中CT在疑难人工耳蜗植入手术中的应用[J]. 中华耳科学杂志, 2018, 16(6): 812-815. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2922.2018.06.014
[26] 唐安洲. 人工耳蜗植入术后耳蜗内电极影像学评估和应用[J]. 中国医学文摘(耳鼻咽喉科学), 2011, 26(2): 88-90. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYEB201102017.htm
[27] Rafferty MA, Siewerdsen JH, Chan Y, et al. Intraoperative cone-beam CT for guidance of temporal bone surgery[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2006, 134(5): 801-808. doi: 10.1016/j.otohns.2005.12.007
[28] Majdani O, Bartling SH, Leinung M, et al. [Image-guided minimal-invasive cochlear implantation——experiments on cadavers][J]. Laryngorhinootologie, 2008, 87(1): 18-22. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-966775
[29] Erovic BM, Daly MJ, Chan HH, et al. Evaluation of intraoperative cone beam computed tomography and optical drill tracking in temporal bone surgery[J]. Laryngoscope, 2013, 123(11): 2823-2828. doi: 10.1002/lary.24130
[30] Arndt S, Beck R, Schild C, et al. Management of cochlear implantation in patients with malformations[J]. Clin Otolaryngol, 2010, 35(3): 220-227. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-4486.2010.02124.x
[31] Rotter N, Schmitz B, Sommer F, et al. First use of flat-panel computed tomography during cochlear implant surgery: Perspectives for the use of advanced therapies in cochlear implantation[J]. HNO, 2017, 65(1): 61-65. doi: 10.1007/s00106-016-0213-z
[32] Yamamoto N, Okano T, Yamazaki H, et al. Intraoperative Evaluation of Cochlear Implant Electrodes Using Mobile Cone-Beam Computed Tomography[J]. Otol Neurotol, 2019, 40(2): 177-183. doi: 10.1097/MAO.0000000000002097
[33] Venail F, Bell B, Akkari M, et al. Manual Electrode Array Insertion Through a Robot-Assisted Minimal Invasive Cochleostomy: Feasibility and Comparison of Two Different Electrode Array Subtypes[J]. Otol Neurotol, 2015, 36(6): 1015-1022. doi: 10.1097/MAO.0000000000000741
[34] Labadie RF, Balachandran R, Noble JH, et al. Minimally invasive image-guided cochlear implantation surgery: first report of clinical implementation[J]. Laryngoscope, 2014, 124(8): 1915-1922. doi: 10.1002/lary.24520
[35] Caversaccio M, Gavaghan K, Wimmer W, et al. Robotic cochlear implantation: surgical procedure and first clinical experience[J]. Acta Otolaryngol, 2017, 137(4): 447-454. doi: 10.1080/00016489.2017.1278573
[36] Morrel WG, Jayawardena A, Amberg SM, et al. Revision surgery following minimally invasive image-guided cochlear implantation[J]. Laryngoscope, 2019, 129(6): 1458-1461. doi: 10.1002/lary.27636
[37] 范新泰, 王娜, 侯凌霄, 等. 锥形束CT对人工耳蜗植入术后电极位置的评估[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2019, 54(8): 566-570. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-0860.2019.08.002
[38] Ketterer MC, Aschendorff A, Arndt S, et al. The influence of cochlear morphology on the final electrode array position[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2018, 275(2): 385-394. doi: 10.1007/s00405-017-4842-y
[39] Mosnier I, Célérier C, Bensimon JL, et al. Cone beam computed tomography and histological evaluations of a straight electrode array positioning in temporal bones[J]. Acta Otolaryngol, 2017, 137(3): 229-234. doi: 10.1080/00016489.2016.1227477
[40] Zou J, Hannula M, Lehto K, et al. X-ray microtomographic confirmation of the reliability of CBCT in identifying the scalar location of cochlear implant electrode after round window insertion[J]. Hear Res, 2015, 326: 59-65. doi: 10.1016/j.heares.2015.04.005
[41] Dietz A, Gazibegovic D, Tervaniemi J, et al. Insertion characteristics and placement of the Mid-Scala electrode array in human temporal bones using detailed cone beam computed tomography[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2016, 273(12): 4135-4143. doi: 10.1007/s00405-016-4099-x
[42] Iso-Mustajärvi M, Matikka H, Risi F, et al. A New Slim Modiolar Electrode Array for Cochlear Implantation: A Radiological and Histological Study[J]. Otol Neurotol, 2017, 38(9): e327-e334. doi: 10.1097/MAO.0000000000001542
[43] Sipari S, Iso-Mustajärvi M, Matikka H, et al. Cochlear Implantation With a Novel Long Straight Electrode: the Insertion Results Evaluated by Imaging and Histology in Human Temporal Bones[J]. Otol Neurotol, 2018, 39(9): e784-e793. doi: 10.1097/MAO.0000000000001953
[44] Sipari S, Iso-Mustajärvi M, Löppönen H, et al. The Insertion Results of a Mid-scala Electrode Assessed by MRI and CBCT Image Fusion[J]. Otol Neurotol, 2018, 39(10): e1019-e1025. doi: 10.1097/MAO.0000000000002045
[45] Sipari S, Iso-Mustajärvi M, Könönen M, et al. The Image Fusion Technique for Cochlear Implant Imaging: A Study of its Application for Different Electrode Arrays[J]. Otol Neurotol, 2020, 41(2): e216-e222. doi: 10.1097/MAO.0000000000002479
-

| 引用本文: | 黄健健, 夏巍, 唐翔龙, 等. 锥形束CT在人工耳蜗植入中的研究进展[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2021, 35(6): 567-572. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2021.06.019 |
| Citation: | HUANG Jianjian, XIA Wei, TANG Xianglong, et al. Progress of research on cone beam CT in cochlear implantation[J]. J Clin Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2021, 35(6): 567-572. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2021.06.019 |
- Figure 1.



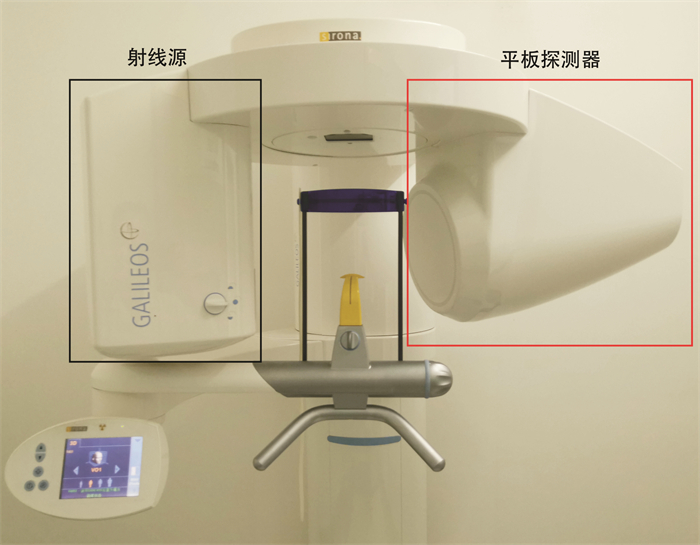
 下载:
下载: